- The paper demonstrates that AI awareness significantly increases communication frequency and reduces turn durations in design tasks.
- It employs a Wizard-of-Oz methodology to simulate real-time design interactions and gathers detailed quantitative and qualitative data.
- Findings emphasize the need for adjustable AI awareness mechanisms to improve collaboration while addressing ethical concerns like privacy.
An Exploratory Study on How AI Awareness Impacts Human-AI Design Collaboration
This essay explores the impacts of enabling AI awareness in human-AI design collaboration, as examined in the paper "An Exploratory Study on How AI Awareness Impacts Human-AI Design Collaboration" (2502.16833). The research investigates how AI's understanding of designers' activities and the context of collaboration influences communication fluidity and overall collaboration efficiency. By employing a Wizard-of-Oz (WoZ) experiment, the paper evaluates both quantitative and qualitative outcomes, providing insights into the design implications for future human-AI collaborative design systems.
Human-AI Collaborative Design System
The authors developed a human-AI collaborative design system prototype with specific focus areas: interface design, system functions, and interactions (Figure 1). The interface features include a canvas for design operations, a chatbox for communication history, and a camera screen for awareness functionalities, limited to the Aware condition. The system architecture is depicted in Figure 2, showcasing the interaction flow between participants and backend support through a Wizard setup.
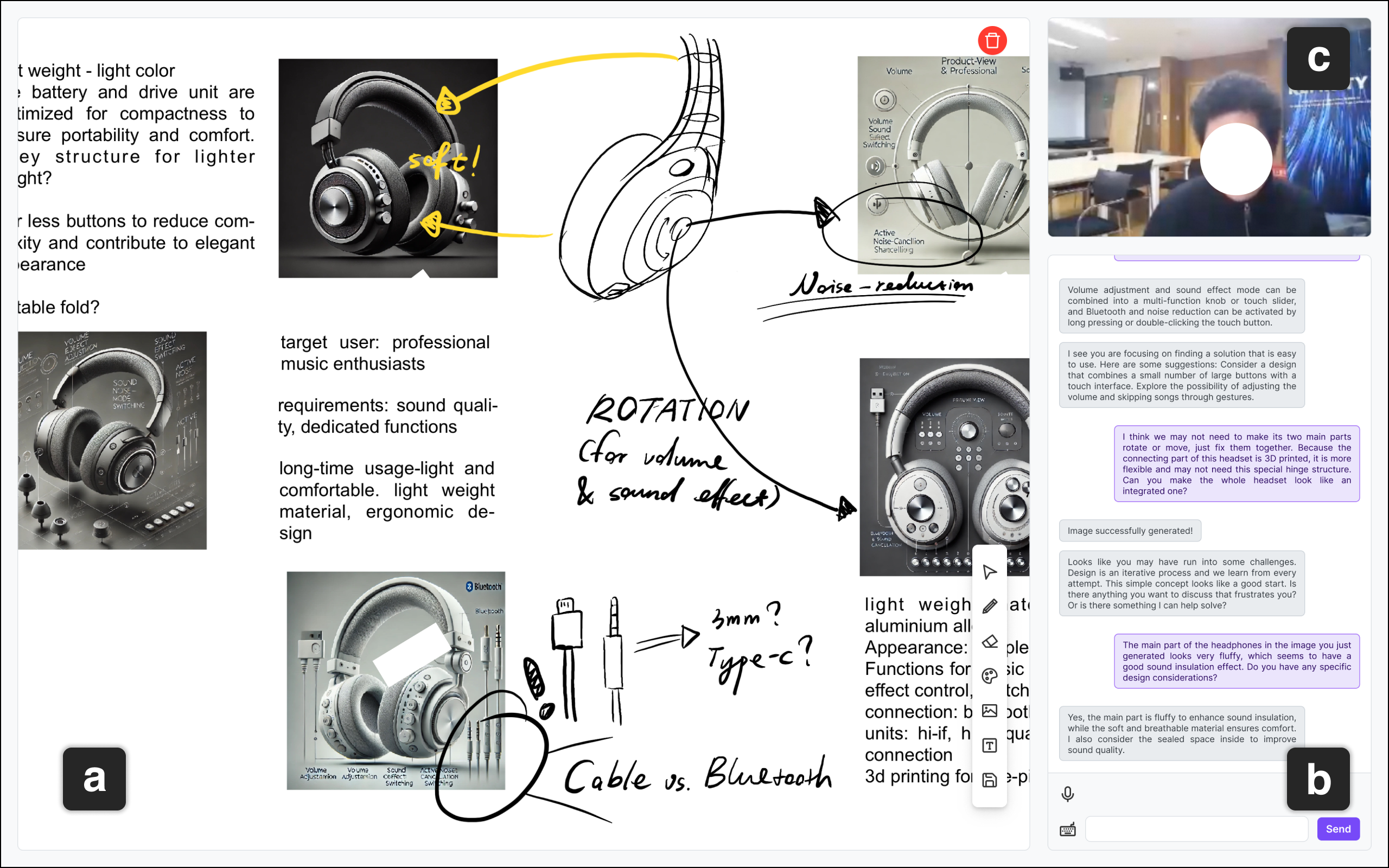
Figure 1: The interface example of the human-AI design collaborative system.
