- The paper presents Tether, an LLM-powered desktop application offering personalized, workflow-specific support for software engineers with ADHD.
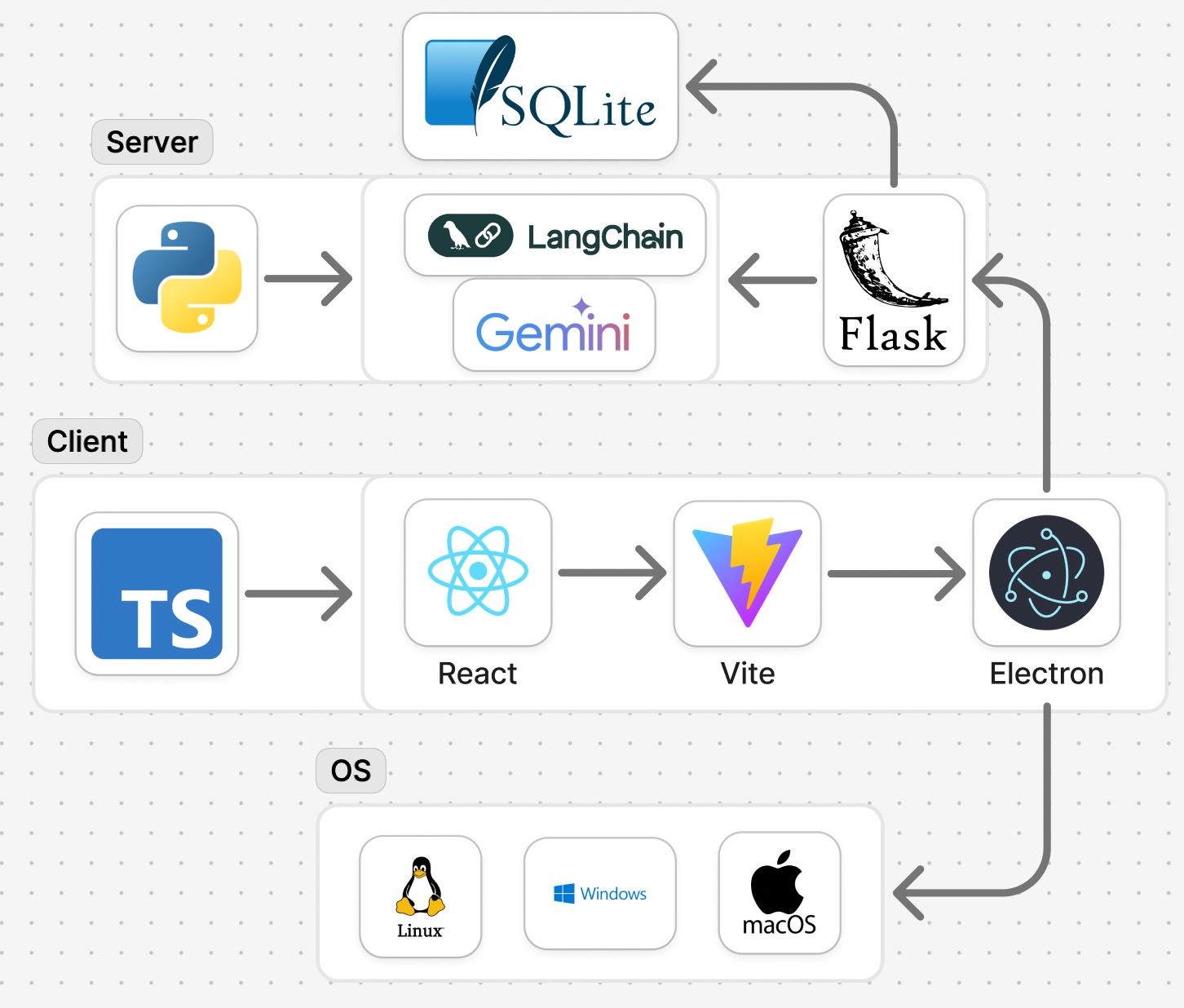
- It utilizes a modular architecture with activity monitoring, a RAG pipeline, and local execution to ensure privacy and adaptive intervention.
