- The paper introduces the AI-45° Law as a balanced approach uniting AI capability and safety to address rapid, fragmented development.
- The paper presents a three-layer Causal Ladder framework that enables value alignment, intervention during inference, and reflective reasoning in AGI.
- The paper emphasizes robust governance measures and early warning indicators to mitigate existential risks and foster proactive, trustworthy AI.
Towards Trustworthy AGI: Balancing Capability and Safety with the AI-45∘ Law
This paper introduces the AI-45∘ Law, a principle advocating for the balanced advancement of AI capabilities and safety measures, and proposes the Causal Ladder of Trustworthy AGI as a framework to achieve this balance. The framework offers a structured approach to addressing safety and trustworthiness in AGI development, drawing inspiration from Judea Pearl's "Ladder of Causation."
The Crippled State of AI Development
The paper highlights the rapid progress in AI capabilities, driven by innovations in scaling laws and model architectures. This advancement has led to systems like ChatGPT and GPT-4, demonstrating remarkable abilities in understanding and generating human-like language. However, the authors note that the development and deployment of these advanced systems often outpace the implementation of safety measures, leading to a "reactive approach" in AI safety. Current AI safety measures are often domain-specific and lack a unified framework, resulting in fragmented efforts to address potential risks like adversarial attacks, data poisoning, and model theft. The authors describe this reactive and fragmented nature as "crippled AI," where the rapid development of AI capabilities outpaces safety efforts, potentially undermining public trust and limiting AI adoption.
The AI-45∘ Law: A Guiding Principle
The AI-45∘ Law is introduced as a guiding principle to balance AI capability and safety. The law posits that advancements in both dimensions should ideally progress in parallel, represented by a 45∘ line in a capability-safety coordinate system (Figure 1).
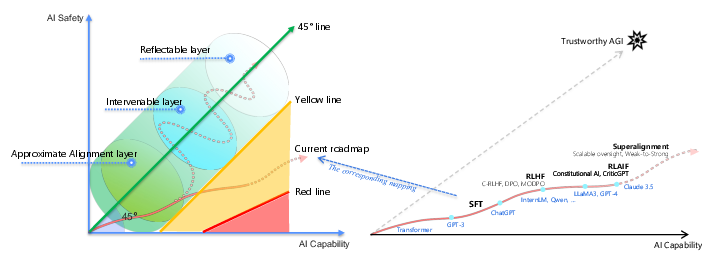
Figure 1: Illustration of the AI-45∘ Law, showing the balance between AI capability and safety, and key milestone models in AI capability development.
The authors acknowledge flexibility within a defined range but emphasize the current deviation from this ideal, with safety lagging behind capability. The paper also defines "Red Lines" representing existential risks and "Yellow Lines" as early warning indicators to proactively mitigate potential dangers.
The Causal Ladder of Trustworthy AGI: A Three-Layer Framework
To implement the AI-45∘ Law, the paper proposes a three-layer technical framework based on the "Ladder of Causation" (Figure 2).
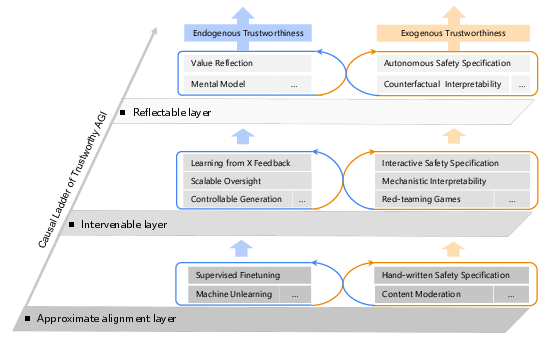
Figure 2: The Causal Ladder of Trustworthy AGI framework, integrating Endogenous and Exogenous Trustworthiness across three layers: Approximate Alignment, Intervenable, and Reflectable.
This framework aims to address safety and trustworthiness requirements in AGI development. The framework defines two key dimensions of AGI trustworthiness: Endogenous Trustworthiness (intrinsic safety technologies) and Exogenous Trustworthiness (external assurance mechanisms).
Layer 1: Approximate Alignment Layer
This layer focuses on aligning AI models with human values, addressing the limitations of current models in accurately reflecting human value systems. This involves technical advancements in value representation and alignment at the conceptualization and encoding levels. Methods include supervised fine-tuning and machine unlearning to ensure models understand and adhere to human values.
Layer 2: Intervenable Layer
The Intervenable Layer addresses the need for safety verification and intervention during model inference. This layer emphasizes the decoupling of the inference process and rethinking reasoning mechanisms at the model architecture level to ensure traceability and verifiability. Relevant technologies include feedback-based value alignment, scalable oversight, mechanistic interpretability, and adversarial training.
Layer 3: Reflectable Layer
This layer aims to overcome limitations in existing reasoning paradigms by introducing a novel reflective reasoning framework. This involves integrating self-reflective capabilities, enabling systems to evaluate their decisions and adapt to environmental changes. Key methods include world models, value reflection, and counterfactual interpretability.
The Matrix of Trustworthy AGI
The paper defines five levels of AGI trustworthiness: Perception Trustworthiness, Reasoning Trustworthiness, Decision-making Trustworthiness, Autonomy Trustworthiness, and Collaboration Trustworthiness. These levels form a comprehensive framework for a trustworthy AI system, supporting balanced development of trustworthiness and capabilities in AGI. The dependence on each layer of the causal ladder varies across these levels (Figure 3).
(Figure 3)
Figure 3: The Matrix of Trustworthy AGI, illustrating the positions of representative models within the matrix based on the Causal Ladder and levels of trustworthiness.
For example, achieving Perception Trustworthiness does not necessitate techniques from the Reflectable Layer, while Reasoning Trustworthiness does to some extent.
Governance Measures
The paper identifies key challenges in AI governance, including lifecycle management, multi-stakeholder involvement, and governance for societal well-being. It emphasizes the recognition of AI safety as a global public good, requiring effective governance and safeguard mechanisms to mitigate risks.
Conclusion
The paper introduces the AI-45∘ Law and the Causal Ladder of Trustworthy AGI as a framework for balancing AI safety and capability. It defines five levels of AGI trustworthiness and discusses governance measures to ensure the responsible development of AGI systems. The authors note that further research is needed to refine methodologies, integrate ethical considerations, and ensure adaptability in real-world environments. Future work will focus on empirically validating the proposed framework and exploring its applicability across domains and AI architectures.

