Responsible Artificial Intelligence: A Structured Literature Review
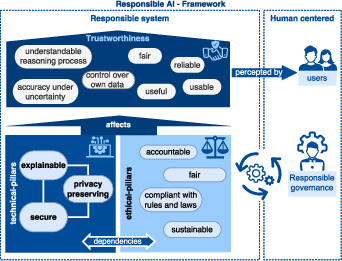
Abstract: Our research endeavors to advance the concept of responsible AI, a topic of increasing importance within EU policy discussions. The EU has recently issued several publications emphasizing the necessity of trust in AI, underscoring the dual nature of AI as both a beneficial tool and a potential weapon. This dichotomy highlights the urgent need for international regulation. Concurrently, there is a need for frameworks that guide companies in AI development, ensuring compliance with such regulations. Our research aims to assist lawmakers and machine learning practitioners in navigating the evolving landscape of AI regulation, identifying focal areas for future attention. This paper introduces a comprehensive and, to our knowledge, the first unified definition of responsible AI. Through a structured literature review, we elucidate the current understanding of responsible AI. Drawing from this analysis, we propose an approach for developing a future framework centered around this concept. Our findings advocate for a human-centric approach to Responsible AI. This approach encompasses the implementation of AI methods with a strong emphasis on ethics, model explainability, and the pillars of privacy, security, and trust.
- European Commission. White Paper on Artificial Intelligence A European approach to excellence and trust. European Commission,.; 2020. Available from: https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/library/communication-fostering-european-approach-artificial-intelligence.
- European Commission. Coordinated Plan on Artificial Intelligence 2021 Review. European Commission.; 2021. Available from: https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/library/coordinated-plan-artificial-intelligence-2021-review.
- European Commission. Proposal for a REGULATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL LAYING DOWN HARMONISED RULES ON ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ACT) AND AMENDING CERTAIN UNION LEGISLATIVE ACTS. European Commission.; 2021. Available from: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1623335154975&uri=CELEX%3A52021PC0206.
- Systematic literature reviews in software engineering – A systematic literature review. Information and Software Technology. 2009;51:7-15.
- Towards Responsible AI for Financial Transactions. In: 2020 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI); 2020. p. 16-21.
- Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Information Fusion. 2020;58:82-115. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1566253519308103.
- Eitel-Porter R. Beyond the promise: implementing ethical AI. AI and Ethics. 2021;1(1):73-80.
- Establishing Data Provenance for Responsible Artificial Intelligence Systems. ACM Transactions on Management Information Systems. 2022 Jun;13(2):1-23. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3503488.
- How Different Groups Prioritize Ethical Values for Responsible AI. In: 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. Seoul Republic of Korea: ACM; 2022. p. 310-23. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3531146.3533097.
- European Commission. Ethics guidelines for trustworthy AI e. European Commission.; 2019. Available from: https://digital-strategy.ec.europa.eu/en/policies/expert-group-ai.
- Trustworthiness of Artificial Intelligence. In: 2020 6th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS); 2020. p. 907-12.
- Knowledge-Intensive Language Understanding for Explainable AI. IEEE Internet Computing. 2021;25(5):19-24.
- Wing JM. Trustworthy AI. Commun ACM. 2021;64(10):64-71.
- Trusted Artificial Intelligence: Technique Requirements and Best Practices. In: 2021 International Conference on Cyberworlds (CW); 2021. p. 303-6. ISSN: 2642-3596.
- Trustworthy AI: From Principles to Practices. ACM Computing Surveys. 2022 Aug:3555803. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3555803.
- Strobel M, Shokri R. Data Privacy and Trustworthy Machine Learning. IEEE Security & Privacy. 2022 Sep;20(5):44-9. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9802763/.
- Trustworthy AI in the Age of Pervasive Computing and Big Data. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops); 2020. p. 1-6.
- Floridi L, Taddeo M. What is data ethics? Philosophical Transactions of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences. 2016 12;374:20160360.
- Hickok M. Lessons learned from AI ethics principles for future actions. AI and Ethics. 2021;1(1):41-7.
- A Comparative Assessment and Synthesis of Twenty Ethics Codes on AI and Big Data. In: 2020 7th Swiss Conference on Data Science (SDS); 2020. p. 41-6.
- Ethics as a Service: A Pragmatic Operationalisation of AI Ethics. Minds and Machines. 2021.
- Ibáñez JC, Olmeda MV. Operationalising AI ethics: how are companies bridging the gap between practice and principles? An exploratory study. AI & SOCIETY. 2021.
- Principled artificial intelligence: Mapping consensus in ethical and rights-based approaches to principles for AI. Berkman Klein Center Research Publication. 2020;(2020-1).
- AI Ethics: Algorithmic Determinism or Self-Determination? The GPDR Approach. IEEE Access. 2021;9:58455-66.
- AI4People—an ethical framework for a good AI society: opportunities, risks, principles, and recommendations. Minds and Machines. 2018;28(4):689-707.
- Shneiderman B. Bridging the Gap Between Ethics and Practice: Guidelines for Reliable, Safe, and Trustworthy Human-Centered AI Systems. ACM Trans Interact Intell Syst. 2020;10(4).
- Trust, regulation, and human-in-the-loop AI: within the European region. Communications of the ACM. 2022 Apr;65(4):64-8. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3511597.
- Trustworthy AI. In: 8th ACM IKDD CODS and 26th COMAD. CODS COMAD 2021. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 449-53.
