Infogent: An Agent-Based Framework for Web Information Aggregation (2410.19054v1)
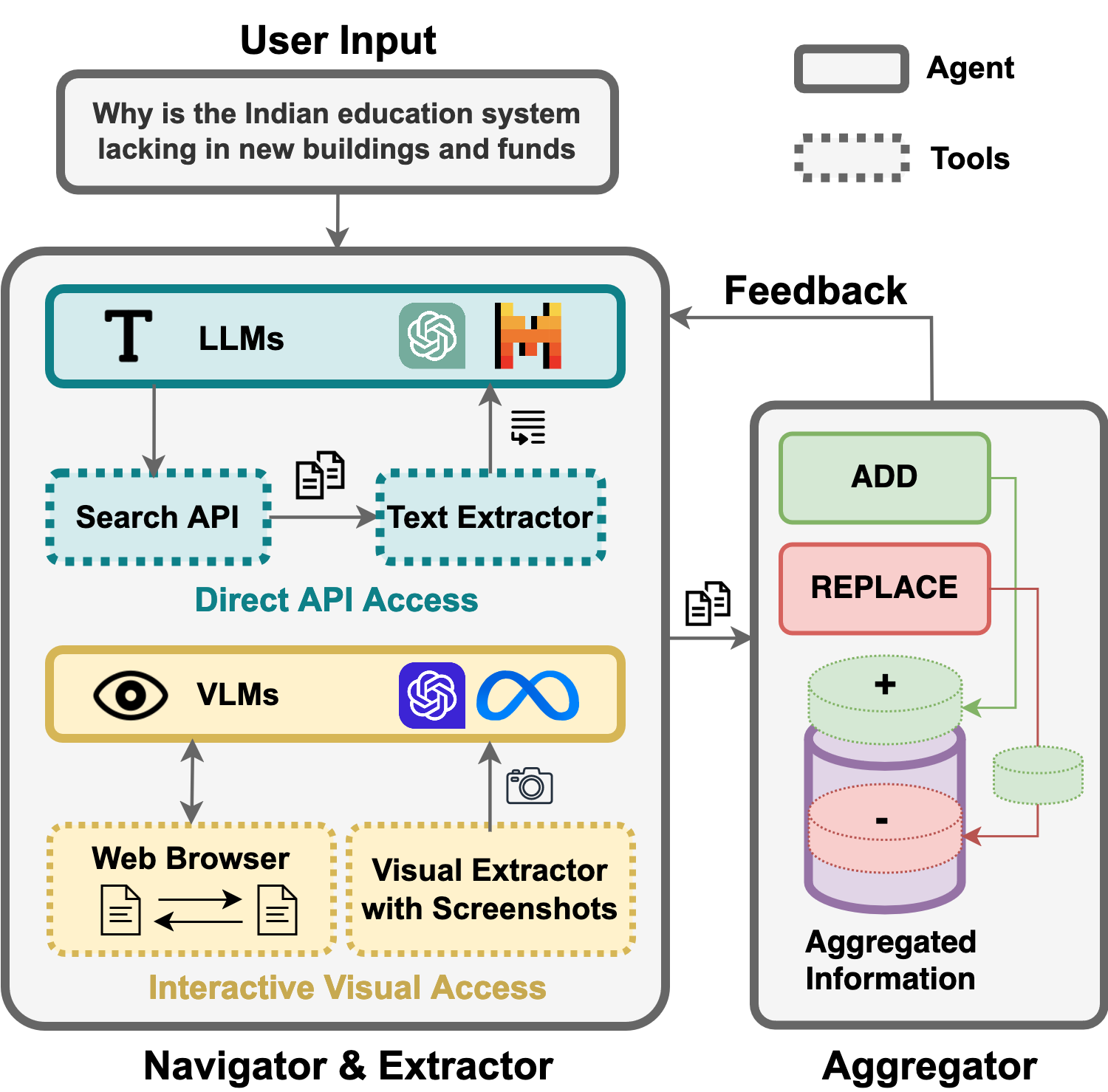
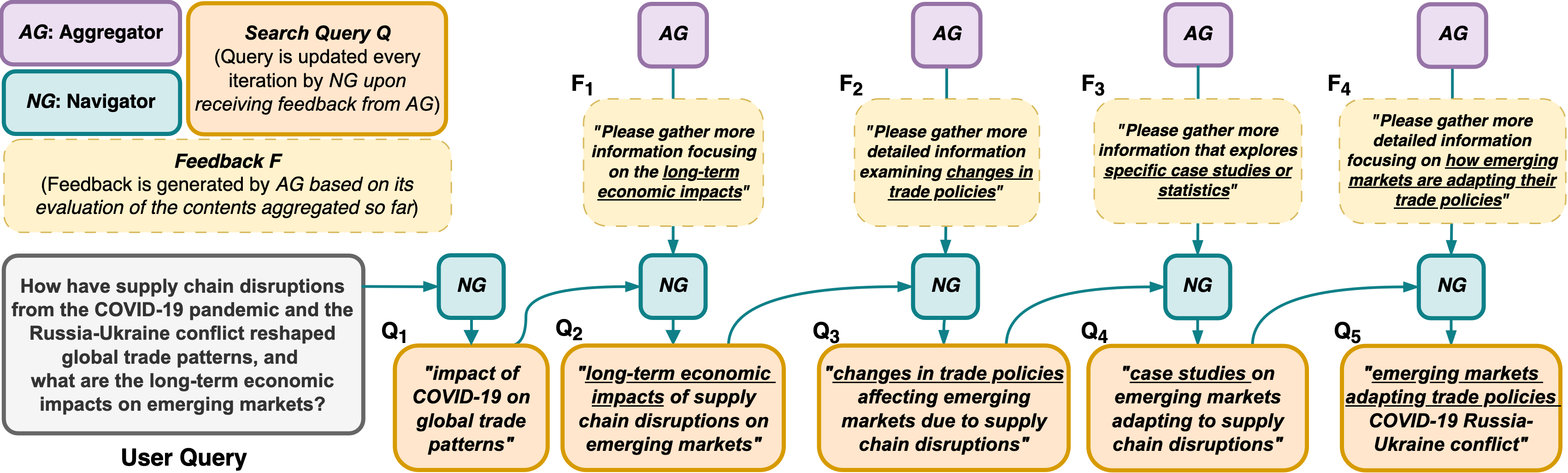
Abstract: Despite seemingly performant web agents on the task-completion benchmarks, most existing methods evaluate the agents based on a presupposition: the web navigation task consists of linear sequence of actions with an end state that marks task completion. In contrast, our work focuses on web navigation for information aggregation, wherein the agent must explore different websites to gather information for a complex query. We consider web information aggregation from two different perspectives: (i) Direct API-driven Access relies on a text-only view of the Web, leveraging external tools such as Google Search API to navigate the web and a scraper to extract website contents. (ii) Interactive Visual Access uses screenshots of the webpages and requires interaction with the browser to navigate and access information. Motivated by these diverse information access settings, we introduce Infogent, a novel modular framework for web information aggregation involving three distinct components: Navigator, Extractor and Aggregator. Experiments on different information access settings demonstrate Infogent beats an existing SOTA multi-agent search framework by 7% under Direct API-Driven Access on FRAMES, and improves over an existing information-seeking web agent by 4.3% under Interactive Visual Access on AssistantBench.
- Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08774.
- Mindsearch: Mimicking human minds elicits deep ai searcher. Preprint, arXiv:2407.20183.
- Lin Chin-Yew. 2004. Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Text Summarization Branches Out, 2004.
- Mind2web: Towards a generalist agent for the web. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36.
- Llm as os, agents as apps: Envisioning aios, agents and the aios-agent ecosystem. arXiv e-prints, pages arXiv–2312.
- Webvoyager: Building an end-to-end web agent with large multimodal models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.13919.
- Omniact: A dataset and benchmark for enabling multimodal generalist autonomous agents for desktop and web. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.17553.
- Visualwebarena: Evaluating multimodal agents on realistic visual web tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.13649.
