- The paper presents MAPTA, a multi-agent AI that autonomously assesses web vulnerabilities using LLM-guided orchestration and sandboxed execution.
- It achieves a 76.9% success rate on 104 challenges, excelling in SSRF, injection, and misconfiguration tests while minimizing resource costs.
- MAPTA couples strategic planning with secure, isolated execution and proof-of-concept validation to optimize penetration testing and resource allocation.
Multi-Agent Architectures for Autonomous Web Application Penetration Testing: An Analysis of MAPTA
Introduction
The paper "Multi-Agent Penetration Testing AI for the Web" (2508.20816) presents MAPTA, a multi-agent system for autonomous web application security assessment. MAPTA is designed to address the scalability crisis in security auditing precipitated by the proliferation of AI-generated code, which is frequently insecure. The system leverages LLM orchestration, tool-grounded execution, and mandatory end-to-end exploit validation to autonomously discover and verify vulnerabilities in web applications. This essay provides a technical analysis of MAPTA’s architecture, evaluation methodology, empirical results, and implications for the future of AI-driven security assessment.
System Architecture and Agent Design
MAPTA’s architecture is predicated on a three-role agent model: Coordinator, Sandbox, and Validation agents. The Coordinator agent is responsible for high-level attack-path reasoning, tool orchestration, and report synthesis. Sandbox agents execute tactical steps within a shared per-job Docker container, providing isolated LLM contexts for focused sub-tasks. The Validation agent is tasked with converting candidate findings into verified, end-to-end proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits, returning pass/fail evidence based on concrete execution.
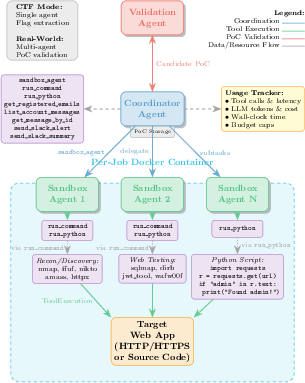
Figure 1: MAPTA multi-agent architecture with single-pass controller and evidence-gated branching. The Coordinator orchestrates, Sandbox agents execute in a shared container, and the Validation agent verifies PoCs.
This separation of concerns enables MAPTA to couple high-level strategic planning with secure, isolated execution and empirical validation. The architecture supports both blackbox (CTF-style) and whitebox (source-available) assessment modes, with dynamic orchestration logic that adapts to the operational context. All agents for a given assessment share a single Docker container, amortizing setup costs and enabling stateful reuse of artifacts, while maintaining LLM context isolation to prevent cross-talk and prompt bloat.
Evaluation Methodology
MAPTA is evaluated on the XBOW benchmark, comprising 104 web application security challenges designed for autonomous penetration testing. The evaluation is conducted under blackbox conditions, with MAPTA receiving only the target URL and challenge description. The system’s performance is measured using four objective metrics: binary success (flag discovery), time to solution, computational cost (LLM API usage), and tool execution efficiency.
MAPTA achieves a 76.9% overall success rate, with perfect performance on SSRF and misconfiguration vulnerabilities, 83% on broken authorization, and strong results on injection attacks (SSTI: 85%, SQLi: 83%). Cross-site scripting (XSS) and blind SQL injection remain challenging, with 57% and 0% success rates, respectively.
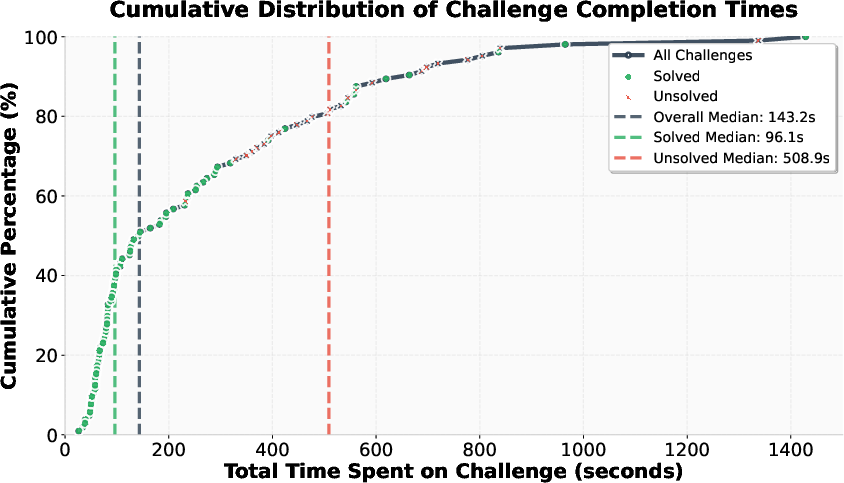
Figure 2: Cumulative distribution of challenge completion times. Solved challenges have a median time of 96.1s; unsolved challenges, 508.9s.