- Beckert B. The European way of doing Artificial Intelligence: The state of play implementing Trustworthy AI. In: 2021 60th FITCE Communication Days Congress for ICT Professionals: Industrial Data – Cloud, Low Latency and Privacy (FITCE); 2021. p. 1-8.
- Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence: A Review. ACM Computing Surveys. 2023 Mar;55(2):1-38. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3491209.
- In AI we trust? Perceptions about automated decision-making by artificial intelligence. AI & SOCIETY. 2020;35(3):611-23.
- Knowles B, Richards JT. The Sanction of Authority: Promoting Public Trust in AI. In: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. FAccT ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 262-71.
- Lee MK, Rich K. Who Is Included in Human Perceptions of AI?: Trust and Perceived Fairness around Healthcare AI and Cultural Mistrust. In: Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. .
- The Relationship between Trust in AI and Trustworthy Machine Learning Technologies. In: Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. FAT* ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 272-83.
- Wang J, Moulden A. AI Trust Score: A User-Centered Approach to Building, Designing, and Measuring the Success of Intelligent Workplace Features. In: Extended Abstracts of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. CHI EA ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. .
- An Instrument for Measuring Teachers’ Trust in AI-Based Educational Technology. In: LAK22: 12th International Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference. Online USA: ACM; 2022. p. 56-66. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3506860.3506866.
- Liao QV, Sundar SS. Designing for Responsible Trust in AI Systems: A Communication Perspective. In: 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. Seoul Republic of Korea: ACM; 2022. p. 1257-68. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3531146.3533182.
- Toward verified artificial intelligence. Communications of the ACM. 2022 Jul;65(7):46-55. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3503914.
- Patient and public involvement to build trust in artificial intelligence: A framework, tools, and case studies. Patterns. 2022 Jun;3(6):100506. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2666389922000988.
- Thuraisingham B. Trustworthy Machine Learning. IEEE Intelligent Systems. 2022 Jan;37(1):21-4. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9756264/.
- Trust and ethics in AI. AI & SOCIETY. 2022 May. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00146-022-01473-4.
- Formalizing Trust in Artificial Intelligence: Prerequisites, Causes and Goals of Human Trust in AI. In: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. FAccT ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 624-35.
- Dual humanness and trust in conversational AI: A person-centered approach. Computers in Human Behavior. 2021;119:106727. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0747563221000492.
- Information fusion as an integrative cross-cutting enabler to achieve robust, explainable, and trustworthy medical artificial intelligence. Information Fusion. 2022 Mar;79:263-78. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1566253521002050.
- An Adversarial Perspective on Accuracy, Robustness, Fairness, and Privacy: Multilateral-Tradeoffs in Trustworthy ML. IEEE Access. 2022:1-1. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9933776/.
- Assessing Trustworthy AI in times of COVID-19. Deep Learning for predicting a multi-regional score conveying the degree of lung compromise in COVID-19 patients. IEEE. 2022:32.
- Federated Trustworthy AI Architecture for Smart Cities. In: 2022 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2). Pafos, Cyprus: IEEE; 2022. p. 1-7. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9922069/.
- Burkart N, Huber MF. A Survey on the Explainability of Supervised Machine Learning. J Artif Int Res. 2021;70:245-317.
- Hanna R, Kazim E. Philosophical foundations for digital ethics and AI Ethics: a dignitarian approach. AI and Ethics. 2021.
- A European Agency for Artificial Intelligence: Protecting fundamental rights and ethical values. Computer Law & Security Review. 2022 Jul;45:105661. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0267364922000097.
- An Overview of Artificial Intelligence Ethics. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence. 2022:1-21. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9844014/.
- Responsible and Regulatory Conform Machine Learning for Medicine: A Survey of Challenges and Solutions. IEEE Access. 2022;10:58375-418. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9783196/.
- Ethical, legal, social, and economic (ELSE) implications of artificial intelligence at a global level: a scientometrics approach. AI and Ethics. 2022 Jan. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-021-00124-6.
- The ethical issues of the application of artificial intelligence in healthcare: a systematic scoping review. AI and Ethics. 2022 Mar. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-021-00131-7.
- Attard-Frost B. The ethics of AI business practices: a review of 47 AI ethics guidelines. AI and Ethics. 2022:18.
- The ethics of algorithms: key problems and solutions. AI & SOCIETY. 2022 Mar;37(1):215-30. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00146-021-01154-8.
- Socially Responsible AI Algorithms: Issues, Purposes, and Challenges. J Artif Int Res. 2021;71:1137-81.
- Benjamins R. A choices framework for the responsible use of AI. AI and Ethics. 2021;1(1):49-53.
- Bourgais A, Ibnouhsein I. Ethics-by-design: the next frontier of industrialization. AI and Ethics. 2021.
- Responsible AI—Two Frameworks for Ethical Design Practice. IEEE Transactions on Technology and Society. 2020;1(1):34-47.
- ECCOLA — A method for implementing ethically aligned AI systems. Journal of Systems and Software. 2021;182:111067. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121221001643.
- Behavioral Use Licensing for Responsible AI. In: 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. Seoul Republic of Korea: ACM; 2022. p. 778-88. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3531146.3533143.
- Focusing on the Ethical Challenges of Data Breaches and Applications. In: 2022 IEEE International Conference on Assured Autonomy (ICAA). Fajardo, PR, USA: IEEE; 2022. p. 74-82. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9763591/.
