Large Language Model based Multi-Agents: A Survey of Progress and Challenges
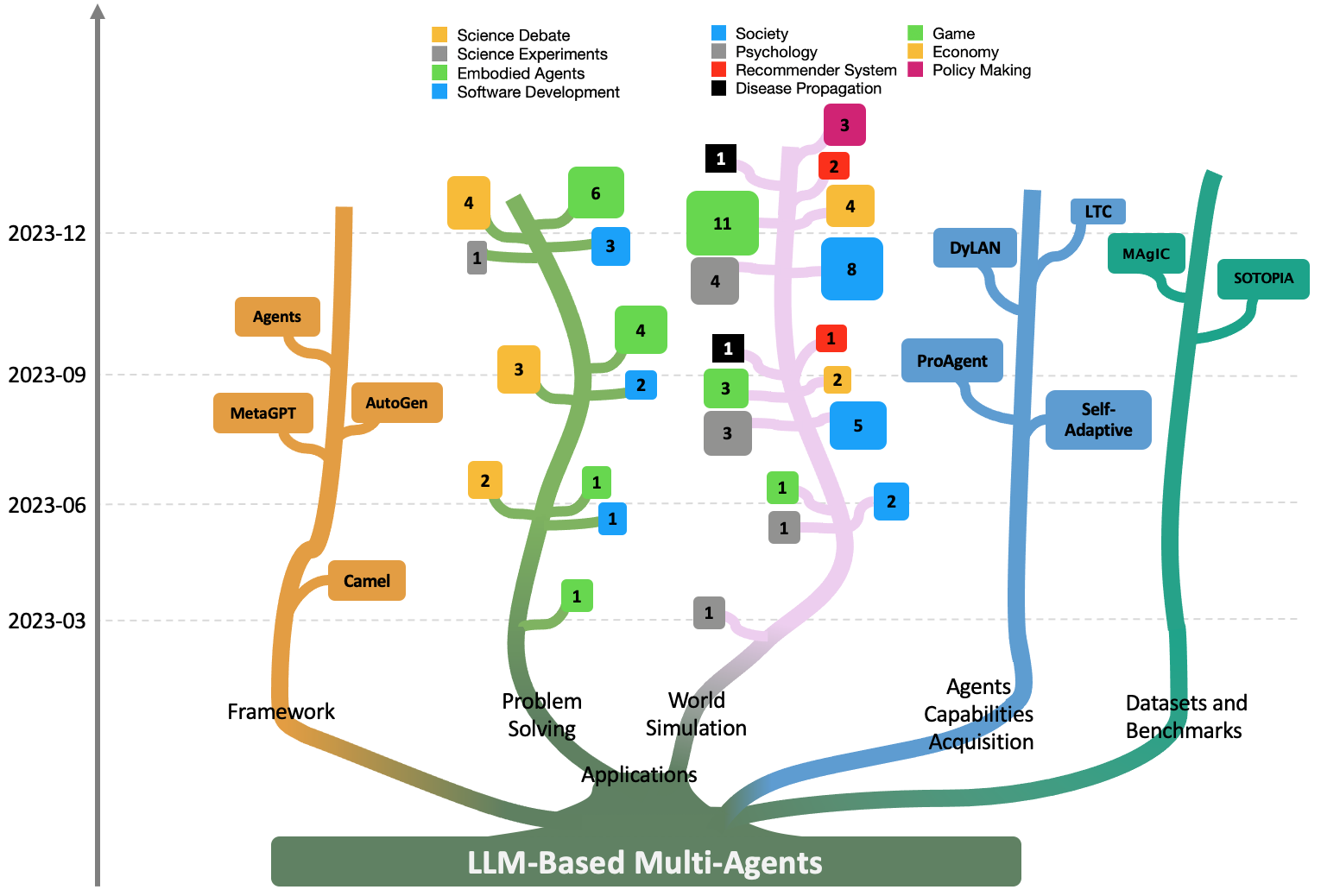
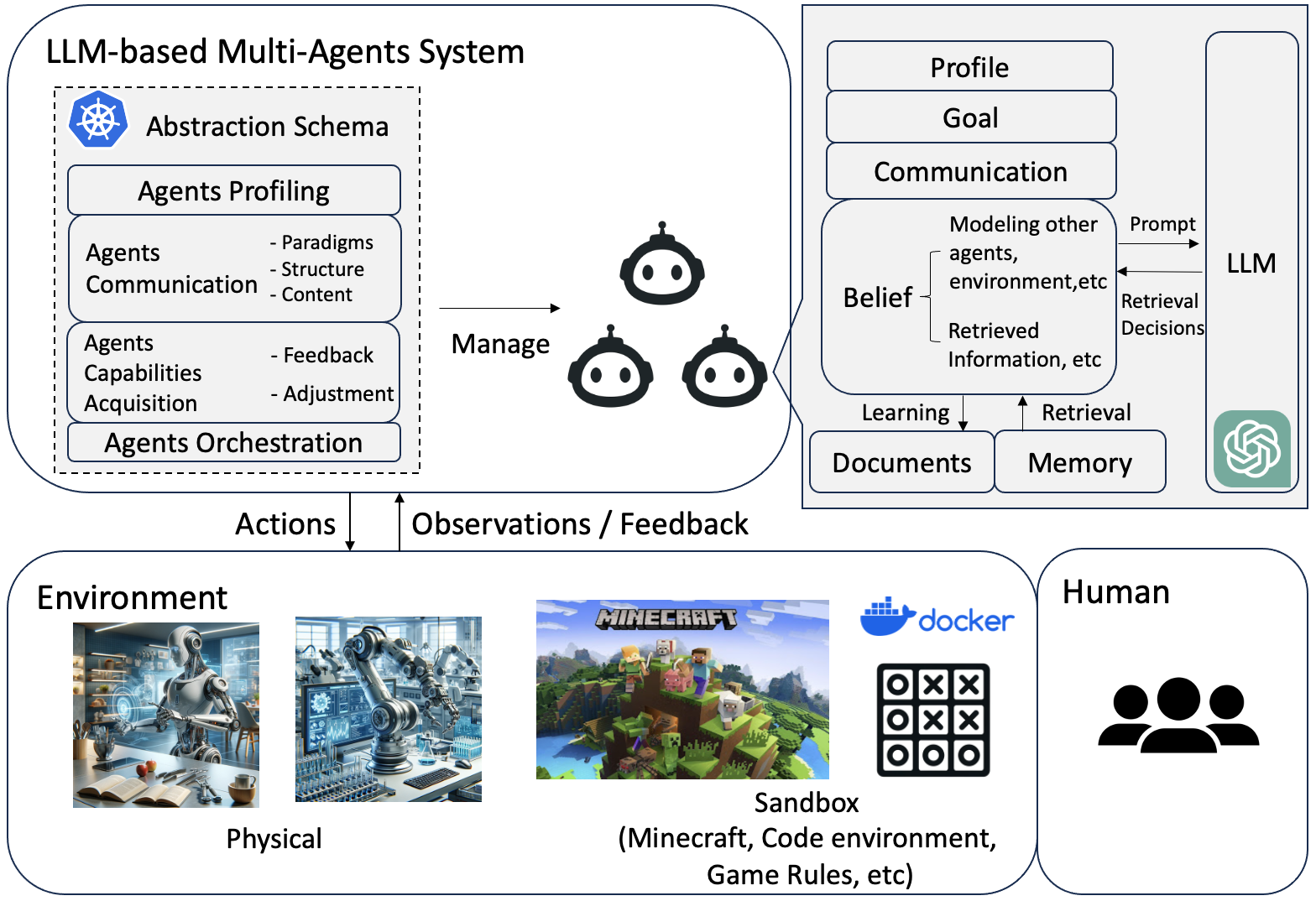
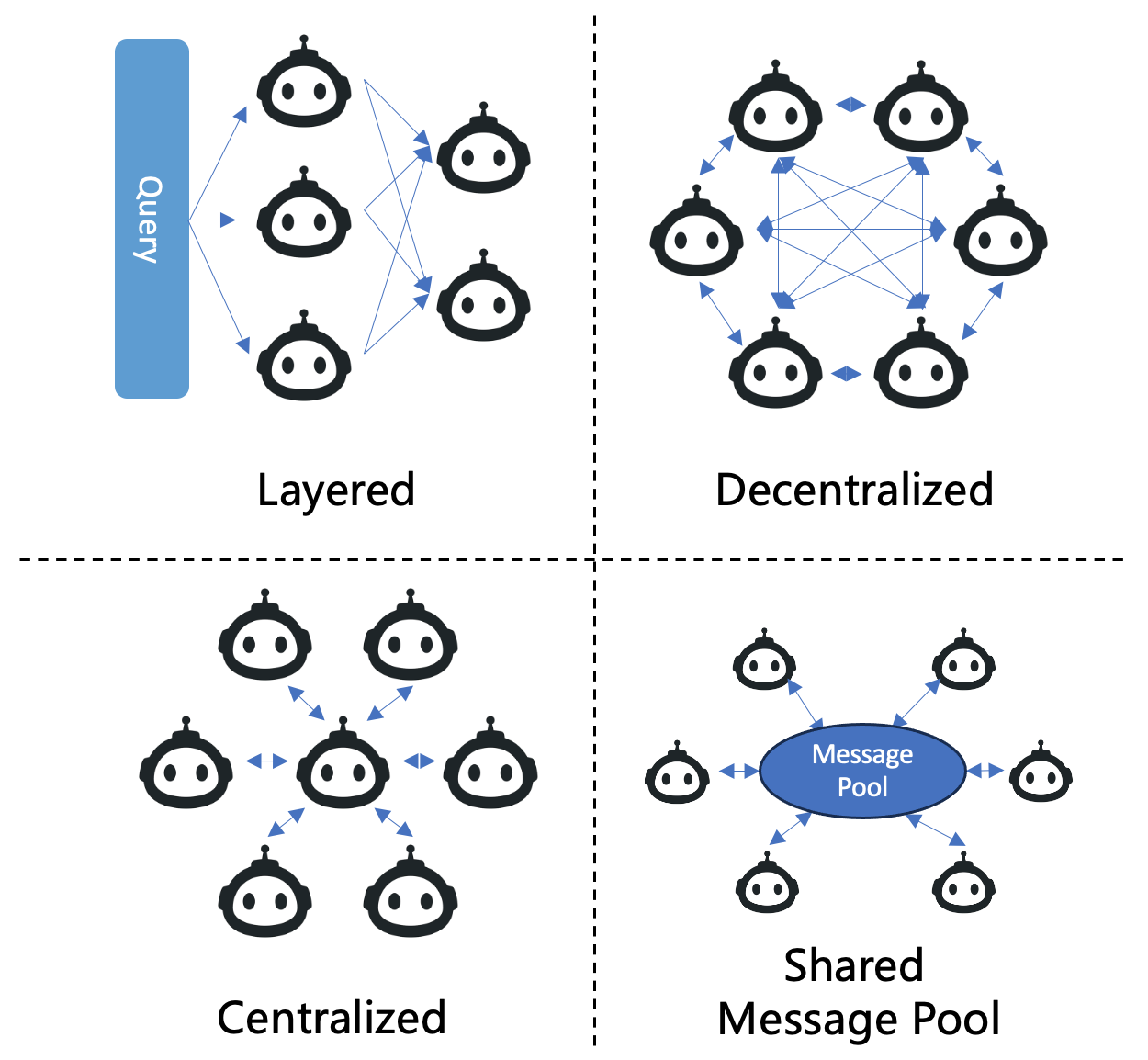
Abstract: LLMs have achieved remarkable success across a wide array of tasks. Due to the impressive planning and reasoning abilities of LLMs, they have been used as autonomous agents to do many tasks automatically. Recently, based on the development of using one LLM as a single planning or decision-making agent, LLM-based multi-agent systems have achieved considerable progress in complex problem-solving and world simulation. To provide the community with an overview of this dynamic field, we present this survey to offer an in-depth discussion on the essential aspects of multi-agent systems based on LLMs, as well as the challenges. Our goal is for readers to gain substantial insights on the following questions: What domains and environments do LLM-based multi-agents simulate? How are these agents profiled and how do they communicate? What mechanisms contribute to the growth of agents' capacities? For those interested in delving into this field of study, we also summarize the commonly used datasets or benchmarks for them to have convenient access. To keep researchers updated on the latest studies, we maintain an open-source GitHub repository, dedicated to outlining the research on LLM-based multi-agent systems.