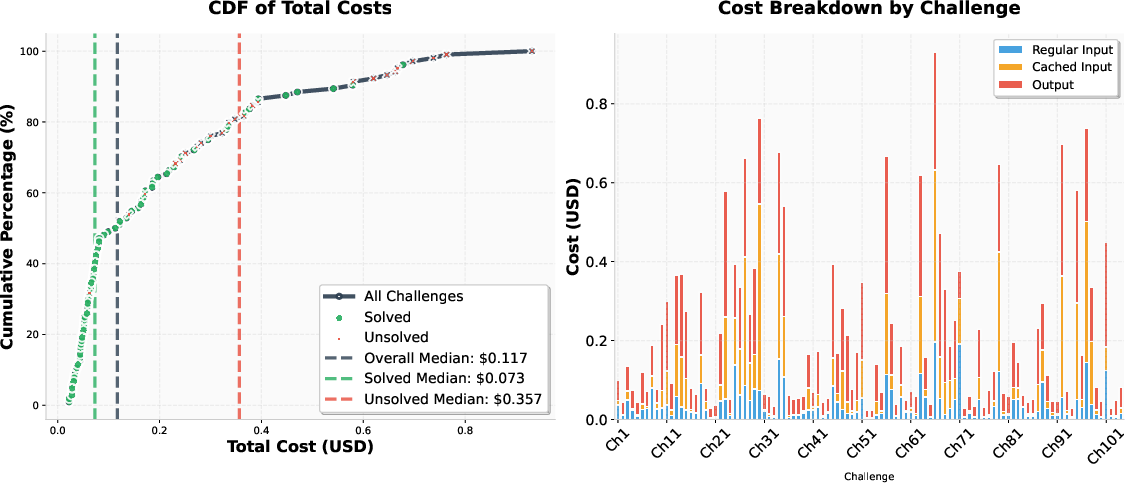
Figure 3: CDF of total costs and per-challenge cost by token type. Solved challenges have a median cost of \$0.073; unsolved, \$0.357. Output tokens are the largest cost component.
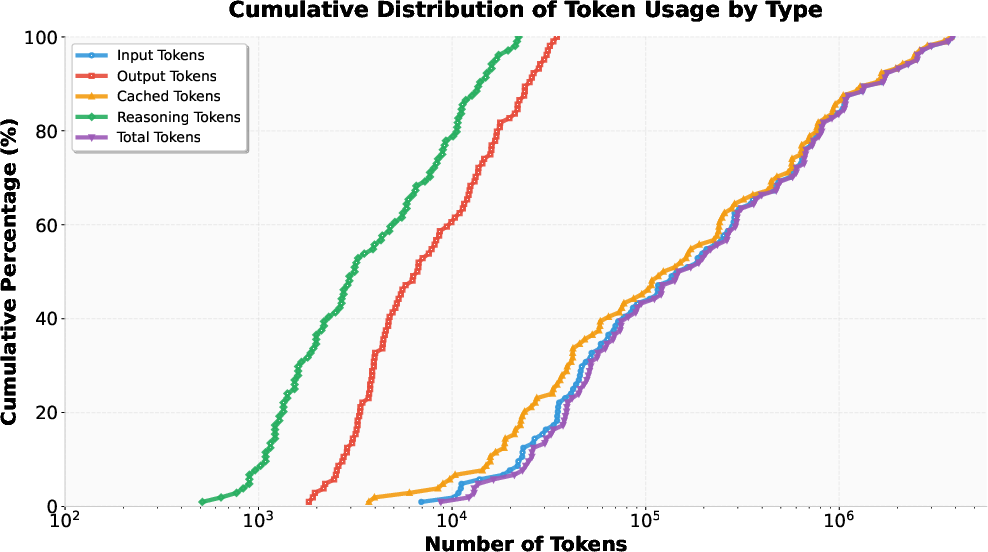
Figure 4: Cumulative distribution of token usage by type. Cached token utilization contributes to cost efficiency; reasoning tokens reflect analytical processing.