- Bruschi D, Diomede N. A framework for assessing AI ethics with applications to cybersecurity. AI and Ethics. 2022 May. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00162-8.
- A responsible AI framework: pipeline contextualisation. AI and Ethics. 2022 Apr. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00154-8.
- Belenguer L. AI bias: exploring discriminatory algorithmic decision-making models and the application of possible machine-centric solutions adapted from the pharmaceutical industry. AI and Ethics. 2022 Feb. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00138-8.
- Svetlova E. AI ethics and systemic risks in finance. AI and Ethics. 2022 Nov;2(4):713-25. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-021-00129-1.
- Li J, Chignell M. FMEA-AI: AI fairness impact assessment using failure mode and effects analysis. AI and Ethics. 2022 Mar. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00145-9.
- From AI ethics principles to data science practice: a reflection and a gap analysis based on recent frameworks and practical experience. AI and Ethics. 2022 Jan. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-021-00127-3.
- Kumar S, Choudhury S. Normative ethics, human rights, and artificial intelligence. AI and Ethics. 2022 May. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00170-8.
- Operationalising ethics in artificial intelligence for healthcare: a framework for AI developers. AI and Ethics. 2022 Jul. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00195-z.
- The AI ethics maturity model: a holistic approach to advancing ethical data science in organizations. AI and Ethics. 2022 Oct. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00228-7.
- REVISE: A Tool for Measuring and Mitigating Bias in Visual Datasets. International Journal of Computer Vision. 2022 Jul;130(7):1790-810. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11263-022-01625-5.
- Ayling J, Chapman A. Putting AI ethics to work: are the tools fit for purpose? AI and Ethics. 2021.
- Petrozzino C. Who pays for ethical debt in AI? AI and Ethics. 2021.
- Rochel J, Evéquoz F. Getting into the engine room: a blueprint to investigate the shadowy steps of AI ethics. AI & SOCIETY. 2020.
- Organisational responses to the ethical issues of artificial intelligence. AI & SOCIETY. 2021.
- Xiaoling P. Discussion on Ethical Dilemma Caused by Artificial Intelligence and Countermeasures. In: 2021 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Image Processing, Electronics and Computers (IPEC); 2021. p. 453-7.
- The AI ethicist’s dilemma: fighting Big Tech by supporting Big Tech. AI and Ethics. 2021 Dec. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43681-021-00123-7.
- Accountability in an Algorithmic Society: Relationality, Responsibility, and Robustness in Machine Learning. In: 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. Seoul Republic of Korea: ACM; 2022. p. 864-76. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3531146.3533150.
- How Do Software Companies Deal with Artificial Intelligence Ethics? A Gap Analysis. In: The International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering 2022. Gothenburg Sweden: ACM; 2022. p. 100-9. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3530019.3530030.
- Weinberg L. Rethinking Fairness: An Interdisciplinary Survey of Critiques of Hegemonic ML Fairness Approaches. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research. 2022 May;74:75-109. Available from: https://jair.org/index.php/jair/article/view/13196.
- Artificial Intelligence Ethical in Environmental Protection. In: 2022 International Seminar on Computer Science and Engineering Technology (SCSET). Indianapolis, IN, USA: IEEE; 2022. p. 137-40. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9700880/.
- Mulligan C, Elaluf-Calderwood S. AI ethics: A framework for measuring embodied carbon in AI systems. AI and Ethics. 2022 Aug;2(3):363-75. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-021-00071-2.
- Waller RR, Waller RL. Assembled Bias: Beyond Transparent Algorithmic Bias. Minds and Machines. 2022 Sep;32(3):533-62. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11023-022-09605-x.
- Hagendorff T. Blind spots in AI ethics. AI and Ethics. 2022 Nov;2(4):851-67. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-021-00122-8.
- Bickley SJ, Torgler B. Cognitive architectures for artificial intelligence ethics. AI & SOCIETY. 2022 Jun. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00146-022-01452-9.
- Fernandez-Quilez A. Deep learning in radiology: ethics of data and on the value of algorithm transparency, interpretability and explainability. AI and Ethics. 2022 Apr. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00161-9.
- Munn L. The uselessness of AI ethics. AI and Ethics. 2022 Aug. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00209-w.
- Hagendorff T. The Ethics of AI Ethics: An Evaluation of Guidelines. Minds and Machines. 2020;30(1):99-120.
- Kiemde SMA, Kora AD. Towards an ethics of AI in Africa: rule of education. AI and Ethics. 2021.
- A Survey on Ethical Principles of AI and Implementations. In: 2020 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI); 2020. p. 3010-7.
- Ethics and Governance of Artificial Intelligence: Evidence from a Survey of Machine Learning Researchers. J Artif Int Res. 2021;71:591-666.
- Forbes K. Opening the path to ethics in artificial intelligence. AI and Ethics. 2021.
- Tartaglione E, Grangetto M. A non-Discriminatory Approach to Ethical Deep Learning. In: 2020 IEEE 19th International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom); 2020. p. 943-50.
- Imagine a More Ethical AI: Using Stories to Develop Teens’ Awareness and Understanding of Artificial Intelligence and its Societal Impacts. In: 2021 Conference on Research in Equitable and Sustained Participation in Engineering, Computing, and Technology (RESPECT); 2021. p. 1-2.
