The Good and The Bad: Exploring Privacy Issues in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
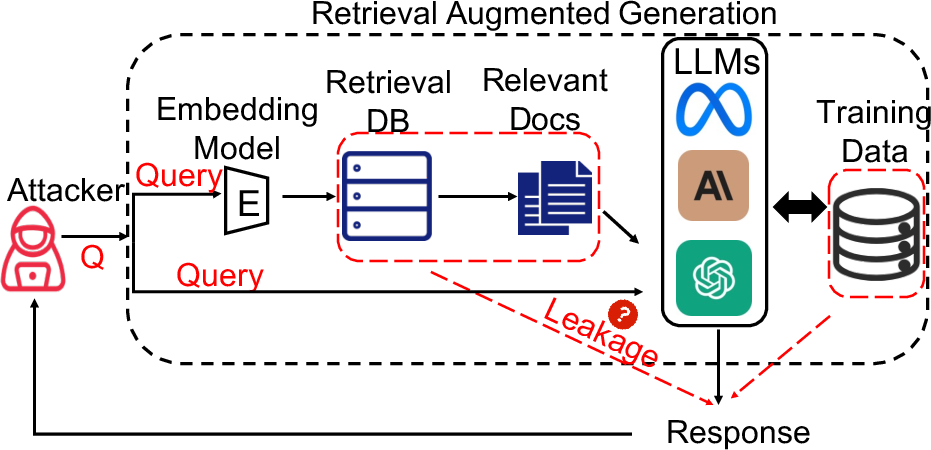
Abstract: Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is a powerful technique to facilitate LLM with proprietary and private data, where data privacy is a pivotal concern. Whereas extensive research has demonstrated the privacy risks of LLMs, the RAG technique could potentially reshape the inherent behaviors of LLM generation, posing new privacy issues that are currently under-explored. In this work, we conduct extensive empirical studies with novel attack methods, which demonstrate the vulnerability of RAG systems on leaking the private retrieval database. Despite the new risk brought by RAG on the retrieval data, we further reveal that RAG can mitigate the leakage of the LLMs' training data. Overall, we provide new insights in this paper for privacy protection of retrieval-augmented LLMs, which benefit both LLMs and RAG systems builders. Our code is available at https://github.com/phycholosogy/RAG-privacy.
- Emergent and predictable memorization in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.11158.
- Improving language models by retrieving from trillions of tokens. In International conference on machine learning, pages 2206–2240. PMLR.
- Quantifying memorization across neural language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.07646.
- Extracting training data from large language models. In 30th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 21), pages 2633–2650.
- Harrison Chase. 2022. Langchain. October 2022. https://github.com/hwchase17/langchain.
- Lift yourself up: Retrieval-augmented text generation with self memory. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.02437.
- Evelyn Fix and Joseph Lawson Hodges. 1989. Discriminatory analysis. nonparametric discrimination: Consistency properties. International Statistical Review/Revue Internationale de Statistique, 57(3):238–247.
- Retrieval-augmented generation for large language models: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.10997.
- Privacy implications of retrieval-based language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14888.
- Preventing verbatim memorization in language models gives a false sense of privacy. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.17546.
- Deduplicating training data mitigates privacy risks in language models. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 10697–10707. PMLR.
- Generalization through memorization: Nearest neighbor language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.00172.
- Reinforcement learning for optimizing rag for domain chatbots. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.06800.
- Do language models plagiarize? In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, pages 3637–3647.
- Deduplicating training data makes language models better. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.06499.
- Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive nlp tasks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33:9459–9474.
- Liu. 2023. Twitter post. https://twitter.com/kliu128/status/1623472922374574080.
- Jerry Liu. 2022. Llamaindex. 11 2022. https://github.com/jerryjliu/llama_index.
- Memorization in nlp fine-tuning methods. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.12506.
- Augmenting large language models with rules for enhanced domain-specific interactions: The case of medical diagnosis. Electronics, 13(2):320.
- Retrieval augmented code generation and summarization. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2021, pages 2719–2734.
- In-context retrieval-augmented language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.00083.
- Enhancing retrieval-augmented large language models with iterative retrieval-generation synergy. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15294.
- Replug: Retrieval-augmented black-box language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.12652.
- Retrieval augmentation reduces hallucination in conversation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.07567.
- Improving the domain adaptation of retrieval augmented generation (rag) models for open domain question answering. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 11:1–17.
- Clinical text summarization: Adapting large language models can outperform human experts. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07430.
- Simon Willison. 2022. Prompt injection attacks against gpt-3. https://simonwillison.net/2022/Sep/12/promptinjection/.
- An explanation of in-context learning as implicit bayesian inference. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.02080.
- Chatdoctor: A medical chat model fine-tuned on llama model using medical domain knowledge. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.14070.
- Exploring memorization in fine-tuned language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.06714.
- Counterfactual memorization in neural language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.12938.
- Yiming Zhang and Daphne Ippolito. 2023. Prompts should not be seen as secrets: Systematically measuring prompt extraction attack success. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.06865.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.