- The paper presents SVDD, a soft value-based decoding method that guides sampling in diffusion models without requiring derivative information.
- It leverages Monte Carlo regression and posterior mean approximation to efficiently optimize reward functions during inference.
- Experimental results across image, molecule, and sequence generation demonstrate enhanced reward performance while preserving sample diversity.
Derivative-Free Guidance in Continuous and Discrete Diffusion Models with Soft Value-Based Decoding
Introduction and Motivation
The paper introduces Soft Value-Based Decoding in Diffusion models (SVDD), a derivative-free guidance method for optimizing downstream reward functions in both continuous and discrete diffusion models. The motivation stems from the limitations of existing guidance techniques: classifier guidance requires differentiable proxy models, which are often infeasible in scientific domains where reward functions (e.g., docking scores, physical simulations) are non-differentiable; RL-based or classifier-free fine-tuning is computationally expensive and risks catastrophic forgetting of pre-trained generative models. SVDD circumvents these issues by leveraging soft value functions to guide the sampling process at inference time, without requiring model fine-tuning or differentiable reward proxies.
Methodology
Soft Value Functions and Decoding
SVDD introduces soft value functions vt−1(xt−1) that estimate the expected future reward obtainable from an intermediate noisy state xt−1 during the denoising process. The optimal policy for sampling is defined as:
pt−1⋆,α(xt−1∣xt)∝pt−1pre(xt−1∣xt)exp(αvt−1(xt−1))
where pt−1pre is the pre-trained denoising policy and α is a temperature parameter controlling the trade-off between reward maximization and sample naturalness.
Inference-Time Algorithm
At each denoising step, SVDD samples M candidate states from the pre-trained model, evaluates their soft value functions, and selects the candidate with the highest value (or samples proportionally to the exponentiated values for α>0). This process is repeated iteratively from the initial noisy state to the final sample.








Figure 1: Generated samples from SVDD across multiple domains, illustrating reward-optimized yet natural outputs.
Value Function Estimation
Two approaches are proposed for estimating soft value functions:
- Monte Carlo Regression (SVDD-MC): Roll out the pre-trained model, collect (xt,r(x0)) pairs, and regress the reward onto the intermediate states.
- Posterior Mean Approximation (SVDD-PM): Use the pre-trained model's posterior mean prediction x^0(xt) and evaluate the reward directly, requiring no additional training.
SVDD-PM is particularly attractive for non-differentiable rewards, as it only requires reward evaluation on the predicted sample.
Comparison to Prior Methods
SVDD is compared to classifier guidance, best-of-N sampling, RL-based fine-tuning, and SMC-based methods. Unlike classifier guidance, SVDD does not require differentiable reward models and is directly applicable to discrete diffusion models. Compared to best-of-N, SVDD is more sample-efficient due to its look-ahead value function. SMC-based methods, while also derivative-free, suffer from poor diversity and parallelization inefficiencies when batch sizes are small.


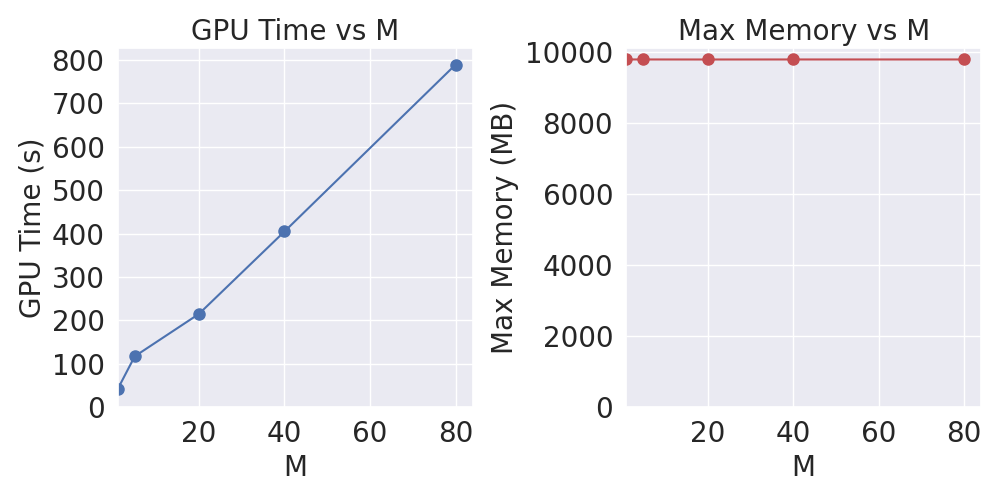
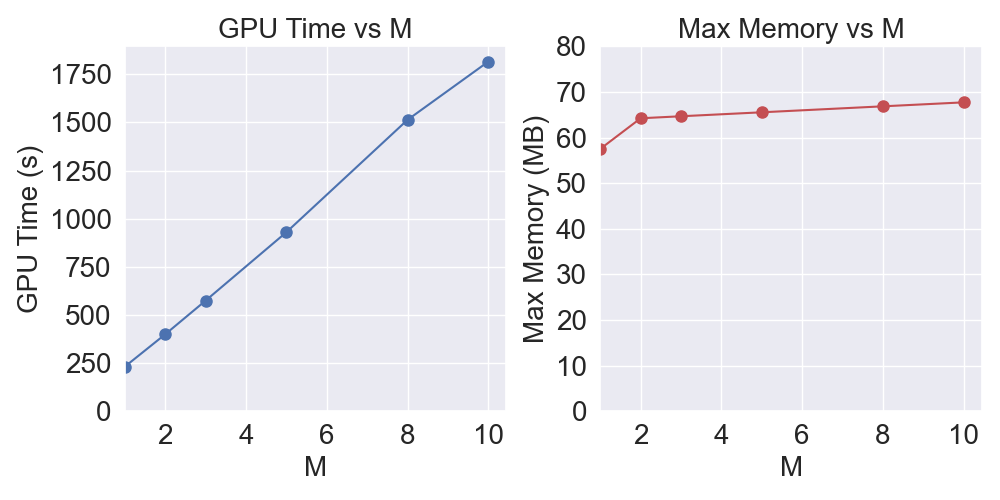
Figure 2: Performance of SVDD compared to baselines, showing superior reward quantiles across domains.