- Assessing the Fairness of AI Systems: AI Practitioners’ Processes, Challenges, and Needs for Support. Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction. 2022 Mar;6(CSCW1):1-26. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3512899.
- Capable but Amoral? Comparing AI and Human Expert Collaboration in Ethical Decision Making. In: CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. New Orleans LA USA: ACM; 2022. p. 1-17. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3491102.3517732.
- Boyd K. Designing Up with Value-Sensitive Design: Building a Field Guide for Ethical ML Development. In: 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. Seoul Republic of Korea: ACM; 2022. p. 2069-82. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3531146.3534626.
- Multi-disciplinary fairness considerations in machine learning for clinical trials. In: 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. Seoul Republic of Korea: ACM; 2022. p. 906-24. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3531146.3533154.
- Software engineering for responsible AI: an empirical study and operationalised patterns. In: Proceedings of the 44th International Conference on Software Engineering: Software Engineering in Practice. Pittsburgh Pennsylvania: ACM; 2022. p. 241-2. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3510457.3513063.
- Toward Involving End-users in Interactive Human-in-the-loop AI Fairness. ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems. 2022 Sep;12(3):1-30. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3514258.
- Rubeis G. iHealth: The ethics of artificial intelligence and big data in mental healthcare. Internet Interventions. 2022 Apr;28:100518. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2214782922000252.
- Algorithmic fairness datasets: the story so far. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery. 2022 Sep. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10618-022-00854-z.
- Bélisle-Pipon JC. Artificial intelligence ethics has a black box problem. AI and Society. 2022:16.
- Häußermann JJ, Lütge C. Community-in-the-loop: towards pluralistic value creation in AI, or—why AI needs business ethics. AI and Ethics. 2022 May;2(2):341-62. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-021-00047-2.
- Fung P, Etienne H. Confucius, cyberpunk and Mr. Science: comparing AI ethics principles between China and the EU. AI and Ethics. 2022 Jun. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00180-6.
- Explainability as fig leaf? An exploration of experts’ ethical expectations towards machine learning in psychiatry. AI and Ethics. 2022 Jun. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00177-1.
- Stahl BC. From computer ethics and the ethics of AI towards an ethics of digital ecosystems. AI and Ethics. 2022 Feb;2(1):65-77. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-021-00080-1.
- Brusseau J. From the ground truth up: doing AI ethics from practice to principles. AI & SOCIETY. 2022 Jan. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00146-021-01336-4.
- Anderson MM, Fort K. From the ground up: developing a practical ethical methodology for integrating AI into industry. AI & SOCIETY. 2022 Jul. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00146-022-01531-x.
- Ramanayake R. Immune moral models? Pro-social rule breaking as a moral enhancement approach for ethical AI. AI & SOCIETY. 2022:13.
- Hunkenschroer AL, Kriebitz A. Is AI recruiting (un)ethical? A human rights perspective on the use of AI for hiring. AI and Ethics. 2022 Jul. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00166-4.
- Recommender systems for mental health apps: advantages and ethical challenges. AI & SOCIETY. 2022 Jan. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00146-021-01322-w.
- Jacobs M, Simon J. Reexamining computer ethics in light of AI systems and AI regulation. AI and Ethics. 2022 Oct. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00229-6.
- Persson E, Hedlund M. The future of AI in our hands? To what extent are we as individuals morally responsible for guiding the development of AI in a desirable direction? AI and Ethics. 2022 Nov;2(4):683-95. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-021-00125-5.
- Towards Explainability for AI Fairness. In: Holzinger A, Goebel R, Fong R, Moon T, Müller KR, Samek W, editors. xxAI - Beyond Explainable AI. vol. 13200. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2022. p. 375-86. Series Title: Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-031-04083-2_18.
- Maclure J. AI, Explainability and Public Reason: The Argument from the Limitations of the Human Mind. Minds and Machines. 2021;31(3):421-38.
- Vellido A. The importance of interpretability and visualization in machine learning for applications in medicine and health care. Neural Computing and Applications. 2020;32(24):18069-83.
- Explainable AI. Communications of the ACM. 2022 Apr;65(4):27-9. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3490699.
- Ratti E, Graves M. Explainable machine learning practices: opening another black box for reliable medical AI. AI and Ethics. 2022 Feb. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s43681-022-00141-z.
- Interpreting Interpretability: Understanding Data Scientists’ Use of Interpretability Tools for Machine Learning. In: Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. CHI ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 1-14.
- Machine Learning – The Results Are Not the only Thing that Matters! What About Security, Explainability and Fairness? In: Krzhizhanovskaya VV, Závodszky G, Lees MH, Dongarra JJ, Sloot PMA, Brissos S, et al., editors. Computational Science – ICCS 2020. vol. 12140. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2020. p. 615-28.
- Giulia Vilone, Luca Longo. Notions of explainability and evaluation approaches for explainable artificial intelligence. Information Fusion. 2021;76:89-106. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1566253521001093.
- Brennen A. What Do People Really Want When They Say They Want Explainable AI? We Asked 60 Stakeholders. In: Extended Abstracts of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. CHI EA ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 1-7.
- XAI Tools in the Public Sector: A Case Study on Predicting Combined Sewer Overflows. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM Joint Meeting on European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering. ESEC/FSE 2021. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 1032-44.
- Explainable, trustworthy, and ethical machine learning for healthcare: A survey. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2022 Oct;149:106043. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0010482522007569.
