- The paper demonstrates that tailored communication strategies effectively bridge knowledge gaps between AI developers and stakeholders.
- It outlines methods like shared documentation and visual aids to build trust and align expectations among diverse team members.
- The study suggests practical improvements for collaboration tools and communication protocols to enhance interdisciplinary AI projects.
Overcoming Communication Barriers in Multidisciplinary AI Teams
The case paper presented in "How AI Developers Overcome Communication Challenges in a Multidisciplinary Team: A Case Study" addresses the intricacies of communication gaps encountered by AI developers working within multidisciplinary teams. As AI systems are deployed in increasingly complex contexts, coordinating amongst diverse expert groups becomes critical. This paper thoroughly examines how challenges in communication are addressed when implementing AI solutions in diverse, enterprise environments.
Communication Gaps Identified
The paper highlights three principal sources of communication barriers experienced by AI developers: knowledge gaps, trust-building across roles, and managing expectations. These challenges arise primarily because of differences in expertise between AI developers, who have technical proficiency in data science, and stakeholders, who may not share the same level of familiarity with AI methodologies.
Knowledge Gaps
A recurring theme is the disparity in domain-specific knowledge between AI developers and stakeholders. AI systems involve sophisticated models and algorithms which require developers to effectively bridge their technical understanding with the stakeholders' domain knowledge. Educational initiatives such as informal sessions and workshops are often undertaken to reduce this gap. However, these efforts can be resource-intensive and are not standardized, leading to inefficiencies (Figure 1).
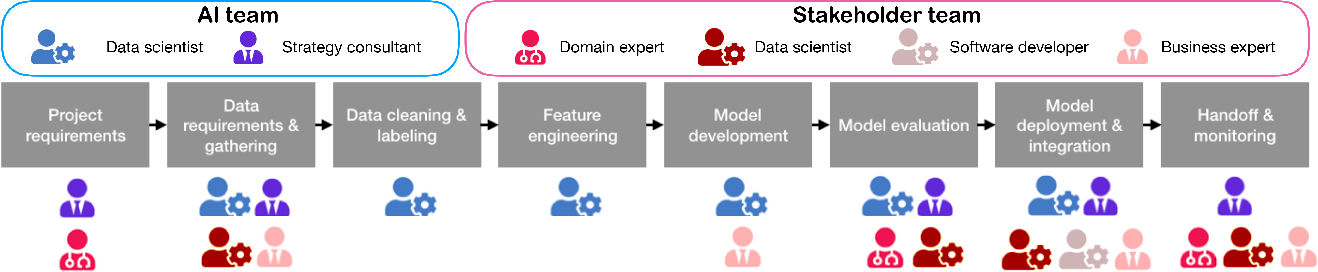
Figure 1: Aggregated view of our interviewees' different roles involved in each stage of AI development, highlighting diverse expertise areas.
Trust and Expectations
According to the paper, building trusted relationships is foundational for successful interdisciplinary collaboration. Trust facilitates open dialogues concerning AI's limitations and capabilities. This is achieved through regular interactions that include updates on AI's development stages and transparent communication about potential setbacks (Figure 2). Managing expectations involves clarifying the unpredictable nature of AI system performance to stakeholders who might expect deterministic results.
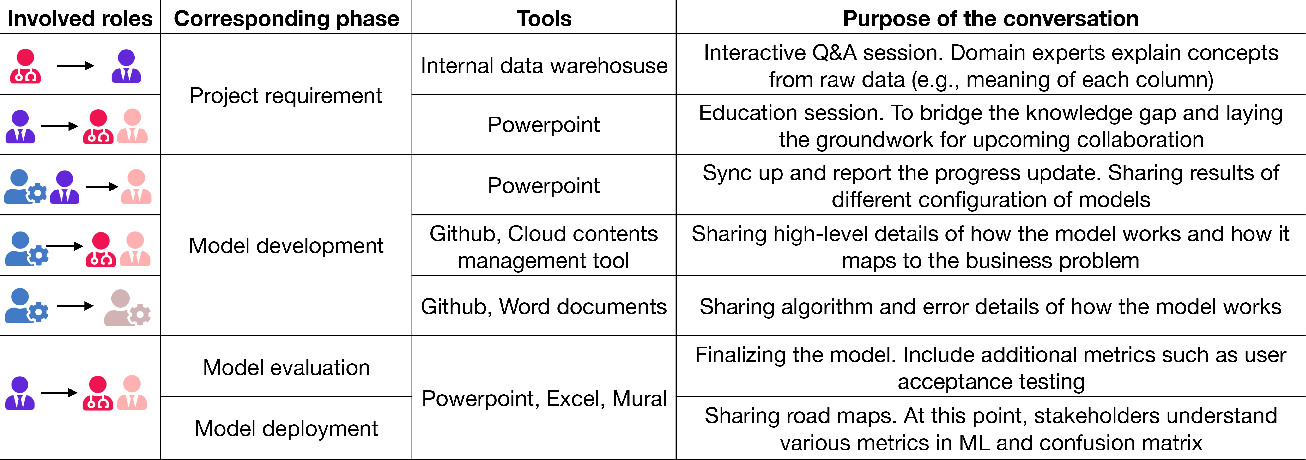
Figure 2: Different tools used for inter-team communication and the reasons behind these interactions.
Strategies for Overcoming Gaps
This research illuminates specific strategies undertaken by AI teams to address these communication barriers. AI developers actively tailor their communication strategies to their audience's expertise level, simplifying explanations and utilizing visual aids and tailored presentations (Figure 3).
