- The paper introduces the innovative Masked Channel Residual Vector Quantization (MCRVQ) to effectively distribute audio information across codec channels.
- Experimental results on LibriTTS and LJSpeech demonstrate improved UTMOS, PESQ, and STOI metrics compared to baseline models.
- The framework enhances downstream TTS applications by significantly improving speaker similarity and reducing word error rates in zero-shot models.
Language-Codec: Bridging Discrete Codec Representations and Speech LLMs
Introduction
The paper "Language-Codec: Bridging Discrete Codec Representations and Speech LLMs" presents an innovative approach called Language-Codec, which aims to ameliorate the gaps between discrete acoustic codec representations and speech LLMs. Discrete codecs have become pivotal in high-quality generative tasks involving speech and audio, replacing traditional mel-spectrograms with more compact representations. However, discrepancies arise due to limited training datasets and inefficient codec designs. Language-Codec proposes the Masked Channel Residual Vector Quantization (MCRVQ) mechanism coupled with enhanced training paradigms to bolster compatibility with downstream speech models.
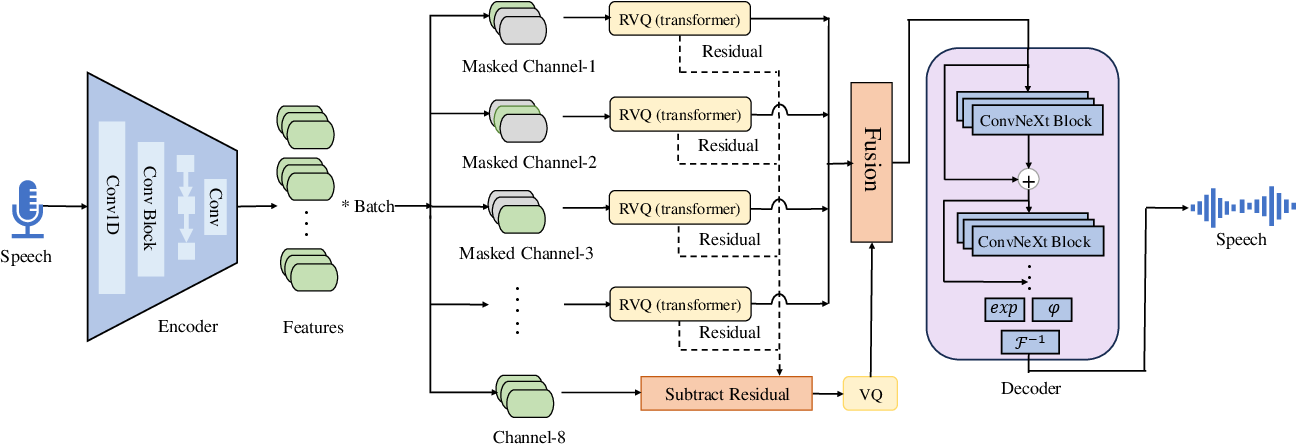
Figure 1: The overall architecture for Language-Codec. On the far left is the encoder downsampling module, which still utilizes the model structure of Encodec. On the far right is the decoder upsampling module, where we have replaced it with Vocos' model structure. the middle part is the Masked Channel Residual Vector Quantization module, with the gray blocks indicating the masked portion of temporal information.
Framework and Architecture
The core innovation of Language-Codec lies in its architectural adjustments and training refinements. The encoder component, derived from Encodec, is responsible for downsampling audio inputs to a latent space. In contrast, the decoder segment employs Vocos' FFT-based upsampling structure, enhancing time-domain to frequency-domain transformations. The transformative aspect is the MCRVQ module, which diversifies information across codec channels, mitigating information overload in initial channels.
MCRVQ utilizes a parallel and serial hybrid quantization scheme that enforces channel masking in the initial quantization stages. This setup distributes audio information uniformly, reducing dependency on initial codec layers and streamlining downstream tasks like speech synthesis. The architecture additionally comprises improved Fourier transform capabilities, robust discriminator designs, and a data-driven approach through extensive datasets covering 50,000 hours.
Experimental Results
Evaluation Metrics
Performance evaluations were conducted using standard datasets like LibriTTS and LJSpeech. Key metrics included UTMOS, PESQ, STOI, and speaker similarity, providing a comprehensive understanding of audio quality and codec model efficacy. Lower bitrates with minimal channel numbers were targeted to reflect practical deployment scenarios.
The empirical results underscore Language-Codec's superiority. Across both LibriTTS and LJSpeech datasets, Language-Codec outperforms baseline models such as Encodec and Vocos in UTMOS, PESQ, and STOI metrics. Especially in challenging noisy environments (LibriTTS Test-Other), Language-Codec maintains robust audio reconstructive fidelity, a testament to its generalization prowess.
Downstream Applications
For zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) models, both VALL-E and MobileSpeech benefitted from Language-Codec's representations, evidenced by enhanced speaker similarity and reduced word error rates (WER). Particularly, MobileSpeech models demonstrated superior MOS-Q and MOS-S scores, affirming the codec's adaptability to different TTS architectures.
Future Directions and Implications
The successful integration of the MCRVQ mechanism showcases a viable pathway for bridging the informational chasm between discrete codecs and speech models. Future work could explore adaptive codebook resizing and multi-scale quantization to further refine codec efficacy in dynamically varying linguistic contexts.
The practical implications are significant, as Language-Codec provides a robust, scalable solution for high-quality speech generation and comprehension tasks, potentially elevating the standards for interactive voice systems and media communications.
Conclusion
Language-Codec marks a significant milestone in discrete codec development. By addressing core issues of codec-channel information distribution and leveraging comprehensive training datasets, it sets a new benchmark in speech and audio processing. As low-rate, high-quality codecs become pivotal in multimedia applications, Language-Codec's foundational insights will inform future advancements in AI-driven audio synthesis.