MAPTA’s resource accounting is rigorous, with a total cost of \$21.38 for all challenges, a median cost of \$0.073 for successful attempts, and \$0.357 for failures. Output tokens are the primary cost driver, reflecting the system’s analytical reasoning requirements. The system demonstrates adaptive tool selection, with a preference for direct command execution (notably curl and bash), and an average of 25.1 tool calls per challenge.
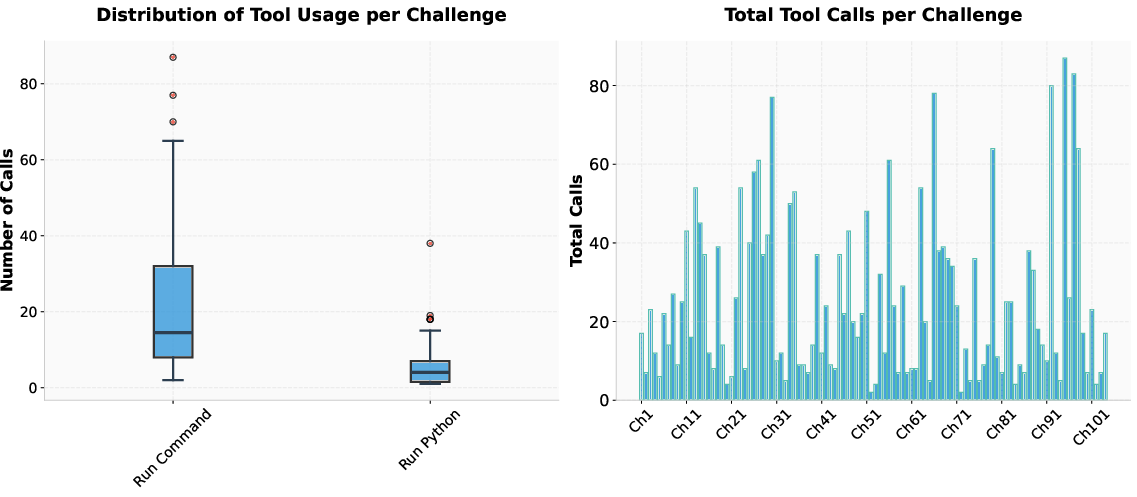
Figure 5: Tool usage patterns across challenges. Command execution dominates over Python runtime calls; total tool invocations per challenge are shown.