- Preliminary evaluations show Tether’s potential to improve task management and reduce cognitive overload through gamified, context-aware strategies.
Tether: A Personalized Support Assistant for Software Engineers with ADHD
Motivation and Context
The paper addresses a critical gap in equity, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) within software engineering (SE), focusing on neurodiversity and specifically the experiences of developers with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Despite representing a significant portion of the SE workforce, developers with ADHD face persistent challenges in sustained attention, task initiation, self-regulation, and time management, exacerbated by workplace norms such as synchronous communication and frequent context switching. Existing digital interventions for ADHD primarily target general behavioral or therapeutic support, lacking adaptation to the cognitive demands and workflow structures of professional software engineering. The paper proposes Tether, an LLM-powered desktop application, as a targeted assistive technology to address these unmet needs.
System Architecture and Implementation
Tether is architected as a privacy-preserving desktop application, integrating multiple components to deliver adaptive, context-aware support for software engineers with ADHD. The system comprises:
All components, except for LLM inference, execute locally to ensure user privacy. The modular design facilitates extensibility and integration with additional sensing channels.
User Workflow and Interaction Model
Tether's workflow is centered on real-time detection of attention loss and context-aware intervention. When user inactivity is detected (e.g., prolonged absence of mouse/keyboard input), the system generates a supportive notification, leveraging recent activity data to personalize the message and avoid abrupt interruptions.

Figure 2: Sample notification for prolonged loss in focus.