- Fact, fetch, and reason: A unified evaluation of retrieval-augmented generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.12941.
- Reinforcement learning on web interfaces using workflow-guided exploration. In International Conference on Learning Representations.
- Weblinx: Real-world website navigation with multi-turn dialogue. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.05930.
- Webgpt: Browser-assisted question-answering with human feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.09332.
- OpenAI. 2023. GPT-4V(ision) System Card.
- Smartbook: Ai-assisted situation report generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.14337.
- World of bits: An open-domain platform for web-based agents. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pages 3135–3144. PMLR.
- Gemini: a family of highly capable multimodal models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.11805.
- A survey on large language model based autonomous agents. Frontiers of Computer Science, 18(6):186345.
- Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Advances in neural information processing systems, 35:24824–24837.
- Grounding open-domain instructions to automate web support tasks. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pages 1022–1032.
- Auto-gpt for online decision making: Benchmarks and additional opinions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.02224.
- Webshop: Towards scalable real-world web interaction with grounded language agents. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35:20744–20757.
- React: Synergizing reasoning and acting in language models. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR).
- Assistantbench: Can web agents solve realistic and time-consuming tasks? Preprint, arXiv:2407.15711.
- Gpt-4v (ision) is a generalist web agent, if grounded. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.01614.
- Gpt-4v(ision) is a generalist web agent, if grounded. In Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning.
- Webarena: A realistic web environment for building autonomous agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.13854.
- FanOutQA: A multi-hop, multi-document question answering benchmark for large language models. In Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), pages 18–37, Bangkok, Thailand. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.