- The paper identifies critical mismatches between data scientists, software engineers, and operational staff that hinder effective ML-enabled system deployment.
- The methodology employs interviews, project mining, and a detailed mapping matrix to correlate system misalignments with performance issues.
- The study proposes ML-Enabled System Element Descriptors for automated mismatch detection to streamline integration and enhance system resilience.
Component Mismatches in ML-Enabled Systems in the Public Sector
Introduction
The integration of Machine Learning (ML) and AI into public sector systems holds great potential for improving functionalities and efficiencies by leveraging large data collections. Nevertheless, deploying these components in real-world applications is hindered by various challenges, primarily the mismatch between different system components. This paper critically examines these mismatches as a bottleneck to successful AI deployment in the public sector. It focuses on the different assumptions made by data scientists, software engineers, and operations staff, and how these assumptions can lead to inefficiencies and degraded system performance (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Elements of a Deployed ML-Enabled System and Operations Perspective.
Mismatches in ML-Enabled Systems
The paper outlines the architecture of ML-enabled systems, highlighting how separate workflows by data scientists, software engineers, and operations staff can lead to mismatches due to different assumptions. These mismatches can severely affect model accuracy, system performance, and operational integration. For instance, discrepancies between the data used for training models and the data encountered in operational environments can lead to reduced model efficacy. Similarly, differing computing resources between testing and deployment environments can result in unexpected system behavior (Figure 2, Figure 3).

Figure 2: Data Scientist Perspective.

Figure 3: Software Engineer Perspective.
System Element Descriptors
To address these issues, the authors propose the development of ML-Enabled System Element Descriptors, which are machine-readable and encompass attributes across the development lifecycle. These descriptors aim to make implicit assumptions explicit, enabling mismatch detection either manually or through automated tools. The authors recognize existing work in data set and model descriptors but emphasize the need for descriptors relevant to software engineering and operational facets, which are not machine-readable in current literature.
Research Methodology
The research follows a three-phased approach beginning with information gathering through interviews and project descriptions mining, followed by the analysis to map mismatches to system attributes, and ending with an evaluation phase for validation. The process involves creating a detailed mapping matrix that correlates mismatches with detectable attributes, thus enabling systematic analysis and intervention (Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6).
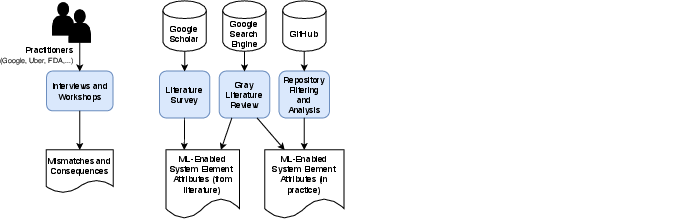
Figure 4: Information Gathering.
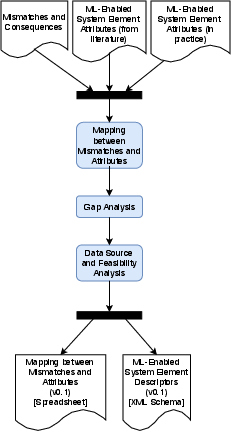
Figure 5: Analysis.
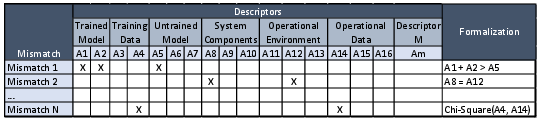
Figure 6: Mapping between Mismatches and ML-Enabled System Element Attributes.
Evaluation and Future Work
The paper concludes by emphasizing the potential development of tools for automated mismatch detection, which could be incorporated into ML system development toolchains. Future work will focus on refining the descriptors and enhancing the mismatches detection framework, potentially contributing to more robust ML-enabled systems. Demonstrations are being developed to showcase feasible automated detection methods for a subset of identified mismatches (Figure 7).
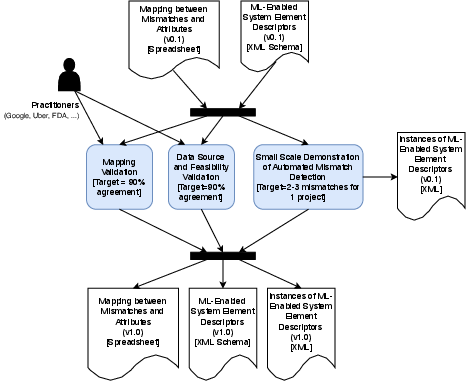
Figure 7: Evaluation.
Conclusion
This research identifies critical bottlenecks in the deployment of ML/AI systems due to mismatches between system components. By introducing systematic descriptors and a rigorous mapping framework, it aims to bridge the gap between diverse perspectives within software system development and deployment processes. These efforts anticipate streamlining integration for more effective ML/AI application in the public sector. Future implications include the widespread adoption of mismatch detection during the design and operational phases, ultimately contributing to more resilient and efficient AI-enabled systems in public institutions.






