- The paper presents MAIC, a novel framework integrating LLM-driven agents to enhance personalized online learning at scale.
- It utilizes a dual-stage course preparation workflow and adaptive multi-agent classroom environment to generate dynamic, tailored content.
- Pilot evaluations at Tsinghua University show improved student engagement while highlighting ethical and scalability considerations.
From MOOC to MAIC: Reshaping Online Teaching and Learning through LLM-driven Agents
Introduction
The research paper "From MOOC to MAIC: Reshaping Online Teaching and Learning through LLM-driven Agents" outlines the conceptual development and technical implementation of a novel form of online education termed MAIC (Massive AI-empowered Course). Leveraging the capabilities of LLMs and multi-agent systems, MAIC aims to overcome the limitations of traditional MOOCs by enhancing adaptability and scalability in online learning environments. The core proposal involves integrating LLM-driven multi-agent systems to create an AI-augmented classroom that provides personalized learning experiences while maintaining the advantages of large-scale online education.
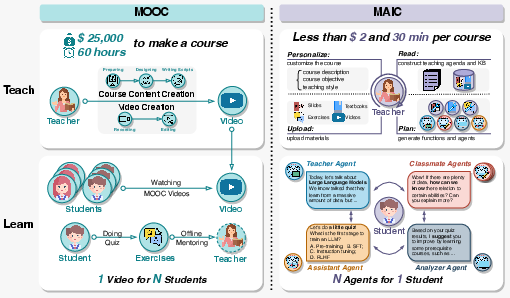
Figure 1: MOOC V.S. MAIC from the aspects of teaching and learning.
Evolution of Online Education
In the backdrop of the evolution of online education, marked notably by Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs), the limitations concerning personalized learning have become prominent. MOOCs excel in scalability, offering access to education from prestigious institutions to millions worldwide. However, their one-size-fits-all approach lacks adaptability, which is crucial for personalized education. Consequently, integrating AI technologies such as LLMs has been explored to address these limitations.
By facilitating deeper integration of various educational AI applications into a coherent framework, MAIC introduces a new paradigm. It employs LLM-driven agents to provide customized educational interactions, aiming to replicate tailored educational experiences in an online context.
Implementation and Technical Details
Teaching: Course Preparation Workflow
The course preparation process within MAIC involves transforming unstructured learning resources into formatted, adaptive instructional materials. This transformation is facilitated through a multi-agent system that extracts and organizes content from instructor-provided slides.
The workflow includes two primary stages:
- Read Stage: Utilizes multi-modal LLMs to process visual and textual content from slides, resulting in structured representations of course content and extracting core knowledge.
- Plan Stage: Focuses on crafting instructional scripts and integrating them with AI-driven teaching functionalities, allowing for dynamic class scenarios and personalized educational experiences.
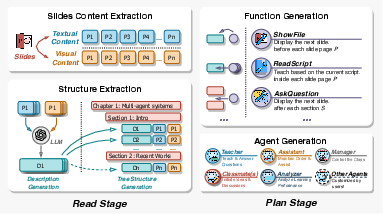
Figure 2: An illustration of the course preparation workflow of MAIC.
Learning: Multi-agent Classroom Environment
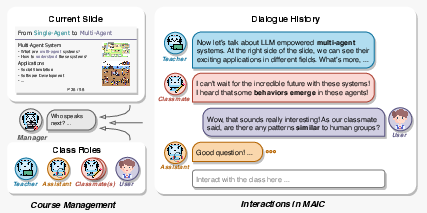
MAIC's classroom environment models a "1 Student user + N AI Agents" configuration, in which AI agents mimic the roles of teachers, teaching assistants, and classmates. This setup allows for real-time adaptability to student interactions, providing a more engaging and personalized learning journey.
To achieve this, MAIC employs:
Evaluation and Results
Teaching Side Evaluation
MAIC's ability to generate lecture scripts was benchmarked against existing methods, demonstrating superior overall performance, particularly in clarity and content alignment. This underscores the system's potential to produce high-quality instructional materials that align closely with educational objectives.
Learning Side Evaluation
The classroom manager agent demonstrated competent decision-making capabilities, though areas for improvement were identified to enhance classroom interaction. Engagement metrics highlighted the effectiveness of the agent-driven environment in promoting active learning behaviors among students.
Behavioral Experiment
In a pilot study at Tsinghua University involving over 500 students, MAIC's performance was evaluated through qualitative surveys and academic assessments. The results indicated positive student perceptions of MAIC's teaching quality and learning environment, with notable improvement in student engagement and adaptability in classroom activities.
Predicted Impact and Ethical Considerations
MAIC's introduction is anticipated to significantly enhance the scalability and personalization of online education. However, ethical concerns such as data privacy, potential biases, and the role of educators remain pivotal. The system must ensure equitable access and maintain rigorous data protection protocols to mitigate these issues.
Conclusion
MAIC represents a significant step forward in the evolution of online education, providing a framework for scalable and personalized learning supported by LLM-driven multi-agent systems. The framework's initial implementation has shown promising results, indicating its potential to reshape online learning landscapes. Future work will focus on refining the platform, addressing ethical considerations, and expanding its application to ensure broader and equitable educational benefits.