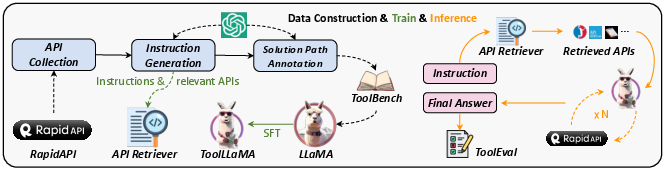
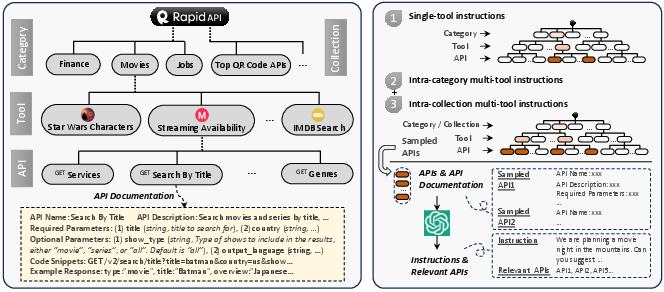
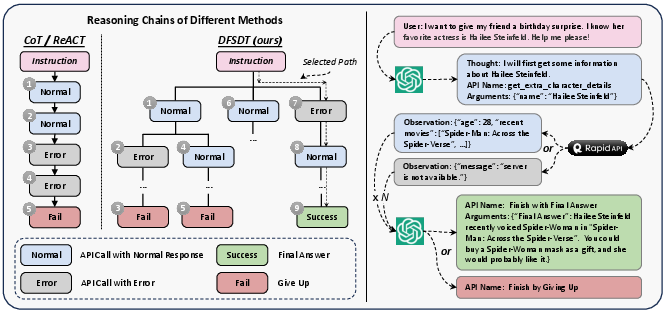
ToolLLM: Facilitating Large Language Models to Master 16000+ Real-world APIs (2307.16789v2)
Abstract: Despite the advancements of open-source LLMs, e.g., LLaMA, they remain significantly limited in tool-use capabilities, i.e., using external tools (APIs) to fulfill human instructions. The reason is that current instruction tuning largely focuses on basic language tasks but ignores the tool-use domain. This is in contrast to the excellent tool-use capabilities of state-of-the-art (SOTA) closed-source LLMs, e.g., ChatGPT. To bridge this gap, we introduce ToolLLM, a general tool-use framework encompassing data construction, model training, and evaluation. We first present ToolBench, an instruction-tuning dataset for tool use, which is constructed automatically using ChatGPT. Specifically, the construction can be divided into three stages: (i) API collection: we collect 16,464 real-world RESTful APIs spanning 49 categories from RapidAPI Hub; (ii) instruction generation: we prompt ChatGPT to generate diverse instructions involving these APIs, covering both single-tool and multi-tool scenarios; (iii) solution path annotation: we use ChatGPT to search for a valid solution path (chain of API calls) for each instruction. To enhance the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, we develop a novel depth-first search-based decision tree algorithm. It enables LLMs to evaluate multiple reasoning traces and expand the search space. Moreover, to evaluate the tool-use capabilities of LLMs, we develop an automatic evaluator: ToolEval. Based on ToolBench, we fine-tune LLaMA to obtain an LLM ToolLLaMA, and equip it with a neural API retriever to recommend appropriate APIs for each instruction. Experiments show that ToolLLaMA demonstrates a remarkable ability to execute complex instructions and generalize to unseen APIs, and exhibits comparable performance to ChatGPT. Our ToolLLaMA also demonstrates strong zero-shot generalization ability in an out-of-distribution tool-use dataset: APIBench.
- Do as i can, not as i say: Grounding language in robotic affordances. ArXiv preprint, abs/2204.01691, 2022.
- Promptsource: An integrated development environment and repository for natural language prompts. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, pp. 93–104, 2022.
- Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with gpt-4. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.12712, 2023.
- Extending context window of large language models via positional interpolation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.15595, 2023.
- Vicuna: An open-source chatbot impressing gpt-4 with 90%* chatgpt quality, March 2023. URL https://lmsys.org/blog/2023-03-30-vicuna/.
- BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), pp. 4171–4186, Minneapolis, Minnesota, 2019. Association for Computational Linguistics. doi: 10.18653/v1/N19-1423. URL https://aclanthology.org/N19-1423.
- Enhancing chat language models by scaling high-quality instructional conversations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14233, 2023.
- Assistgpt: A general multi-modal assistant that can plan, execute, inspect, and learn. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.08640, 2023.
- Visual programming: Compositional visual reasoning without training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14953–14962, 2023.
- Toolkengpt: Augmenting frozen language models with massive tools via tool embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11554, 2023.
- Language models as zero-shot planners: Extracting actionable knowledge for embodied agents. In Kamalika Chaudhuri, Stefanie Jegelka, Le Song, Csaba Szepesvári, Gang Niu, and Sivan Sabato (eds.), International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2022, 17-23 July 2022, Baltimore, Maryland, USA, volume 162 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 9118–9147. PMLR, 2022a.
- Inner monologue: Embodied reasoning through planning with language models. ArXiv preprint, abs/2207.05608, 2022b.
- Cumulated gain-based evaluation of ir techniques. ACM Transactions on Information Systems (TOIS), 20(4):422–446, 2002.
- Genegpt: Augmenting large language models with domain tools for improved access to biomedical information. ArXiv, 2023.
- Api-bank: A benchmark for tool-augmented llms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.08244, 2023a.
- Alpacaeval: An automatic evaluator of instruction-following models. https://github.com/tatsu-lab/alpaca_eval, 2023b.
- Cross-task generalization via natural language crowdsourcing instructions. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pp. 3470–3487, 2022.
- Webgpt: Browser-assisted question-answering with human feedback. ArXiv preprint, abs/2112.09332, 2021.
- OpenAI. OpenAI: Introducing ChatGPT, 2022. URL https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt.
- OpenAI. Gpt-4 technical report, 2023.
- Gorilla: Large language model connected with massive apis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15334, 2023.
- The refinedweb dataset for falcon llm: outperforming curated corpora with web data, and web data only. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.01116, 2023.
- Creator: Disentangling abstract and concrete reasonings of large language models through tool creation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14318, 2023.
- Webcpm: Interactive web search for chinese long-form question answering. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.06849, 2023a.
- Tool learning with foundation models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.08354, 2023b.
- Sentence-bert: Sentence embeddings using siamese bert-networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.10084, 2019.
- The probabilistic relevance framework: Bm25 and beyond. Foundations and Trends® in Information Retrieval, 3(4):333–389, 2009.
- Toolformer: Language models can teach themselves to use tools. ArXiv preprint, abs/2302.04761, 2023.
- Hugginggpt: Solving ai tasks with chatgpt and its friends in huggingface, 2023.
- Reflexion: Language agents with verbal reinforcement learning, 2023.
- Restgpt: Connecting large language models with real-world applications via restful apis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.06624, 2023.
- Toolalpaca: Generalized tool learning for language models with 3000 simulated cases. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.05301, 2023.
- Stanford alpaca: An instruction-following llama model. https://github.com/tatsu-lab/stanford_alpaca, 2023.
- Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13971, 2023a.
- Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09288, 2023b.
- Chatgpt for robotics: Design principles and model abilities. Technical Report MSR-TR-2023-8, Microsoft, February 2023.
- Self-instruct: Aligning language model with self generated instructions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.10560, 2022.
- Finetuned language models are zero-shot learners. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.01652, 2021.
- Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models, 2023.
- Visual chatgpt: Talking, drawing and editing with visual foundation models. ArXiv preprint, abs/2303.04671, 2023.
- Wizardlm: Empowering large language models to follow complex instructions, 2023a.
- On the tool manipulation capability of open-source large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16504, 2023b.
- Chatgpt is not enough: Enhancing large language models with knowledge graphs for fact-aware language modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.11489, 2023.
- React: Synergizing reasoning and acting in language models. ArXiv preprint, abs/2210.03629, 2022.
- Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10601, 2023.
- Large language model as autonomous decision maker. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.12519, 2023.
- Toolqa: A dataset for llm question answering with external tools. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.13304, 2023.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.