- Explaining deep neural networks: A survey on the global interpretation methods. Neurocomputing. 2022 Nov;513:165-80. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0925231222012218.
- Tiddi I, Schlobach S. Knowledge graphs as tools for explainable machine learning: A survey. Artificial Intelligence. 2022 Jan;302:103627. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0004370221001788.
- Unbox the black-box for the medical explainable AI via multi-modal and multi-centre data fusion: A mini-review, two showcases and beyond. Information Fusion. 2022 Jan;77:29-52. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1566253521001597.
- Explainable AI for Healthcare 5.0: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Access. 2022;10:84486-517. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9852458/.
- Explainable artificial intelligence: a comprehensive review. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2022 Jun;55(5):3503-68. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10462-021-10088-y.
- Debiased-CAM to mitigate image perturbations with faithful visual explanations of machine learning. In: CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. New Orleans LA USA: ACM; 2022. p. 1-32. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3491102.3517522.
- Exploration into the Explainability of Neural Network Models for Power Side-Channel Analysis. In: Proceedings of the Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI 2022. Irvine CA USA: ACM; 2022. p. 59-64. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3526241.3530346.
- Investigating Explainability of Generative AI for Code through Scenario-based Design. In: 27th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces. Helsinki Finland: ACM; 2022. p. 212-28. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3490099.3511119.
- Model Explanations with Differential Privacy. In: 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. Seoul Republic of Korea: ACM; 2022. p. 1895-904. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3531146.3533235.
- Terziyan V, Vitko O. Explainable AI for Industry 4.0: Semantic Representation of Deep Learning Models. Procedia Computer Science. 2022;200:216-26. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1877050922002290.
- Knowledge graph-based rich and confidentiality preserving Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI). Information Fusion. 2022 May;81:91-102. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1566253521002414.
- Bacciu D, Numeroso D. Explaining Deep Graph Networks via Input Perturbation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems. 2022:1-12. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9761788/.
- Mery D, Morris B. On Black-Box Explanation for Face Verification. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, HI, USA: IEEE; 2022. p. 1194-203. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9706895/.
- Explaining predictions and attacks in federated learning via random forests. Applied Intelligence. 2022 Apr. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10489-022-03435-1.
- CERTIFAI: A Common Framework to Provide Explanations and Analyse the Fairness and Robustness of Black-Box Models. In: Proceedings of the AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society. AIES ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 166-72.
- Sokol K, Flach P. One Explanation Does Not Fit All. KI - Künstliche Intelligenz. 2020;34(2):235-50.
- A Multidisciplinary Survey and Framework for Design and Evaluation of Explainable AI Systems. ACM Trans Interact Intell Syst. 2021;11(3–4).
- How Can I Choose an Explainer? An Application-Grounded Evaluation of Post-Hoc Explanations. In: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. FAccT ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 805-15.
- Agree to Disagree: When Deep Learning Models With Identical Architectures Produce Distinct Explanations. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, HI, USA: IEEE; 2022. p. 1524-33. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9706847/.
- How Good is your Explanation? Algorithmic Stability Measures to Assess the Quality of Explanations for Deep Neural Networks. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, HI, USA: IEEE; 2022. p. 1565-75. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9706798/.
- Expanding Explainability: Towards Social Transparency in AI Systems. In: Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. .
- Capturing the Trends, Applications, Issues, and Potential Strategies of Designing Transparent AI Agents. In: Extended Abstracts of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. CHI EA ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. .
- Beyond Expertise and Roles: A Framework to Characterize the Stakeholders of Interpretable Machine Learning and Their Needs. In: Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. .
- Tsiakas K, Murray-Rust D. Using human-in-the-loop and explainable AI to envisage new future work practices. In: The15th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments. Corfu Greece: ACM; 2022. p. 588-94. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3529190.3534779.
- A manifesto on explainability for artificial intelligence in medicine. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. 2022 Nov;133:102423. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0933365722001750.
- X-MIR: EXplainable Medical Image Retrieval. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, HI, USA: IEEE; 2022. p. 1544-54. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9706900/.
- Black is the new orange: how to determine AI liability. Artificial Intelligence and Law. 2022 Jan. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10506-022-09308-9.
- Abolfazlian K. Trustworthy AI Needs Unbiased Dictators! In: Maglogiannis I, Iliadis L, Pimenidis E, editors. Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2020. p. 15-23.
- Bertino E. Privacy in the Era of 5G, IoT, Big Data and Machine Learning. In: 2020 Second IEEE International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Intelligent Systems and Applications (TPS-ISA); 2020. p. 134-7.
- Differential Privacy Defenses and Sampling Attacks for Membership Inference. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security. AISec ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 193-202. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1145/3474369.3486876.
- Security and Privacy Issues in Deep Learning: A Brief Review. SN Computer Science. 2020;1(5):253.
- Adversarial Robustness is Not Enough: Practical Limitations for Securing Facial Authentication. In: Proceedings of the 2022 ACM on International Workshop on Security and Privacy Analytics. Baltimore MD USA: ACM; 2022. p. 2-12. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3510548.3519369.
- Jankovic A, Mayer R. An Empirical Evaluation of Adversarial Examples Defences, Combinations and Robustness Scores. In: Proceedings of the 2022 ACM on International Workshop on Security and Privacy Analytics. Baltimore MD USA: ACM; 2022. p. 86-92. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3510548.3519370.
