FilmAgent: A Multi-Agent Framework for End-to-End Film Automation in Virtual 3D Spaces
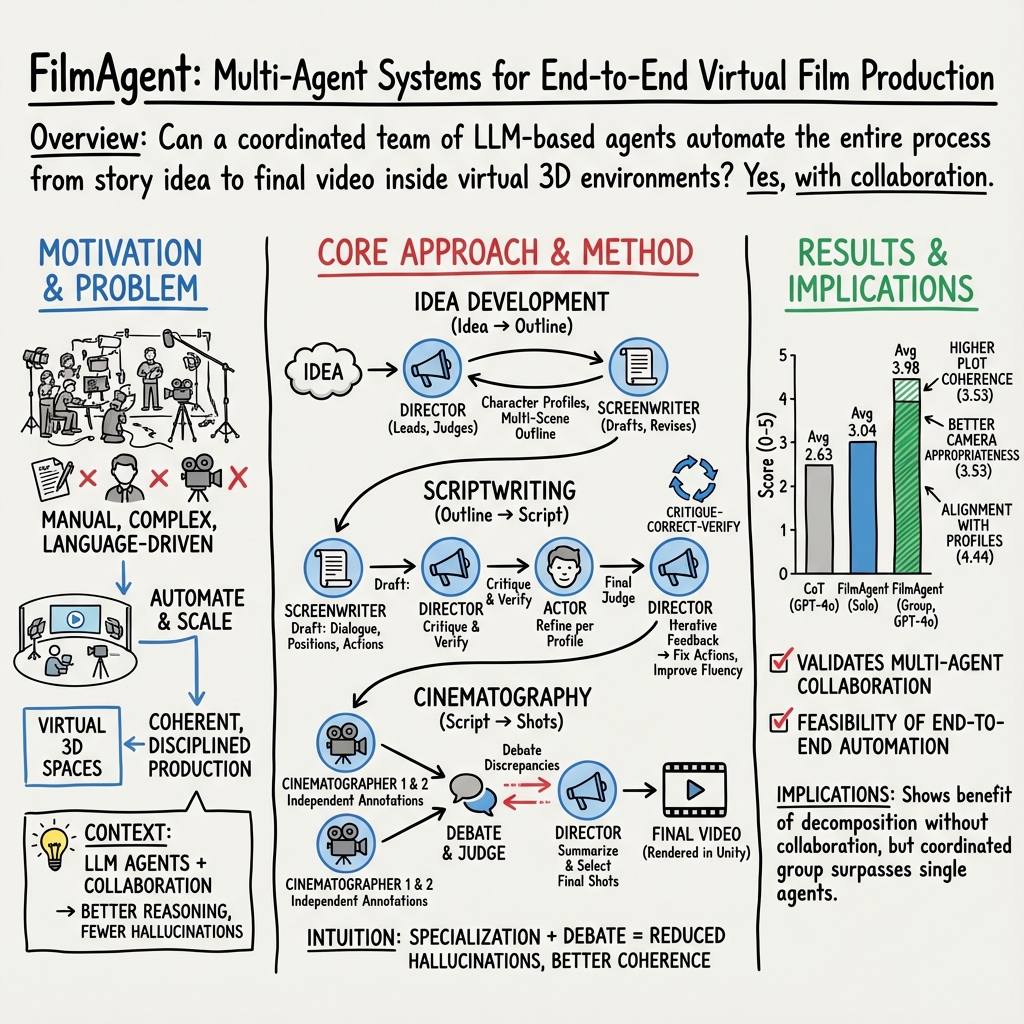
Abstract: Virtual film production requires intricate decision-making processes, including scriptwriting, virtual cinematography, and precise actor positioning and actions. Motivated by recent advances in automated decision-making with language agent-based societies, this paper introduces FilmAgent, a novel LLM-based multi-agent collaborative framework for end-to-end film automation in our constructed 3D virtual spaces. FilmAgent simulates various crew roles, including directors, screenwriters, actors, and cinematographers, and covers key stages of a film production workflow: (1) idea development transforms brainstormed ideas into structured story outlines; (2) scriptwriting elaborates on dialogue and character actions for each scene; (3) cinematography determines the camera setups for each shot. A team of agents collaborates through iterative feedback and revisions, thereby verifying intermediate scripts and reducing hallucinations. We evaluate the generated videos on 15 ideas and 4 key aspects. Human evaluation shows that FilmAgent outperforms all baselines across all aspects and scores 3.98 out of 5 on average, showing the feasibility of multi-agent collaboration in filmmaking. Further analysis reveals that FilmAgent, despite using the less advanced GPT-4o model, surpasses the single-agent o1, showing the advantage of a well-coordinated multi-agent system. Lastly, we discuss the complementary strengths and weaknesses of OpenAI's text-to-video model Sora and our FilmAgent in filmmaking.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Practical Applications
Practical Applications of FilmAgent’s Findings, Methods, and Innovations
Below are actionable applications derived from the paper’s LLM-based multi-agent workflow (Director, Screenwriter, Actor, Cinematographer), its Critique-Correct-Verify and Debate-Judge collaboration strategies, and the Unity-based 3D virtual production stack. Each item names sectors, outlines potential tools/products/workflows, and notes assumptions/dependencies that impact feasibility.
