- The paper introduces a Model Predictive Control framework integrating demand forecasting to preemptively rebalance self-driving fleets.
- It utilizes an LSTM-based prediction model and MILP optimization to significantly reduce customer wait times by 89.6%.
- The framework is validated using real-world DiDi Chuxing data, demonstrating scalability and real-time operational efficiency.
Data-Driven Model Predictive Control of Autonomous Mobility-on-Demand Systems
This essay explores strategies for implementing Model Predictive Control (MPC) in Autonomous Mobility-on-Demand (AMoD) systems. The paper provides a comprehensive framework designed to optimize the performance of self-driving vehicle fleets operating in urban environments. The proposed approach notably enhances the efficiency of these systems by predicting and addressing potential imbalances in customer demand distribution across regions.
Introduction to AMoD Systems
The intersection of Mobility-on-Demand (MoD) services and autonomous technology has given rise to AMoD systems, which leverage self-driving vehicles to fulfil transportation needs on a demand basis. These systems face unique operational challenges, particularly related to the spatial imbalance of vehicles due to asymmetrical demand. Traditional methods often rely on reactive control strategies, which are insufficient for managing rapidly changing demand.
To address these challenges, this paper integrates short-term demand forecasting into the control mechanisms of AMoD systems. This integration is achieved through an MPC framework that anticipates demand imbalances and executes preemptive rebalancing strategies to better serve customer requests.
The AMoD system is modeled as a time-expanded network, where regions in an urban environment are connected through routes with defined travel times. The optimal dispatching of vehicles is determined according to this network model. The formulation includes variables for vehicle routes serving both customer demand (passenger carrying) and system rebalancing (empty vehicle movements).
Optimization Problem
The optimization problem seeks to minimize the cost associated with vehicle rebalancing while ensuring all customer demands are met. Vehicles are dynamically repositioned based on short-term predicted demand, with an emphasis on minimizing customer wait times and maximizing fleet utilization.
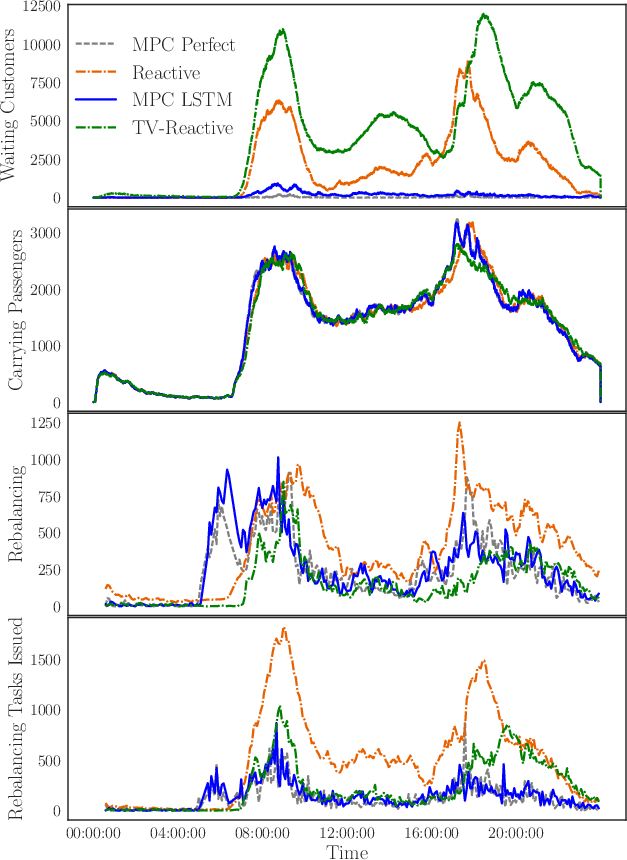
Figure 1: Results from the MPC-Perfect (gray), MPC-LSTM (blue), and Reactive scenarios, illustrating the effectiveness of different control strategies.
The problem formulation is characterized by:
- Constraints ensuring customer demand satisfaction.
- Continuity constraints to maintain a balanced availability of vehicles.
- A cost structure that penalizes waiting and unfulfilled demand.
Model Predictive Control Framework
The MPC strategy uses forecasts derived from historical data to dynamically adjust the positioning of vehicles. The approach leverages the flexibility of AMoD systems to actively manage fleet distribution in response to predicted demand.
Algorithm Overview
The control algorithm is iterative and follows these steps:
- Capture the current state of the system, including vehicle availability and outstanding customer requests.
- Predict future demand using an LSTM neural network trained on past travel data.
- Solve an optimization problem to determine the optimal rebalancing strategy for the specified planning horizon.
- Assign rebalancing tasks based on the computed strategy.
Numerical Experiments and Results
The proposed framework was validated using data from DiDi Chuxing, a prominent ridesharing service in China. The experiments demonstrated significant improvements in operational efficiency and reduced customer wait times compared to traditional reactive strategies.
Sensitivity Analysis
A key finding from the experiments was the marked performance improvement when employing forecasts with longer horizons. The integration of customer demand predictions allowed the system to preemptively address demand surges, resulting in a substantial reduction (89.6%) in mean wait times compared to state-of-the-art reactive controllers.
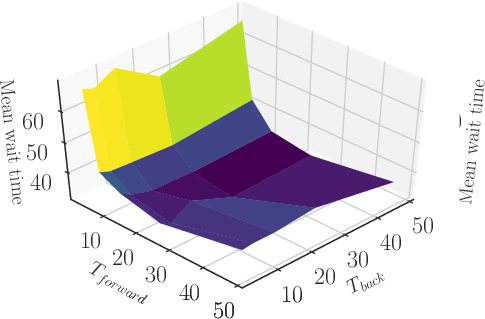
Figure 2: Mean wait times for different combinations of Tforward and Tback, illustrating the effect of forecast horizon on system performance.
Computational Efficiency
The proposed MPC framework's MILP-based optimization achieves real-time feasibility due to its insensitivity to fleet size, allowing for scalability to large urban networks. The computational efficiency was validated, with typical problem instances being solved swiftly on standard hardware.
Conclusions
The paper's MPC framework represents a robust approach for managing AMoD systems, effectively balancing demand through predictive rebalancing strategies. The results underscore the importance of integrating forecasting techniques into AMoD operations, yielding significant improvements in customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Future avenues for research include the development of stochastic models to account for uncertainty in demand predictions, integration with other transportation modalities, and the enhancement of forecasting methods to better accommodate diverse data sources and scenarios. These advancements hold promise for further optimizing AMoD systems in dynamic urban contexts.