- What Does it Mean for a Language Model to Preserve Privacy? In: 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. Seoul Republic of Korea: ACM; 2022. p. 2280-92. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3531146.3534642.
- Adversarial attacks on graph-level embedding methods: a case study. Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence. 2022 Oct. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10472-022-09811-4.
- Muhr T, Zhang W. Privacy-Preserving Detection of Poisoning Attacks in Federated Learning. In: 2022 19th Annual International Conference on Privacy, Security & Trust (PST). Fredericton, NB, Canada: IEEE; 2022. p. 1-10. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9851993/.
- ShieldFL: Mitigating Model Poisoning Attacks in Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security. 2022;17:1639-54. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9762272/.
- A review of privacy-preserving techniques for deep learning. Neurocomputing. 2020;384:21-45. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231219316431.
- Developing Privacy-preserving AI Systems: The Lessons learned. In: 2020 57th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC); 2020. p. 1-4.
- Sousa S, Kern R. How to keep text private? A systematic review of deep learning methods for privacy-preserving natural language processing. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2022 May. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10462-022-10204-6.
- Visual privacy attacks and defenses in deep learning: a survey. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2022 Aug;55(6):4347-401. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10462-021-10123-y.
- Sergey Zapechnikov. Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning as a Tool for Secure Personalized Information Services. Procedia Computer Science. 2020;169:393-9. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877050920303598.
- Differential Privacy: The Pursuit of Protections by Default. Commun ACM. 2021;64(2):36-43.
- Chasing Your Long Tails: Differentially Private Prediction in Health Care Settings. In: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. FAccT ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 723-34.
- Private-kNN: Practical Differential Privacy for Computer Vision. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2020. p. 11851-9.
- Prescriptive analytics with differential privacy. International Journal of Data Science and Analytics. 2021.
- Differentially Private Deep Learning with Iterative Gradient Descent Optimization. ACM/IMS Transactions on Data Science. 2021 Nov;2(4):1-27. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3491254.
- Add noise to remove noise: Local differential privacy for feature selection. Computers & Security. 2022 Dec;123:102934. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0167404822003261.
- Lal AK, Karthikeyan S. Deep Learning Classification of Fetal Cardiotocography Data with Differential Privacy. In: 2022 International Conference on Connected Systems & Intelligence (CSI). Trivandrum, India: IEEE; 2022. p. 1-5. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9924087/.
- Differential Privacy Preservation in Robust Continual Learning. IEEE Access. 2022;10:24273-87. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9721905/.
- Gupta R, Singh AK. A Differential Approach for Data and Classification Service-Based Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning Model in Cloud Environment. New Generation Computing. 2022 Jul. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00354-022-00185-z.
- A two-phase random forest with differential privacy. Applied Intelligence. 2022 Oct. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10489-022-04119-6.
- Correlated Differential Privacy of Multiparty Data Release in Machine Learning. Journal of Computer Science and Technology. 2022 Feb;37(1):231-51. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11390-021-1754-5.
- Differentially private multivariate time series forecasting of aggregated human mobility with deep learning: Input or gradient perturbation? Neural Computing and Applications. 2022 Aug;34(16):13355-69. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00521-022-07393-0.
- Yuan L, Shen G. A Training Scheme of Deep Neural Networks on Encrypted Data. In: Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Cyberspace Innovation of Advanced Technologies. CIAT 2020. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 490-5.
- Privacy-Preserving Fair Learning of Support Vector Machine with Homomorphic Encryption. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022. Virtual Event, Lyon France: ACM; 2022. p. 3572-83. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3485447.3512252.
- Efficient and Privacy-Preserving Logistic Regression Scheme based on Leveled Fully Homomorphic Encryption. In: IEEE INFOCOM 2022 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS). New York, NY, USA: IEEE; 2022. p. 1-6. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9797933/.
- Efficient homomorphic encryption framework for privacy-preserving regression. Applied Intelligence. 2022 Aug. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10489-022-04015-z.
- An efficient approach for privacy preserving decentralized deep learning models based on secure multi-party computation. Neurocomputing. 2021;422:245-62. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231220315095.
- A novel privacy-preserving speech recognition framework using bidirectional LSTM. Journal of Cloud Computing. 2020;9(1):36.
- When Machine Learning Meets Privacy: A Survey and Outlook. ACM Computing Surveys. 2021;54(2).
- Federated Learning-Based Privacy-Preserving and Security: Survey. In: 2021 Computing, Communications and IoT Applications (ComComAp); 2021. p. 312-7.
- Federated learning and privacy. Communications of the ACM. 2022 Apr;65(4):90-7. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3500240.
- Federated Learning for Healthcare: Systematic Review and Architecture Proposal. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology. 2022 Aug;13(4):1-23. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3501813.
- Federated Learning for Smart Healthcare: A Survey. ACM Computing Surveys. 2023 Apr;55(3):1-37. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3501296.
- A Review of Medical Federated Learning: Applications in Oncology and Cancer Research. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, editors. Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2022. p. 3-24.
- Diddee H, Kansra B. CrossPriv: User Privacy Preservation Model for Cross-Silo Federated Software. In: Proceedings of the 35th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering. ASE ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 1370-2.
- Can YS, Ersoy C. Privacy-Preserving Federated Deep Learning for Wearable IoT-Based Biomedical Monitoring. ACM Trans Internet Technol. 2021;21(1).