- Evaluating multi-agent coordination abilities in large language models, 2023.
- Using large language models to simulate multiple humans and replicate human subject studies, 2023.
- Playing repeated games with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16867, 2023.
- Anonymous. Rethinking the buyer’s inspection paradox in information markets with language agents. In Submitted to The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations, 2023. under review.
- Chateval: Towards better llm-based evaluators through multi-agent debate, 2023.
- Autoagents: A framework for automatic agent generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.17288, 2023.
- Multi-agent consensus seeking via large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.20151, 2023.
- Agentverse: Facilitating multi-agent collaboration and exploring emergent behaviors in agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.10848, 2023.
- Scalable multi-robot collaboration with large language models: Centralized or decentralized systems? arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.15943, 2023.
- Training verifiers to solve math word problems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.14168, 2021.
- Collaborating with language models for embodied reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.00763, 2023.
- Victor Dibia. Multi-agent llm applications — a review of current research, tools, and challenges. https://newsletter.victordibia.com/p/multi-agent-llm-applications-a-review, 2023.
- A survey on in-context learning, 2023.
- Self-collaboration code generation via chatgpt, 2023.
- Improving factuality and reasoning in language models through multiagent debate, 2023.
- Can large language models serve as rational players in game theory? a systematic analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.05488, 2023.
- Agent-Based Modeling in Economics and Finance: Past, Present, and Future. INET Oxford Working Papers 2022-10, Institute for New Economic Thinking at the Oxford Martin School, University of Oxford, June 2022.
- S33{}^{3}start_FLOATSUPERSCRIPT 3 end_FLOATSUPERSCRIPT: Social-network simulation system with large language model-empowered agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.14984, 2023.
- Retrieval-augmented generation for large language models: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.10997, 2023.
- Did aristotle use a laptop? a question answering benchmark with implicit reasoning strategies, 2021.
- Generative agent-based modeling: Unveiling social system dynamics through coupling mechanistic models with generative artificial intelligence. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.11456, 2023.
- What indeed can gpt models do in chemistry? a comprehensive benchmark on eight tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.18365, 2023.
- Measuring massive multitask language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.03300, 2020.
- Metagpt: Meta programming for multi-agent collaborative framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.00352, 2023.
- John J Horton. Large language models as simulated economic agents: What can we learn from homo silicus? Technical report, National Bureau of Economic Research, 2023.
- War and peace (waragent): Large language model-based multi-agent simulation of world wars, 2023.
- Agentcoder: Multi-agent-based code generation with iterative testing and optimisation, 2023.
- A survey on hallucination in large language models: Principles, taxonomy, challenges, and open questions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.05232, 2023.
- Lyfe agents: Generative agents for low-cost real-time social interactions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.02172, 2023.
- Decomposed prompting: A modular approach for solving complex tasks, 2023.
- The socialai school: Insights from developmental psychology towards artificial socio-cultural agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.07871, 2023.
- Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive nlp tasks, 2021.
- Psychology-informed recommender systems: A human-centric perspective on recommender systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Human Information Interaction and Retrieval, CHIIR ’22, page 367–368, New York, NY, USA, 2022. Association for Computing Machinery.
- Quantifying the impact of large language models on collective opinion dynamics. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.03313, 2023.
- Camel: Communicative agents for” mind” exploration of large scale language model society. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.17760, 2023.
- Theory of mind for multi-agent collaboration via large language models, 2023.
- Api-bank: A comprehensive benchmark for tool-augmented llms, 2023.
- Large language model-empowered agents for simulating macroeconomic activities, 2023.
- Are you in a masquerade? exploring the behavior and impact of large language model driven social bots in online social networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.10337, 2023.
