- The paper introduces Job2Skills, which integrates multi-resolution skill salience and market-aware signals to enhance job targeting effectiveness.
- It employs a dual data collection strategy using expert annotations and market signals to achieve a 62.67% AUROC improvement and 1.92% increase in job applications.
- The approach offers actionable insights into market trends, reducing suggestion rejection rates by 37% and increasing member coverage by 6.71% on LinkedIn.
"Salience and Market-aware Skill Extraction for Job Targeting"
This essay examines the critical aspects and practical applications of the "Salience and Market-aware Skill Extraction for Job Targeting" paper, which addresses the limitations of traditional skill extraction approaches in job targeting systems. The authors propose a novel machine learning model, Job2Skills, designed to enhance the job matching process by incorporating skill salience and market dynamics.
Introduction and Problem Statement
The task of matching job postings with suitable candidates is a cornerstone of online professional platforms like LinkedIn. Traditional text-based approaches to skill extraction frequently overlook the salience of a skill and its market demand, leading to sub-optimal candidate matching.
The paper introduces Job2Skills, a system that integrates salience and market-awareness into skill extraction, leading to improvements in job recommendation performance, as evidenced by a 1.92% increase in job applications and a 37% reduction in suggestion rejection rate.
Methodology
Data Collection
The authors develop a dual strategy for collecting ground-truth data to train their model:
Model Architecture
The Job2Skills model operates by considering multi-resolution skill salience and incorporating market-aware signals:
- Multi-resolution Skill Salience: Features are extracted at the sentence, segment, and job levels to capture different degrees of skill relevance.
- Market-aware Features: These features capture the popularity and supply of skills across LinkedIn members and job postings, ensuring the selected skills align with market demand.
Evaluation and Results
The offline evaluation demonstrates a significant improvement over baseline models. Job2Skills trained on both expert annotations and market signals shows a 62.67% increase in AUROC for skill extraction tasks.
Online A/B testing of the Job2Skills model integrated into the LinkedIn job recommendation system showed a 1.92% increase in job applications and enhanced member coverage by 6.71%.

Figure 2: Non-expert and expert labeled skills' popularity.
Case Studies and Market Insights
Job2Skills provides valuable insights into market trends and skill demands, proving useful for both job seekers and employers. For example, the model can predict industry expansion and the rise in demand for specific skills, as demonstrated with the case of Macy's tech office expansion (Figure 3) and the volatility of "Azure" popularity (Figure 4).

Figure 3: \% of Macy's jobs posted per month from Jun. to Dec. 2019 that require software development related skills.
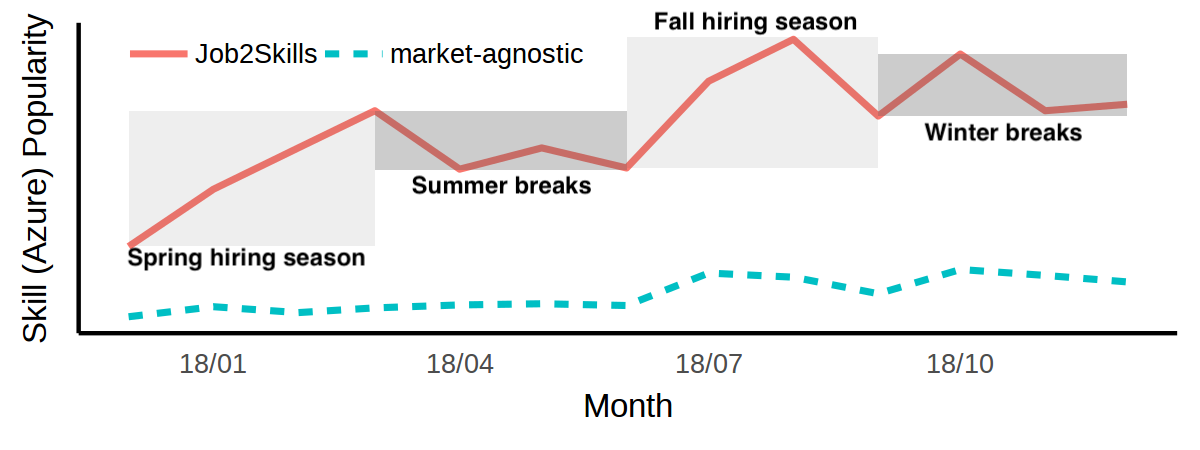
Figure 4: Azure's skill popularity in 2018.
Conclusion
Job2Skills is a practical advancement in job targeting technology, addressing deficiencies in skill extraction methods by incorporating salience and market-awareness. By improving the quality and efficacy of job recommendations, Job2Skills not only enhances user experience on platforms like LinkedIn but also provides deep insights into labor market dynamics. Future developments could explore the integration of temporal dynamics and advanced representation learning for further improvements.