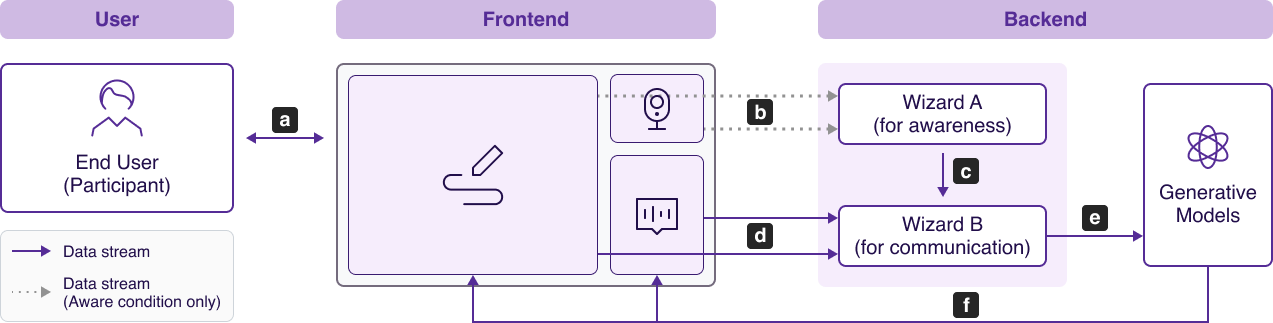
Figure 2: System structure and data stream in human-AI collaborative design.
Wizard Implementation
The system uses two Wizards for backend operations: Wizard A manages awareness information while Wizard B facilitates communication (Figure 3). Wizard A obtains contextual data such as current design activities and canvas status, whereas Wizard B organizes participant inputs and forwards prompts to generative AI models (GPT-4 turbo and DALL-E 3) for feedback generation.
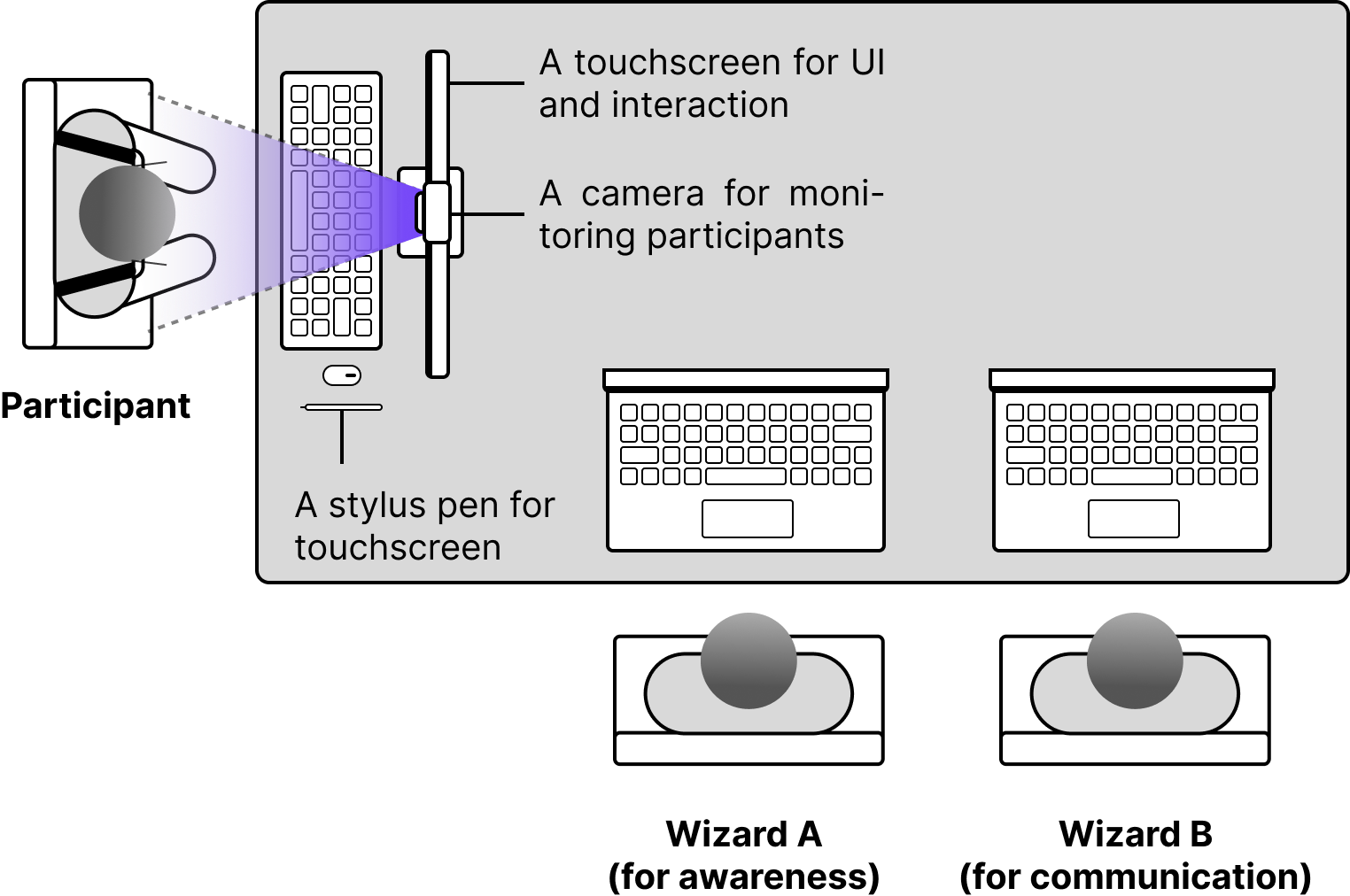
Figure 3: WoZ experiment setup, detailing positions of participants and Wizards.
User Study
Methodology
The user paper comprised two experimental conditions: Aware and Non-aware. Participants executed design tasks on distinct products—e-scooter and headphone—with each condition involving AI's awareness functionality differently controlled. A comprehensive setup ensured that context recognition depended on Wizard A's inputs, impacting communication fluidity. The analysis drew from multiple data sources: experiment recordings, conversation logs, and participant interviews, processed into quantitative measures like turn frequency, duration, and qualitative thematic analysis.
Results
Quantitative findings indicated a significant increase in communication frequency and decrease in turn duration and length in the Aware condition compared to the Non-aware. Additionally, thematic analysis from interviews revealed participant perspectives on communication willingness, effort, and speech style changes spurred by AI's context-aware responses (Figure 4).