Immediate Applications
- Automated Pre-Visualization (Previs) and Animatics
- Sectors: Media & Entertainment (film/TV), Advertising, Game Studios
- What: Convert story ideas into scene outlines, dialog, actor blocking, actions, and camera plans to generate animatics in Unity. Useful for pitch decks, client approvals, and creative iteration.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: “FilmAgent Previs” Unity/Unreal plugin; script-to-animatic pipeline; export to Sequencer/Timeline; quick renders with TTS voice-overs.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Access to GPT-4o-class LLMs; use of preset 3D locations, camera rigs, and action library; team comfortable with Unity/Unreal; human review for final creative approval.
- Script QA and Consistency Assistant (Writers’ Room Copilot)
- Sectors: Media & Entertainment, Publishing
- What: Use Critique-Correct-Verify to flag plot inconsistencies, character-voice drift, and action-dialog misalignments; suggest targeted rewrites aligned with profiles.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Plugins for Final Draft/Celtx; side-by-side revision proposals; change tracking and rationale logging.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: LLM access; structured character profiles; human-in-the-loop acceptance; IP-safe data handling.
- Camera Planning Assistant for Virtual Production
- Sectors: Media & Entertainment, Virtual Production Stages
- What: Apply Debate-Judge to propose, compare, and finalize shots (e.g., medium vs. pan vs. zoom) per line/beat based on usage guidelines.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Director’s monitor companion; shot list auto-generation; camera path previews in-engine.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Preset camera types and rules; team-defined shot guidelines; Unity/Unreal integration.
- Rapid Short-Form 3D Content Generator for Creators
- Sectors: Creator Economy, Social Media
- What: Produce short skits and story-driven clips with consistent characters and physics-compliant staging, ready for TikTok/Reels/YouTube.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: “One-click” templates; library of everyday locations; voice via ChatTTS; export presets for aspect ratios/platforms.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Style realism constrained by available assets; limited action variety; platform content policies.
- Cutscene Blockout and In-Engine Storyboarding
- Sectors: Gaming
- What: Generate playable scene blockouts (dialog, blocking, cameras) as a foundation for polishing cinematic cutscenes.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Export to Unreal Sequencer/Unity Timeline; versioned script-shot breakdowns for designers.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Asset compatibility; studio pipelines for replacing placeholders with final assets.
- Educational Sandbox for Film Schools
- Sectors: Education (film/cinema, media studies)
- What: Interactive labs for learning blocking, coverage, and shot choice; students compare agent-generated alternatives and critique.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Course modules; grading rubrics tied to camera rules; scenario assignments.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Access to lab machines; licensing for engines/LLMs; instructor oversight.
- A/B Testing of Ad Concepts and Camera Variants
- Sectors: Marketing, Advertising, Product Growth
- What: Generate multiple script-camera variants for the same brief; test creative impact before large-scale production.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Variant generator with Debate-Judge logs; quick animatics + TTS; audience testing dashboards.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Clear brand guidelines; human approval; small-scale pilot audiences for signal.
- Synthetic, Labeled Video Data for Vision/ML
- Sectors: AI/Software, Computer Vision
- What: Generate sequences with precise camera metadata, actor positions, and action labels for tasks like tracking, action recognition, and shot classification.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Dataset generator; exporters for annotations (JSON/COCO-like schemas); scripted scene variations.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Domain gap to real footage; limited action diversity; need for controlled randomization.
- Role-Play Training Videos for L&D
- Sectors: Enterprise Training, Customer Service, Healthcare Admin
- What: Produce consistent role-play scenarios (e.g., feedback conversations, basic triage dialogues) with controllable tone and character profiles.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Scenario templates; compliance review checkpoints; LMS integration.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Legal review; sensitive content guardrails; cultural localization.
- Research Testbed for Multi-Agent Collaboration and Narrative Evaluation
- Sectors: Academia (HCI, AI agents, narrative/NLP)
- What: Use the open-source 3D spaces and workflows to study agent debate/critique, hallucination reduction, and human preference.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Baseline scripts; human eval protocols; reproducible prompts and iterations.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Access to APIs; IRB for human studies; documented metrics.