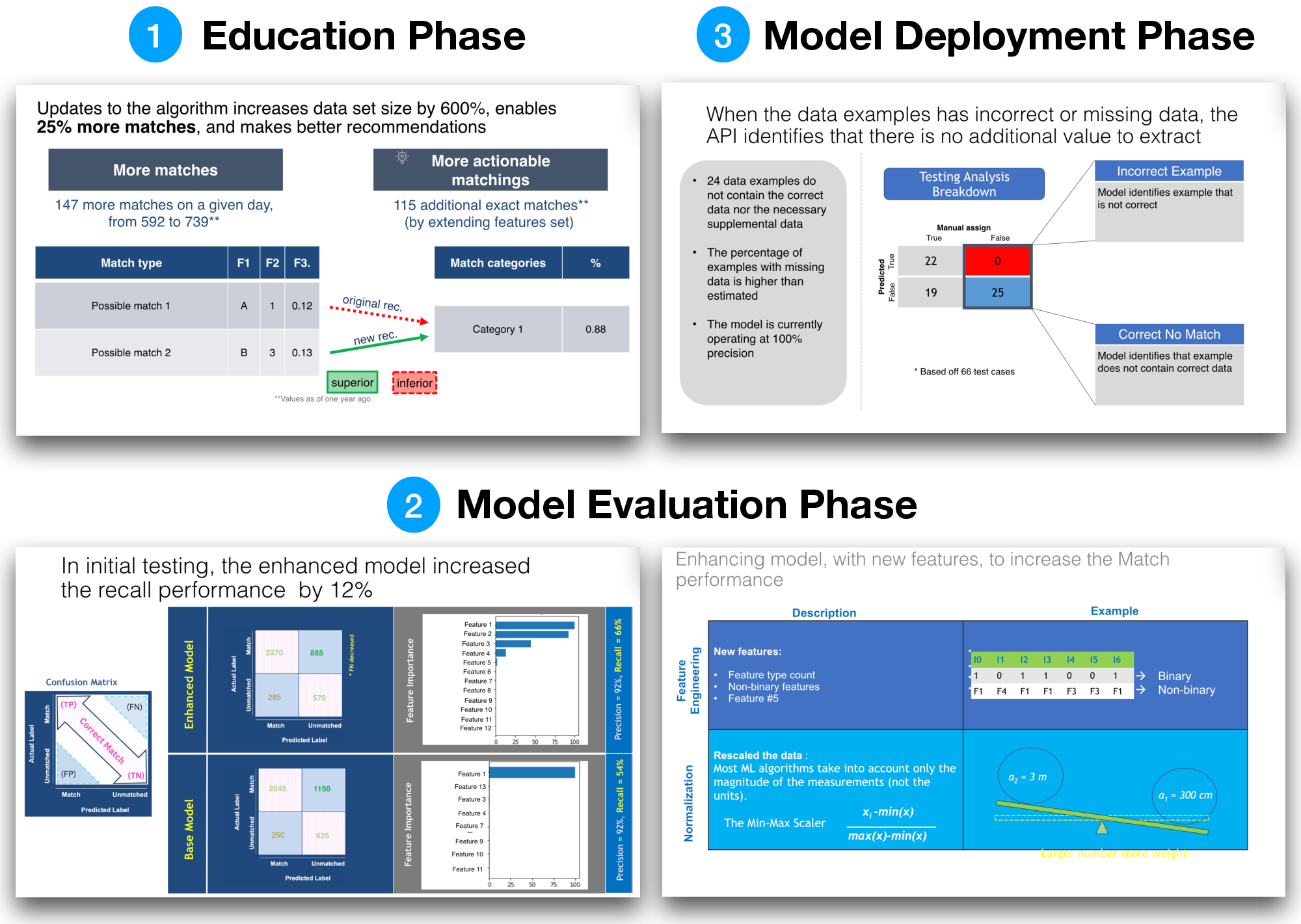
Figure 3: Examples of presentations in the AI development workflow through various phases.
Consistency and Proactivity
To maintain shared understanding, developers often rely on consistent information dissemination using shared documentation spaces and proactively addressing potential misunderstandings before they exacerbate. The inclusion of regularly updated shared documents helps maintain alignment over the project lifecycle, creating a centralized point for information exchange.
Reactive Strategies
When unexpected challenges arise, developers employ reactive strategies by quickly addressing these issues through targeted communication efforts. This includes detailed explanations with specific examples to clarify discrepancies, thereby fostering better alignment and facilitating smoother interactions between multidisciplinary team members.
Practical Implications and Future Considerations
The challenges and strategies identified in this paper have significant implications for the development of collaborative tools tailored to AI environments. This research encourages the creation of software solutions that can dynamically adapt content to different roles, facilitating a more effective and contextualized communication flow.
Future research should further explore the dual perspective of AI developers and stakeholders to develop more holistic solutions, as current insights are one-sided. Moreover, addressing these challenges by leveraging technological solutions such as automated summarization tools or developing standard protocols for interdisciplinary communication can significantly enhance collaborative efforts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this case paper provides valuable insights into the communicative dynamics in multidisciplinary AI teams. By systematically identifying and addressing the challenges within these interactions, it becomes possible to facilitate smoother collaboration and ultimately more effective AI implementations. Enhanced communication strategies are essential for AI to fulfill its potential across varied application domains, ensuring that interdisciplinary teams operate with a shared understanding and aligned objectives.