- A Federated Parallel Data Platform for Trustworthy AI. In: 2021 IEEE 1st International Conference on Digital Twins and Parallel Intelligence (DTPI); 2021. p. 344-7.
- SAFELearn: Secure Aggregation for private FEderated Learning. In: 2021 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW); 2021. p. 56-62.
- Efficient, Private and Robust Federated Learning. In: Annual Computer Security Applications Conference. ACSAC. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 45-60. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1145/3485832.3488014.
- Secure aggregation for federated learning in flower. In: Proceedings of the 2nd ACM International Workshop on Distributed Machine Learning. DistributedML ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 8-14. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1145/3488659.3493776.
- FedV: Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning over Vertically Partitioned Data. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security. AISec ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 181-92. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1145/3474369.3486872.
- FedAT: a high-performance and communication-efficient federated learning system with asynchronous tiers. In: Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis. SC ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 1-16. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1145/3458817.3476211.
- Cross the Chasm: Scalable Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning against Poisoning Attack. In: 2021 18th International Conference on Privacy, Security and Trust (PST); 2021. p. 1-5.
- Device or User: Rethinking Federated Learning in Personal-Scale Multi-Device Environments. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems. SenSys ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 446-52. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1145/3485730.3493449.
- Distributed Learning in Trusted Execution Environment: A Case Study of Federated Learning in SGX. In: 2021 7th IEEE International Conference on Network Intelligence and Digital Content (IC-NIDC); 2021. p. 450-4. ISSN: 2575-4955.
- Implicit model specialization through dag-based decentralized federated learning. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Middleware Conference. Middleware ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 310-22. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1145/3464298.3493403.
- Auto-weighted Robust Federated Learning with Corrupted Data Sources. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology. 2022 Oct;13(5):1-20. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3517821.
- CloudyFL: a cloudlet-based federated learning framework for sensing user behavior using wearable devices. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Embedded and Mobile Deep Learning. Portland Oregon: ACM; 2022. p. 13-8. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3539491.3539592.
- Kalloori S, Klingler S. Cross-silo federated learning based decision trees. In: Proceedings of the 37th ACM/SIGAPP Symposium on Applied Computing. Virtual Event: ACM; 2022. p. 1117-24. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3477314.3507149.
- FedNKD: A Dependable Federated Learning Using Fine-tuned Random Noise and Knowledge Distillation. In: Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval. Newark NJ USA: ACM; 2022. p. 185-93. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3512527.3531372.
- FLARE: Defending Federated Learning against Model Poisoning Attacks via Latent Space Representations. In: Proceedings of the 2022 ACM on Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security. Nagasaki Japan: ACM; 2022. p. 946-58. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3488932.3517395.
- Blockchain Empowered Federated Learning for Data Sharing Incentive Mechanism. Procedia Computer Science. 2022;202:348-53. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1877050922005816.
- Decentralized Federated Learning for Nonintrusive Load Monitoring in Smart Energy Communities. In: 2022 30th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation (MED). Vouliagmeni, Greece: IEEE; 2022. p. 312-7. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9837291/.
- PVD-FL: A Privacy-Preserving and Verifiable Decentralized Federated Learning Framework. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security. 2022;17:2059-73. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9777682/.
- Towards Trustworthy AI: Blockchain-based Architecture Design for Accountability and Fairness of Federated Learning Systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. 2022:1-1. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9686048/.
- Trusted Decentralized Federated Learning. IEEE. 2022:6.
- Trustworthy Federated Learning via Blockchain. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. 2022:1-1. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9866512/.
- When Collaborative Federated Learning Meets Blockchain to Preserve Privacy in Healthcare. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering. 2022:1-11. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9906419/.
- VFL-R: a novel framework for multi-party in vertical federated learning. Applied Intelligence. 2022 Sep. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10489-022-04111-0.
- Privacy-preserving federated neural network learning for disease-associated cell classification. Patterns. 2022 May;3(5):100487. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2666389922000721.
- A contemplative perspective on federated machine learning: Taxonomy, threats & vulnerability assessment and challenges. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences. 2021. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319157821001312.
- Federated Learning with Gaussian Differential Privacy. In: Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Robotics, Intelligent Control and Artificial Intelligence. RICAI 2020. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 296-301.
- Jarin I, Eshete B. PRICURE: Privacy-Preserving Collaborative Inference in a Multi-Party Setting. In: Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Workshop on Security and Privacy Analytics. IWSPA ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 25-35.
- SPEED: secure, PrivatE, and efficient deep learning. Machine Learning. 2021;110(4):675-94.
- MSDP: multi-scheme privacy-preserving deep learning via differential privacy. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing. 2021.
- Federated Learning and Differential Privacy: Software tools analysis, the Sherpa.ai FL framework and methodological guidelines for preserving data privacy. Information Fusion. 2020;64:270-92. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1566253520303213.
- Homomorphic Encryption and Federated Learning based Privacy-Preserving CNN Training: COVID-19 Detection Use-Case. In: EICC 2022: Proccedings of the European Interdisciplinary Cybersecurity Conference. Barcelona Spain: ACM; 2022. p. 85-90. Available from: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3528580.3532845.
- Feng X, Chen L. Data Privacy Protection Sharing Strategy Based on Consortium Blockchain and Federated Learning. In: 2022 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Information Technology (AICIT). Yichang, China: IEEE; 2022. p. 1-4. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9930188/.