Long-Term Applications
- End-to-End Automated Virtual Production (On-Set Co-Director)
- Sectors: Media & Entertainment, Live Events
- What: Real-time co-director coordinating MoCap talent, camera robots, and LED volumes; dynamic coverage suggestions and safety-aware camera moves.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: LiveOps orchestration layer; integration with tracking systems and stage control.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Low-latency multimodal models; safety validation; standardized device APIs; union rules and on-set governance.
- Photorealistic, Long-Form Story Generation with T2V/T2-3D
- Sectors: Streaming, Feature Animation, Advertising
- What: Orchestrate Sora-like text-to-video and text-to-3D for coherent multi-scene films; FilmAgent handles story consistency and blocking; T2V handles final render style.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Pipeline orchestrator (FilmAgent → scene graphs → T2V/T2-3D render → editorial); consistency trackers for characters/props.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Longer-duration, more consistent T2V; controllable scene graph interfaces; IP licensing; compute budgets.
- Procedural Scene, Asset, and Motion Synthesis
- Sectors: Software/3D Tools, Game Tech
- What: Remove dependency on preset spaces by integrating SceneCraft/story-to-motion/camera diffusion; generate new environments, motions, and camera paths on demand.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: “World build” agents; motion synthesis from text; camera diffusion for style-specific coverage.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Reliable text-to-3D/motion models; physics compliance; scalable asset QA.
- Frame-Level, Multimodal Direction and Editing
- Sectors: Media Tech, Post-Production
- What: Move from line-level to beat/frame-level control; multimodal LLMs verify visual continuity, eyelines, 180° rule, and suggest micro-edits, transitions, and trims.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Vision-in-the-loop review; auto-assembly of rough cuts; cut list rationales.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Strong vision-language reasoning; standardized edit decision lists (EDLs); temporal consistency guarantees.
- AI Post-Production Suite (Music, Color, Sound, Editorial)
- Sectors: Media & Entertainment
- What: Expand agent roles to composer, colorist, sound designer, and editor; align score/emotion arcs with script beats; propose color pipelines and mixing notes.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: DAW/NLE integrations; LUT and stem management; beat-synced scoring agents.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Rights to training data; creative oversight; interoperability standards across tools.
- Interactive, Personalized XR Storytelling and Training
- Sectors: Education, Healthcare Simulation, Defense/First Responders
- What: Branching narratives with adaptive camera and blocking in VR/AR; agent-driven scenario variation for skills training and assessment.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: XR runtime integration; assessment metrics mapped to narrative states; instructor dashboards.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Performance on headsets; comfort and safety in XR; privacy and scenario sensitivity.
- Live Sports and Events Coverage Optimization
- Sectors: Sports Broadcast, Live Production
- What: Adapt Debate-Judge to choose optimal angles and cuts across multiple cameras; maintain narrative continuity of play/storylines.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Real-time shot selection with human TD override; replay/iso recommendations and rationale.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Low-latency inference; robust rules for safety and broadcast standards; data rights.
- Standardization, Provenance, and Labor Policy Frameworks
- Sectors: Policy, Standards Bodies, Unions
- What: Define metadata for agent roles, decision logs, and content provenance; guidelines for crediting, consent, and residuals when AI agents contribute.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Open metadata schemas; watermarking/signing; audit trails for AI-assisted edits.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Multi-stakeholder alignment; legal/regulatory adoption; interoperability across vendors.
- Creator Marketplaces and Asset/Agent Ecosystems
- Sectors: Software Platforms, Marketplaces
- What: Stores for reusable agent roles (e.g., “Thriller DP,” “Comedy Writer”), shot packs, and 3D scene kits; revenue-sharing models.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Rating systems; compatibility validators; style transfer for agents.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: IP clarity; curation to prevent misuse; platform governance and moderation.
- Quantitative Film Studies and Style Analytics
- Sectors: Academia, Media Analytics
- What: Large-scale analysis of shot patterns, blocking styles, and narrative structures across generated and real films; study how multi-agent debate affects creative decisions.
- Tools/Products/Workflows: Open datasets with shot/action labels; reproducible experiments; cross-film comparative dashboards.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Access to annotated corpora; fair-use regimes; replicable evaluation metrics.
Notes on cross-cutting assumptions and risks:
- LLM availability, cost, and data governance; reliability of hallucination reduction outside provided domains.
- Asset licensing and IP (voices, music, 3D models); compliance with union/industry rules.
- Human oversight remains essential for brand safety, ethics, and high-stakes content.
- Technical dependencies on game engines (Unity/Unreal), TTS, and emerging multimodal models for higher fidelity and control.
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.