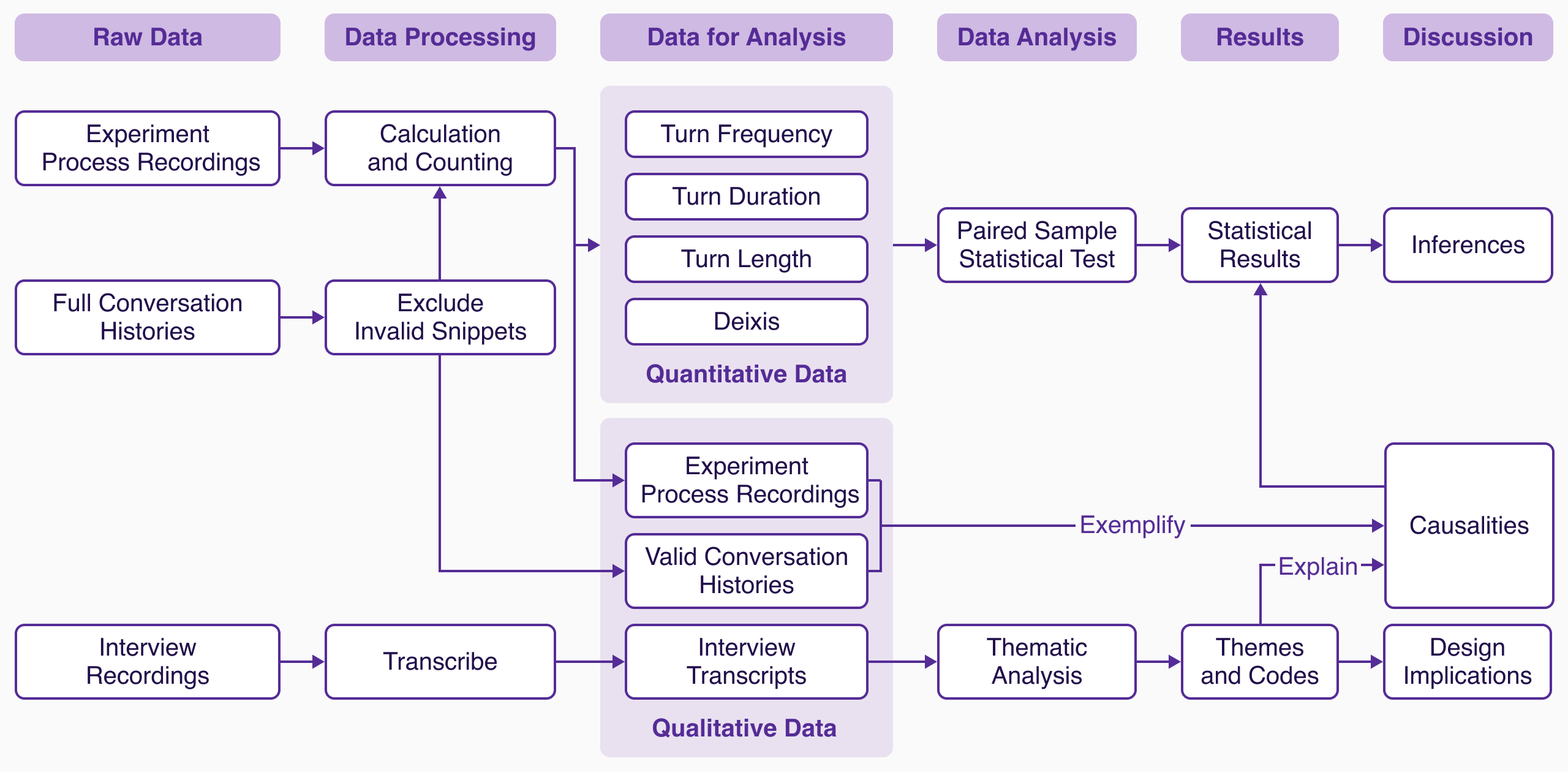
Figure 4: Data analysis process overview, linking raw data to insights.
Discussion
Causal Influences
The results highlight AI awareness as a critical factor enhancing communication efficiency. Participants reported improved alignment and reduced cognitive burden in the Aware condition, reinforcing the notion that AI foresight into task context facilitates smoother collaboration. However, discrepancies in perceived efficiency suggest adaptive AI strategies might be necessary, addressing unique user needs and situational context-sensitive responses.
Design Implications
Key design implications extracted from the paper include developing mechanisms for adjustable AI awareness and mutual awareness facilitation. Incorporating speech-specific features like tone and pace for emotional and situational cues could further refine AI feedback accuracy and relevance. Ensuring interruption potential and timely feedback in communication enhances human-AI interaction dynamics, vital for practical implementation.
Ethical Considerations
The paper raises ethical concerns, notably regarding privacy and the risk of design fixation. AI collaboration models must incorporate safeguards against these risks, emphasizing secure data handling and preserving informational integrity while avoiding undue influence on creative processes.
Conclusion
The research presents substantial evidence supporting the positive role of AI awareness in human-AI design collaboration, driving efficiencies through enhanced communication dynamics. While demonstrating promising outcomes, future system developments should address variability in user experience and ethical implications, guiding the advancement of collaborative AI in dynamic tasks akin to design.