- Tradinggpt: Multi-agent system with layered memory and distinct characters for enhanced financial trading performance, 2023.
- Metaagents: Simulating interactions of human behaviors for llm-based task-oriented coordination via collaborative generative agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.06500, 2023.
- Let gpt be a math tutor: Teaching math word problem solvers with customized exercise generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14386, 2023.
- Avalonbench: Evaluating llms playing the game of avalon, 2023.
- From text to tactic: Evaluating llms playing the game of avalon. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.05036, 2023.
- Dynamic llm-agent network: An llm-agent collaboration framework with agent team optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.02170, 2023.
- Understanding the benefits and challenges of using large language model-based conversational agents for mental well-being support. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15810, 2023.
- Roco: Dialectic multi-robot collaboration with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.04738, 2023.
- Alympics: Language agents meet game theory. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.03220, 2023.
- João Moura. Crewai. https://github.com/joaomdmoura/crewAI, 2023.
- Welfare diplomacy: Benchmarking language model cooperation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.08901, 2023.
- Self-adaptive large language model (llm)-based multiagent systems. In 2023 IEEE International Conference on Autonomic Computing and Self-Organizing Systems Companion (ACSOS-C), pages 104–109. IEEE, 2023.
- Social simulacra: Creating populated prototypes for social computing systems. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, pages 1–18, 2022.
- Generative agents: Interactive simulacra of human behavior. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03442, 2023.
- Communicative agents for software development, 2023.
- Tptu: Large language model-based ai agents for task planning and tool usage, 2023.
- Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach. Prentice Hall Press, USA, 3rd edition, 2009.
- Reflexion: Language agents with verbal reinforcement learning, 2023.
- Cognitive architectures for language agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.02427, 2023.
- Medagents: Large language models as collaborators for zero-shot medical reasoning, 2023.
- Putting humans in the natural language processing loop: A survey, 2021.
- Adapting llm agents through communication, 2023.
- A survey on large language model based autonomous agents, 2023.
- Avalon’s game of thoughts: Battle against deception through recursive contemplation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.01320, 2023.
- Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35:24824–24837, 2022.
- Lilian Weng. Llm powered autonomous agents. https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/, 2023.
- Epidemic modeling with generative agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.04986, 2023.
- Intelligent agents: theory and practice. The Knowledge Engineering Review, 10:115 – 152, 1995.
- Autogen: Enabling next-gen llm applications via multi-agent conversation framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.08155, 2023.
- Chatarena: Multi-agent language game environments for large language models. GitHub repository, 2023.
- The rise and potential of large language model based agents: A survey, 2023.
- Simulating public administration crisis: A novel generative agent-based simulation system to lower technology barriers in social science research. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.06957, 2023.
- Openagents: An open platform for language agents in the wild. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.10634, 2023.
- Examining inter-consistency of large language models collaboration: An in-depth analysis via debate, 2023.
- Magic: Investigation of large language model powered multi-agent in cognition, adaptability, rationality and collaboration, 2023.
- Exploring large language models for communication games: An empirical study on werewolf. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.04658, 2023.
- Language agents with reinforcement learning for strategic play in the werewolf game. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.18940, 2023.
- Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models, 2023.
- Co-navgpt: Multi-robot cooperative visual semantic navigation using large language models, 2023.
- On generative agents in recommendation, 2023.
- Proagent: Building proactive cooperative ai with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.11339, 2023.
- Building cooperative embodied agents modularly with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.02485, 2023.
- Exploring collaboration mechanisms for llm agents: A social psychology view, 2023.
- Agentcf: Collaborative learning with autonomous language agents for recommender systems, 2023.
- Competeai: Understanding the competition behaviors in large language model-based agents, 2023.
- Chatgpt research group for optimizing the crystallinity of mofs and cofs. ACS Central Science, 9(11):2161–2170, 2023.
- Agents: An open-source framework for autonomous language agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07870, 2023.
- Sotopia: Interactive evaluation for social intelligence in language agents, 2023.
- Can large language models transform computational social science? Computational Linguistics, pages 1–53, 2023.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.