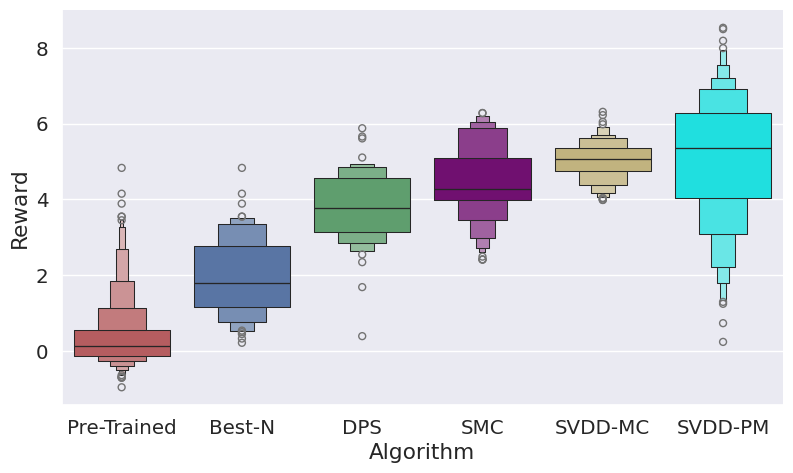
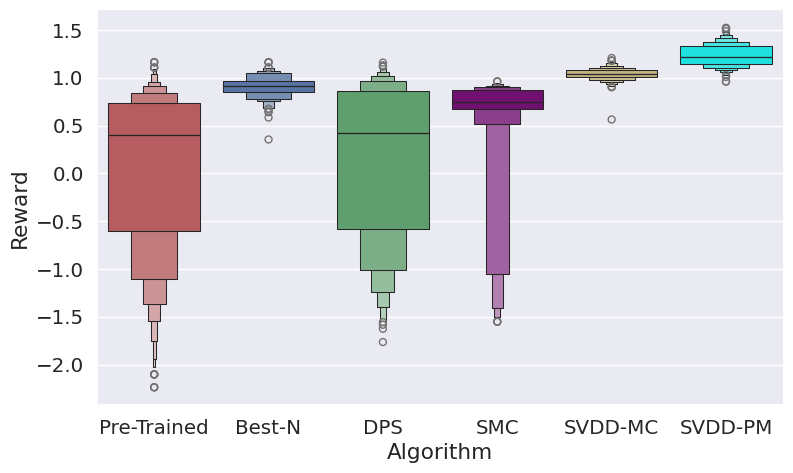
Figure 3: Histogram of generated samples in terms of reward functions, demonstrating SVDD's consistent high-reward generation.
Experimental Results
SVDD is evaluated on image generation (Stable Diffusion), molecule generation (GDSS), and biological sequence generation (discrete diffusion for DNA/RNA). Reward functions include compressibility, aesthetic score, QED, SA, docking scores, and biological activity. SVDD consistently outperforms baselines in top quantile rewards, while maintaining sample validity and diversity.



Figure 4: Training curve of value functions, indicating stable convergence in Monte Carlo regression.

Figure 5: Additional generated samples in molecule domain, optimized for SA score.

Figure 6: Additional generated samples in image domain, optimized for compressibility.

Figure 7: Additional generated samples in image domain, optimized for aesthetic score.

Figure 8: Additional generated samples in molecule domain, optimized for QED score.

Figure 9: Additional generated samples from SVDD, illustrating diversity and reward optimization.

Figure 10: Additional generated samples from SVDD, further validating sample quality.
Implementation Considerations
- Computational Complexity: SVDD requires M times more computation per denoising step, but this can be parallelized. Memory usage scales linearly with M if parallelized.
- Scalability: SVDD is highly parallelizable and robust to small batch sizes, unlike SMC-based methods.
- Applicability: SVDD is agnostic to the reward function's differentiability and is compatible with both continuous and discrete diffusion models.
- Distillation: The inference-time cost can be mitigated by distilling SVDD-guided policies into a new generative model.
Limitations
- Inference Cost: Increased computational and memory requirements at inference, especially for large M.
- Reward Model Quality: SVDD-MC's performance depends on the accuracy of the value function regressor.
- Proximity to Pre-trained Distribution: SVDD maintains closeness to the pre-trained model, which may limit exploration of out-of-distribution regions compared to RL-based fine-tuning.
Theoretical Implications
SVDD formalizes reward-guided sampling in diffusion models as entropy-regularized MDPs, connecting generative modeling and RL. The method provides a principled approach to reward optimization without gradient-based guidance, broadening the applicability of diffusion models in scientific domains.
Future Directions
Potential extensions include policy distillation for efficient deployment, application to protein and 3D molecule generation, and integration with arbitrary proposal distributions for further efficiency gains.
Conclusion
SVDD presents a practical, derivative-free framework for reward-guided sampling in diffusion models, applicable to both continuous and discrete domains. It enables direct optimization of non-differentiable reward functions at inference time, outperforming existing baselines in both reward maximization and sample validity. The approach is theoretically grounded, computationally parallelizable, and broadly applicable, with significant implications for generative modeling in scientific and engineering domains.





