Users can engage with a built-in chatbot for both emotional regulation and task management. The chatbot utilizes RAG to ground responses in ADHD-specific resources and recent user context, offering strategies such as time boxing, stepwise task breakdown, and empathetic conversation. This dual support for technical and emotional challenges is tailored to the cognitive profiles of ADHD users.
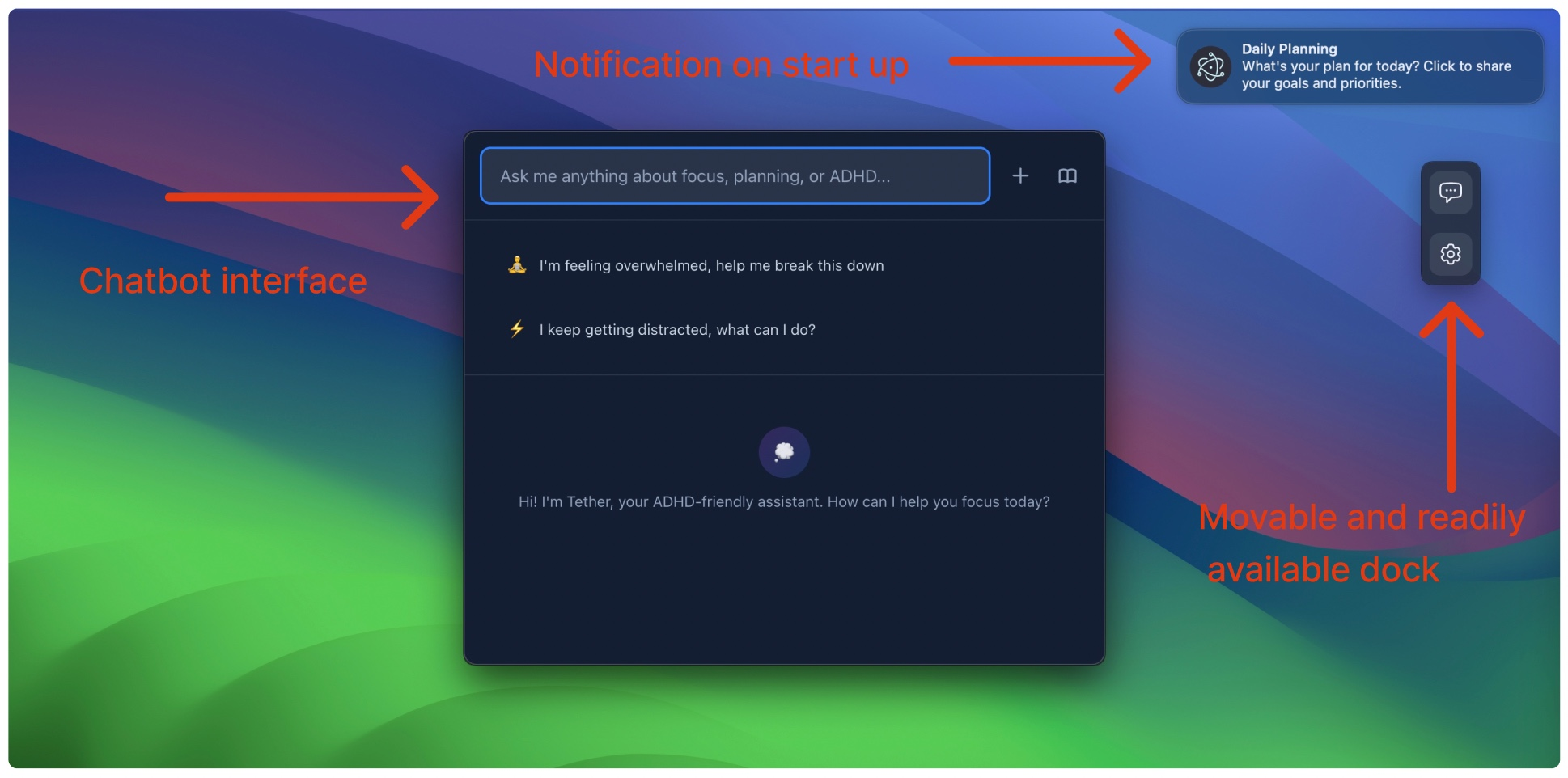
Figure 3: Main user interface and chatbot elements.
Gamification is employed to sustain motivation and engagement. Users earn points and badges for maintaining focus, efficient task switching, and rapid recovery from distractions. Achievements unlock interface customizations and are reinforced through real-time notifications.
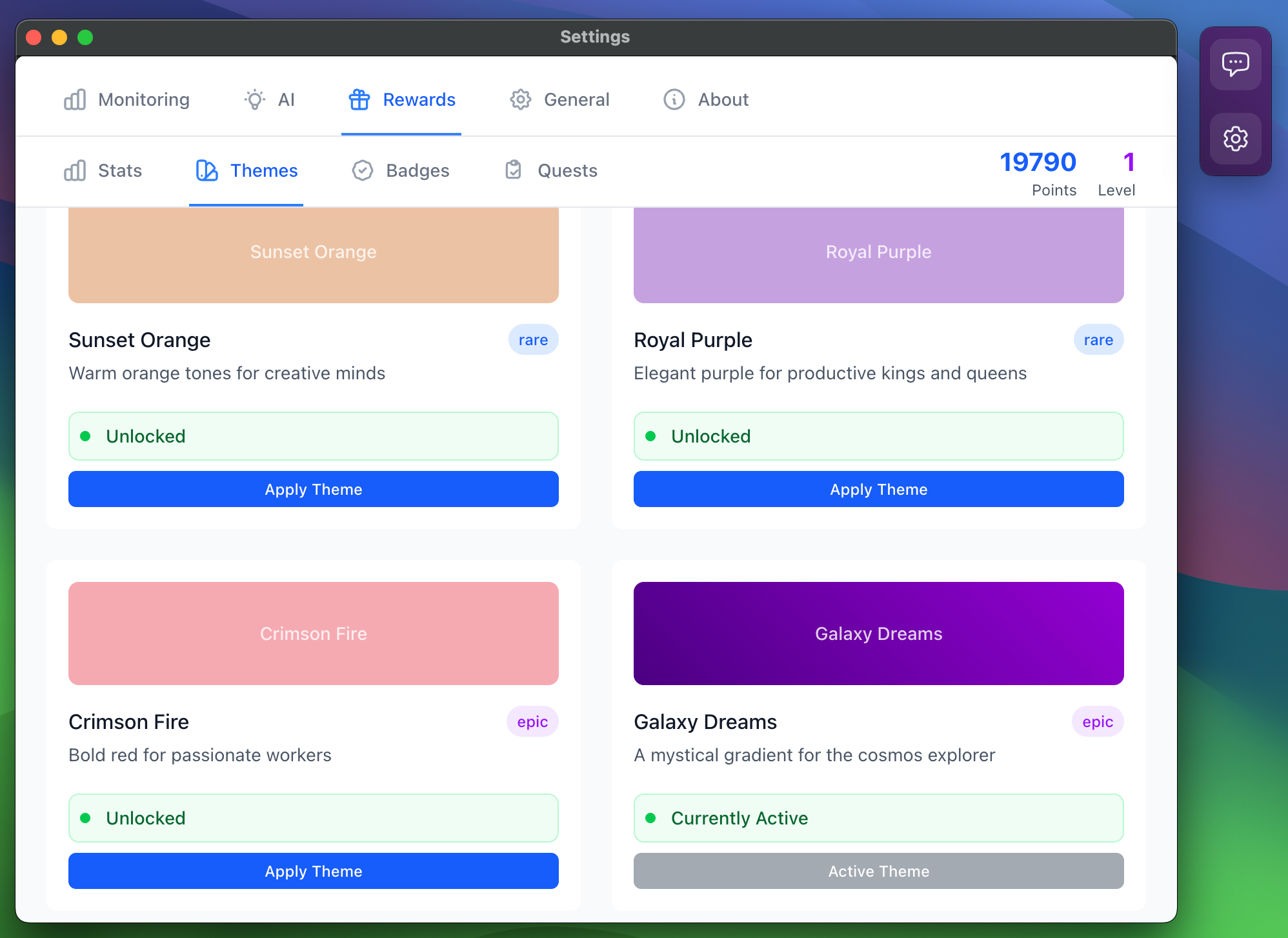
Figure 4: Gamification aspects.
Backend Processes and Prompt Engineering
Tether's backend processes are triggered by either passive detection (e.g., inactivity) or active user engagement (e.g., chatbot queries). The system aggregates desktop activity signals and constructs modular prompts incorporating summaries of recent activity, chat history, and ADHD-informed principles. The RAG pipeline indexes both systematic literature reviews and user-specific data, ensuring factual grounding and personalization. Prompts are routed to Gemini's LLM API, with responses delivered via OS notifications or the chatbot interface, depending on context.
This architecture enables Tether to deliver contextually relevant, adaptive support, minimizing cognitive overhead and aligning with evidence-based ADHD interventions that externalize executive processes.
Comparative Evaluation
A preliminary evaluation compared Tether against existing ADHD-related tools across dimensions of technology, domain specificity, and feature set. Unlike browser extensions, mobile apps, or wearables, Tether is a desktop application designed for professional software engineers, integrating monitoring, conversational support, development workflow awareness, RAG, and gamification. No other surveyed tool offers this combination of features or direct integration into software development workflows.