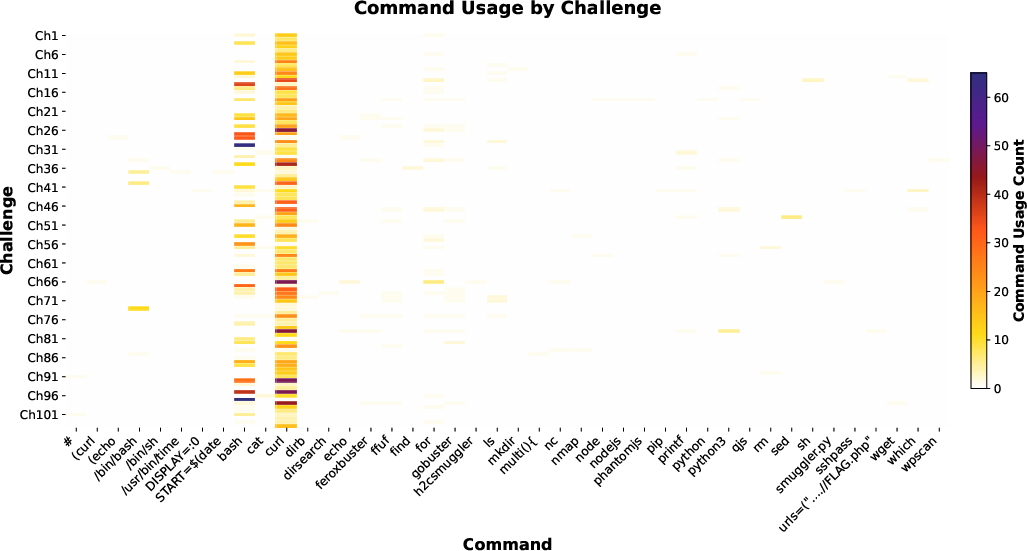
Figure 6: Command usage heatmap. Curl dominates, reflecting HTTP-centric testing; bash usage indicates complex exploitation.
Correlation and Efficiency Analysis
A key contribution of MAPTA is the quantification of negative correlations between resource utilization and success. Statistically significant negative correlations are observed between success and tool usage (r = -0.661), cost (r = -0.606), token usage (r = -0.587), and time (r = -0.557).
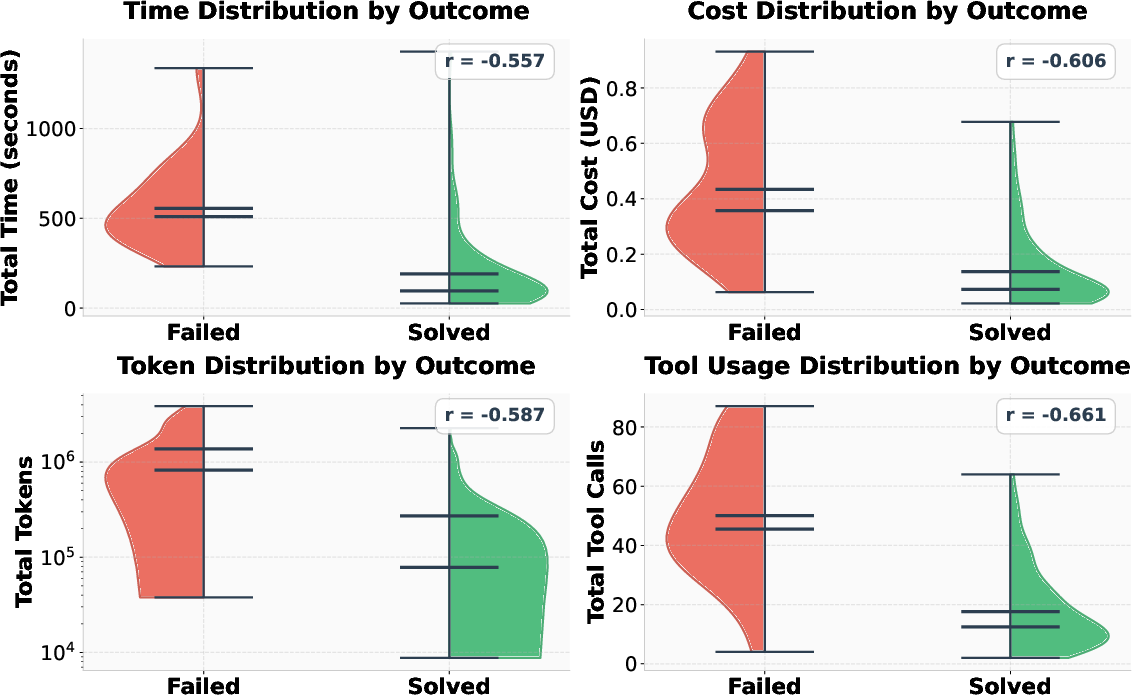
Figure 7: Correlation analysis between challenge success and resource utilization. Negative correlations indicate efficient solutions for successful challenges.
