- The paper introduces MedSAM-2, which segments 3D medical images as video using sequential slice processing for improved accuracy.
- It incorporates a Confidence Memory Bank and Weighted Pick-up strategy to enhance segmentation without continuous user intervention.
- MedSAM-2 achieves superior Dice scores across 15 diverse medical datasets and outperforms few-shot methods in one-prompt segmentation.
Introduction
The paper "Medical SAM 2: Segment medical images as video via Segment Anything Model 2" introduces MedSAM-2, an advancement in the domain of medical image segmentation. Building on the capabilities of the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2), MedSAM-2 leverages the concept of treating medical images as video sequences to enhance segmentation performance on both 2D and 3D datasets.
Methodology
SAM 2 Application on 3D Medical Images
MedSAM-2 utilizes SAM 2, originally designed for video segmentation, by conceptualizing 3D medical images as video sequences. This technique capitalizes on the inherent continuity in 3D data, akin to video frames, allowing for improved segmentation by leveraging the temporal associations between image slices. The model employs a memory system for sequential slice processing, wherein slice embeddings are conditioned with historical data to refine accuracy.

Figure 1: An illustration showcasing the capability of MedSAM-2, depicting the segmentation of temporally-associated frames from a single prompt in a 3D slice.
One-prompt Segmentation for 2D Medical Images
MedSAM-2's notable feature is its ability to perform One-prompt Segmentation on 2D medical images, which involves segmenting similar targets across unrelated frames using a single prompt. By treating sets of 2D medical images as video sequences, MedSAM-2 surpasses the generalization capabilities of existing models, allowing clinicians to efficiently manage segmentation tasks with minimal user input.
Framework Components
MedSAM-2 incorporates two key mechanisms: the Confidence Memory Bank and the Weighted Pick-up strategy. These components facilitate memory-enhanced segmentation without continuous user intervention. The Confidence Memory Bank selectively retains high-confidence predictions, while the Weighted Pick-up strategy optimizes embedding merging to improve task generalization.

Figure 2: MedSAM-2 Framework highlighting its approach to treating medical images as videos with the addition of specialized memory components and strategies.
MedSAM-2 Architecture
The architecture of MedSAM-2 extends SAM 2’s capabilities, featuring an image encoder, memory encoder, and attention mechanisms. This design enables real-time segmentation refining through user inputs and facilitates significant performance improvements in both universal and One-prompt Segmentation tasks.
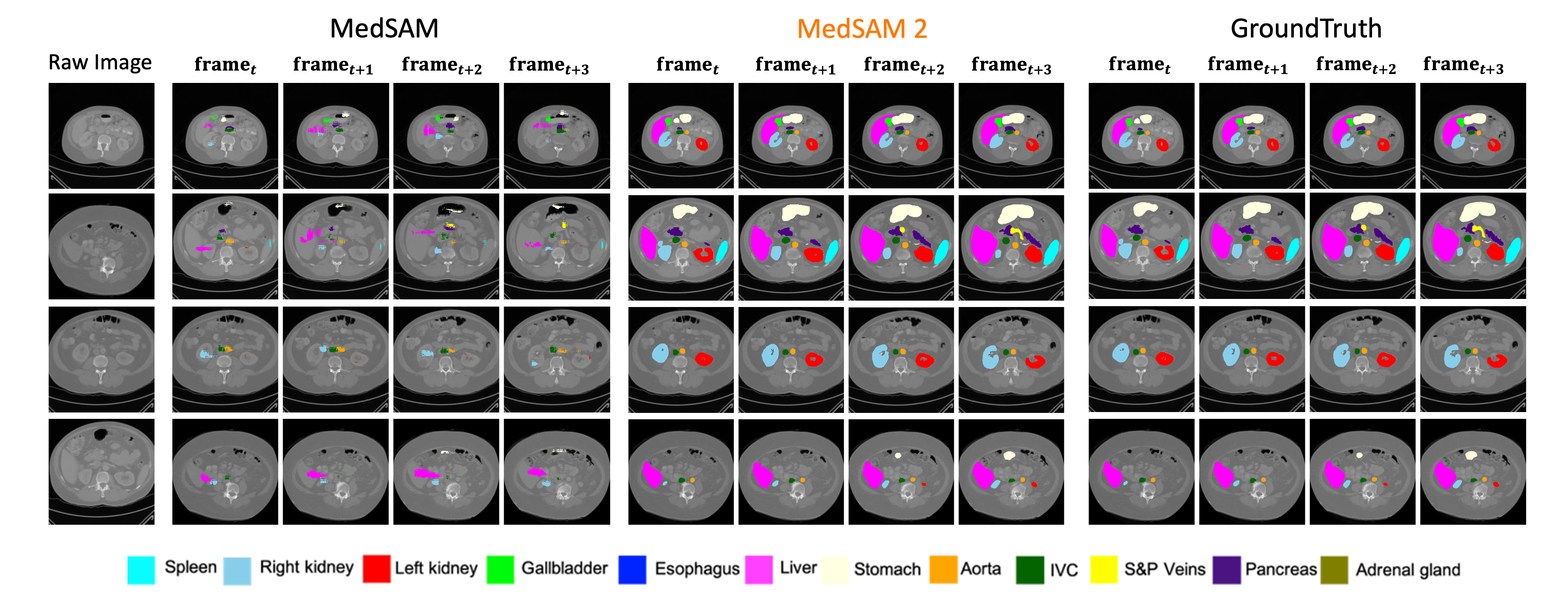
Figure 3: A comparative analysis of MedSAM, MedSAM-2, and ground truth reflects MedSAM-2’s enhanced segmentation accuracy in sequential 3D medical image tasks.
Experimental Evaluation
MedSAM-2 was tested across 15 datasets encompassing various segmentation tasks, including abdominal, brain, thyroid, and skin modalities. The model consistently delivered superior Dice scores compared to state-of-the-art interactive and fully-supervised systems, demonstrating versatile applicability and robust segmentation fidelity across multiple medical imaging contexts.
One-Prompt Segmentation Evaluation
In a challenging One-prompt Segmentation setting, MedSAM-2 outperformed existing few-shot and one-shot methods across ten datasets with different prompts. This exceptional capacity underscores MedSAM-2’s strength in generalizing from minimal input and processing disjointed data sequences with precision.

Figure 4: MedSAM-2 versus Few/One-shot Models across different datasets under One-prompt Segmentation, highlighting MedSAM-2’s superior average scores.
Conclusion
MedSAM-2 presents a significant advancement in medical image segmentation, aiming to democratize access to highly accurate, low-interaction segmentation methods by leveraging video processing principles. This research proposes a paradigm shift wherein medical images are processable with singular prompts, simplifying clinical workflows and enhancing diagnostic accuracy across a spectrum of medical applications.
The framework promises flexibility and performance across diverse medical imaging tasks, setting a precedent for future adaptations in real-time segmentation models and automated diagnostic tools in clinical settings. Further exploration into its application outside medical domains could extend its utility, making MedSAM-2 a versatile tool in AI-aided analysis.