Key differentiators:
- Local execution for privacy
- Contextual, workflow-aware interventions
- RAG for factual grounding and personalization
- Gamified feedback tailored to professional engagement
Limitations and Threats to Validity
The evaluation was conducted in a simulated setting without direct involvement of neurodivergent professionals or healthcare experts. The absence of formal user studies and clinical validation limits the generalizability of findings. The tool's effectiveness in real-world SE environments remains to be established, and further expert validation is required.
Implications and Future Directions
Tether introduces a new paradigm for neurodiversity-aware assistive technologies in SE, leveraging LLMs and RAG to deliver personalized, context-sensitive support. The approach has implications for both research and industry:
- Research: Enables empirical studies on neuroinclusive practices, grounded in behavioral data and adaptive interaction models.
- Industry: Provides a deployable, lightweight support mechanism that integrates with existing developer tooling, potentially reducing friction and improving engagement for neurodivergent professionals.
Future work includes expanding sensing modalities (e.g., gaze detection, ambient noise analysis), enhancing task-specific chatbot support, and conducting validation studies with healthcare professionals and ADHD-affected software engineers.
Conclusion
Tether represents an early-stage, LLM-powered support assistant for software engineers with ADHD, integrating activity monitoring, RAG, and gamification to deliver adaptive, context-aware interventions. Preliminary results indicate promise for personalized, low-disruption support in professional workflows, with potential to advance neurodiversity inclusion in SE. Further development and rigorous validation are necessary to establish its efficacy and inform broader adoption.