These findings indicate that successful challenges are solved quickly and efficiently, while failures are characterized by extensive exploration and higher resource consumption. This enables the implementation of practical early-stopping thresholds (e.g., 40 tool calls, \$0.30, or 300 seconds), optimizing resource allocation in production deployments.
MAPTA’s performance is analyzed across 13 vulnerability categories, spanning the majority of the OWASP Top 10 (2021) and several API Top 10 (2023) families.
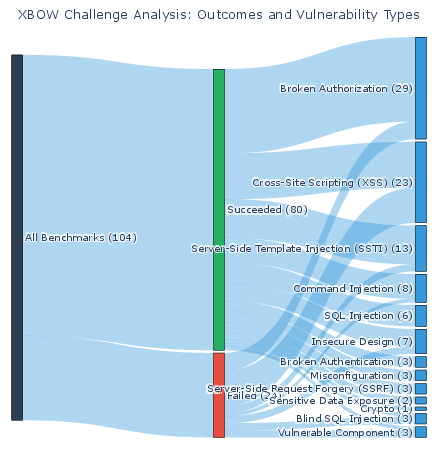
Figure 8: Vulnerability category distribution across 104 XBOW challenges. 13 categories spanning 8/10 OWASP Top 10 (2021).
MAPTA excels at SSRF, misconfiguration, and injection vulnerabilities (SSTI, SQLi, command injection), but underperforms on XSS and blind SQLi. Authorization vulnerabilities (IDOR, privilege escalation) are detected with high accuracy (83%), while authentication and business logic flaws remain challenging. The system’s empirical validation approach reduces false positives but may yield false negatives for complex business logic vulnerabilities that require deeper semantic understanding.
Real-World Application Assessment
MAPTA is further evaluated on 10 popular open-source web applications (8K–70K GitHub stars), representing diverse technology stacks. The system discovers 19 vulnerabilities across 6 applications, with 14 classified as high or critical severity (including RCE, command injection, secret exposure, and arbitrary file write). The average assessment cost is \$3.67 per application, with a mean assessment time of 50.7 minutes.
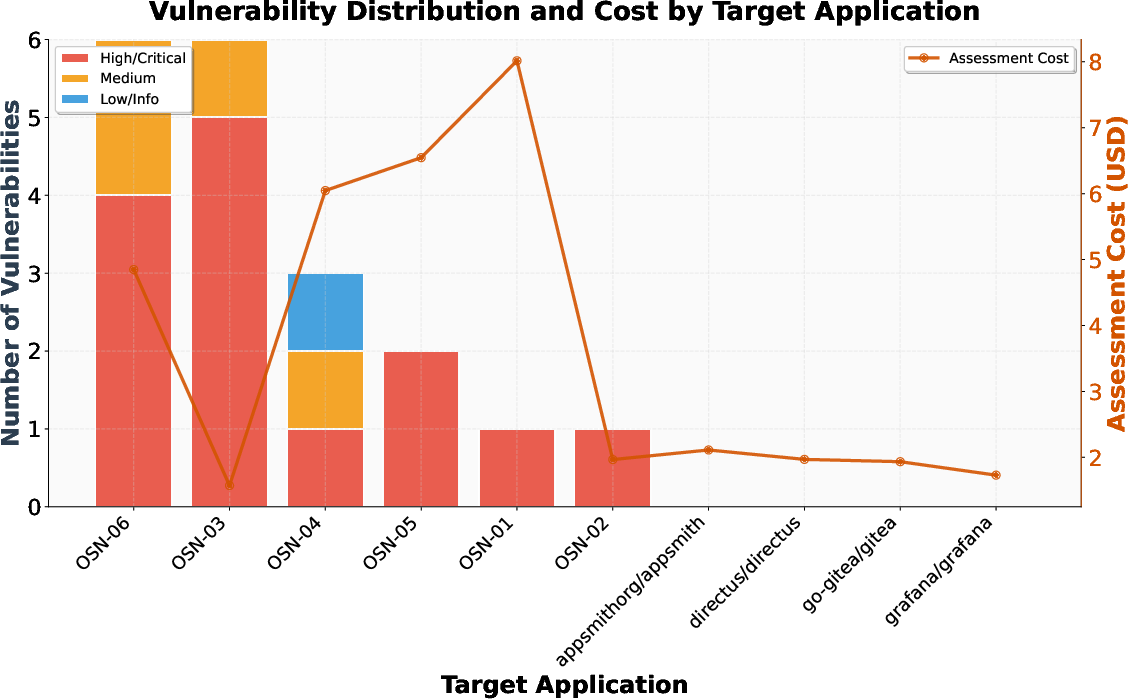
Figure 9: Vulnerability distribution and assessment costs across targets. Stacked bars show severity; orange line indicates assessment costs.