- Can We Use Split Learning on 1D CNN Models for Privacy Preserving Training? In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security. ASIA CCS ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 305-18.
- Biscotti: A Blockchain System for Private and Secure Federated Learning. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems. 2021;32(7):1513-25.
- Secular: A Decentralized Blockchain-based Data Privacy-preserving Model Training Platform. In: 2021 International Mobile, Intelligent, and Ubiquitous Computing Conference (MIUCC); 2021. p. 357-63.
- Privacy preservation through facial de-identification with simultaneous emotion preservation. Signal, Image and Video Processing. 2020.
- Human-in-the-Loop-Aided Privacy-Preserving Scheme for Smart Healthcare. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence. 2020:1-10.
- Human-in-the-Loop-Aided Privacy-Preserving Scheme for Smart Healthcare. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, title=Human-in-the-Loop-Aided Privacy-Preserving Scheme for Smart Healthcare. 2020 Jan:1-10.
- Privacy Risk Assessment of Training Data in Machine Learning. In: ICC 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Communications. Seoul, Korea, Republic of: IEEE; 2022. p. 1015-5. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9839062/.
- Privacy vs Accuracy Trade-Off in Privacy Aware Face Recognition in Smart Systems. In: 2022 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC). Rhodes, Greece: IEEE; 2022. p. 1-8. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9912465/.
- Privacy-Preserving Case-Based Explanations: Enabling Visual Interpretability by Protecting Privacy. IEEE Access. 2022;10:28333-47. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9729808/.
- Privacy-Preserving Classification Scheme Based on Support Vector Machine. IEEE Systems Journal. 2022:1-11. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9732431/.
- PrivPAS: A real time Privacy-Preserving AI System and applied ethics. In: 2022 IEEE 16th International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC). Laguna Hills, CA, USA: IEEE; 2022. p. 9-16. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9736272/.
- Sphinx: Enabling Privacy-Preserving Online Learning over the Cloud. In: 2022 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). San Francisco, CA, USA: IEEE; 2022. p. 2487-501. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9833648/.
- Towards Personalized Federated Learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems. 2022:1-17. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9743558/.
- Gambelin O. Brave: what it means to be an AI Ethicist. AI and Ethics. 2021;1(1):87-91.
- Gill KS. Ethical dilemmas // Ethical dilemmas: Ned Ludd and the ethical machine. AI & SOCIETY. 2021;36(3):669-76.
- Stahl BC. Ethical Issues of AI. In: Stahl BC, editor. Artificial Intelligence for a Better Future: An Ecosystem Perspective on the Ethics of AI and Emerging Digital Technologies. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2021. p. 35-53.
- Charles D Raab. Information privacy, impact assessment, and the place of ethics*. Computer Law & Security Review. 2020;37:105404. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0267364920300091.
- Prunkl C, Whittlestone J. Beyond Near- and Long-Term: Towards a Clearer Account of Research Priorities in AI Ethics and Society. In: Proceedings of the AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society. AIES ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 138-43.
- Operationalizing Human-Centered Perspectives in Explainable AI. In: Extended Abstracts of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. CHI EA ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. .
- Explainability in deep reinforcement learning. Knowledge-Based Systems. 2021;214:106685. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950705120308145.
- Sibyl: Explaining Machine Learning Models for High-Stakes Decision Making. In: Extended Abstracts of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. CHI EA ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. .
- Sokol K, Flach P. Explainability Fact Sheets: A Framework for Systematic Assessment of Explainable Approaches. In: Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. FAT* ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 56-67.
- An Empirical Evaluation of AI Deep Explainable Tools. In: 2020 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps); 2020. p. 1-6.
- Colaner N. Is explainable artificial intelligence intrinsically valuable? AI & SOCIETY. 2021.
- Evaluating Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning in Critical Infrastructures: A Case Study on Time-Series Classification. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics. 2021:1-1. Conference Name: IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics.
- Machine learning concepts for correlated Big Data privacy. Journal of Big Data. 2021 Dec;8(1):157. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-021-00530-x.
- Chang H, Shokri R. On the Privacy Risks of Algorithmic Fairness. In: 2021 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS P); 2021. p. 292-303.
- A survey on security and privacy of federated learning. Future Generation Computer Systems. 2021;115:619-40. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167739X20329848.
- A Light-Weight Crowdsourcing Aggregation in Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning System. In: 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN); 2020. p. 1-8. ISSN: 2161-4407.
- Privacy Preserving Distributed Extremely Randomized Trees. In: Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing. SAC ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 1102-5.
- Anonymization as homeomorphic data space transformation for privacy-preserving deep learning. Procedia Computer Science. 2021;180:867-76. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877050921003914.
- TransNet: Training Privacy-Preserving Neural Network over Transformed Layer. Proc VLDB Endow. 2020;13(12):1849-62.
- Data minimization for GDPR compliance in machine learning models. AI and Ethics. 2021.
- “I Never Thought About Securing My Machine Learning Systems”: A Study of Security and Privacy Awareness of Machine Learning Practitioners. In: Mensch Und Computer 2021. MuC ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2021. p. 520-46.
- Differentially private ensemble learning for classification. Neurocomputing. 2021;430:34-46. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231220319512.
- XGNN: Towards Model-Level Explanations of Graph Neural Networks. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. KDD ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2020. p. 430-8.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.