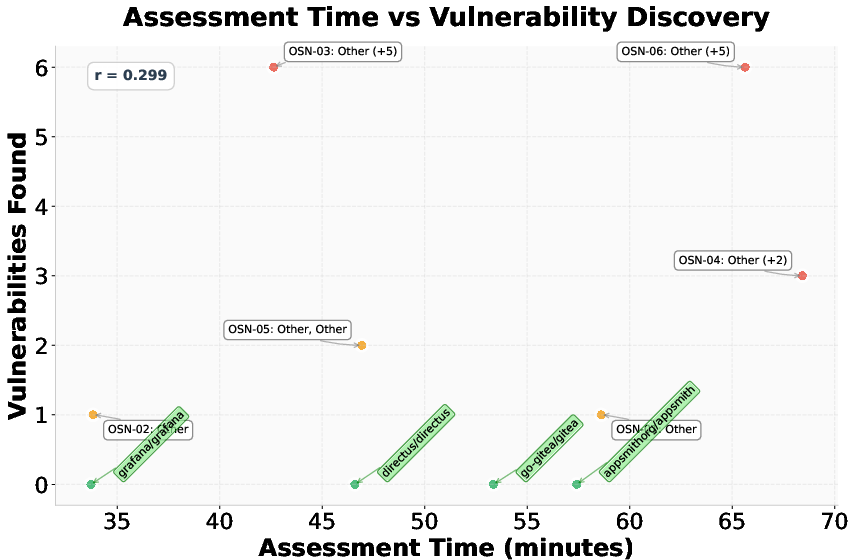
Figure 10: Assessment time versus vulnerability discovery patterns. Labels indicate vulnerability types found.
Notably, the cost of assessment does not directly correlate with the number or severity of findings, indicating that some complex applications are secure while others yield critical vulnerabilities at low computational cost. All findings are responsibly disclosed, with 10 under CVE review.
Implications and Future Directions
MAPTA demonstrates that multi-agent LLM-driven architectures can achieve competitive performance in autonomous web application security assessment, with rigorous cost-performance accounting and empirical exploit validation. The system’s open-source implementation and reproducible evaluation methodology address the reproducibility gap in prior commercial and academic systems.
The negative correlation between resource usage and success provides actionable heuristics for early stopping and resource budgeting, a critical consideration for large-scale or continuous deployment. The empirical validation approach reduces false positives, but further research is needed to address false negatives in business logic and timing-based vulnerabilities (e.g., blind SQLi).
Future developments may include enhanced payload generation, feedback-driven exploration, integration of browser-based agents for DOM-centric vulnerabilities, and automated canary placement for business logic validation. Scaling MAPTA to larger, more complex applications and integrating with CI/CD pipelines for continuous assessment are promising directions.
Conclusion
MAPTA establishes a new standard for autonomous penetration testing by combining multi-agent orchestration, tool-grounded execution, and mandatory exploit validation. The system achieves 76.9% success on the XBOW benchmark, with strong performance on critical vulnerability classes and comprehensive cost accounting. The open-science approach, rigorous evaluation, and actionable resource optimization strategies position MAPTA as a practical and scientifically robust framework for AI-driven security assessment. The results underscore the feasibility of deploying autonomous agents for continuous, scalable web application security testing, while highlighting open challenges in business logic and advanced exploitation scenarios.











