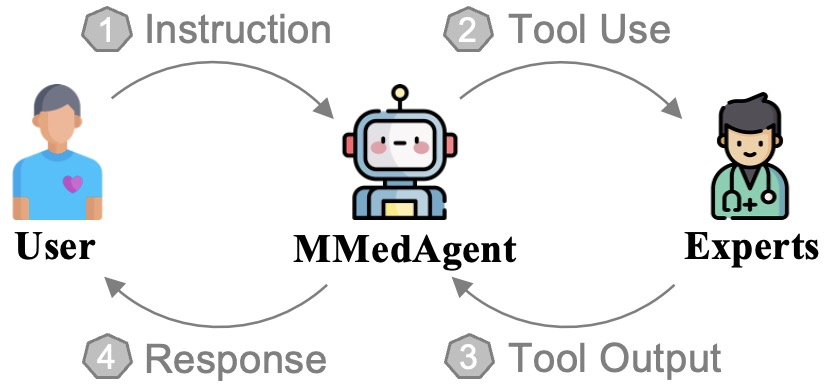
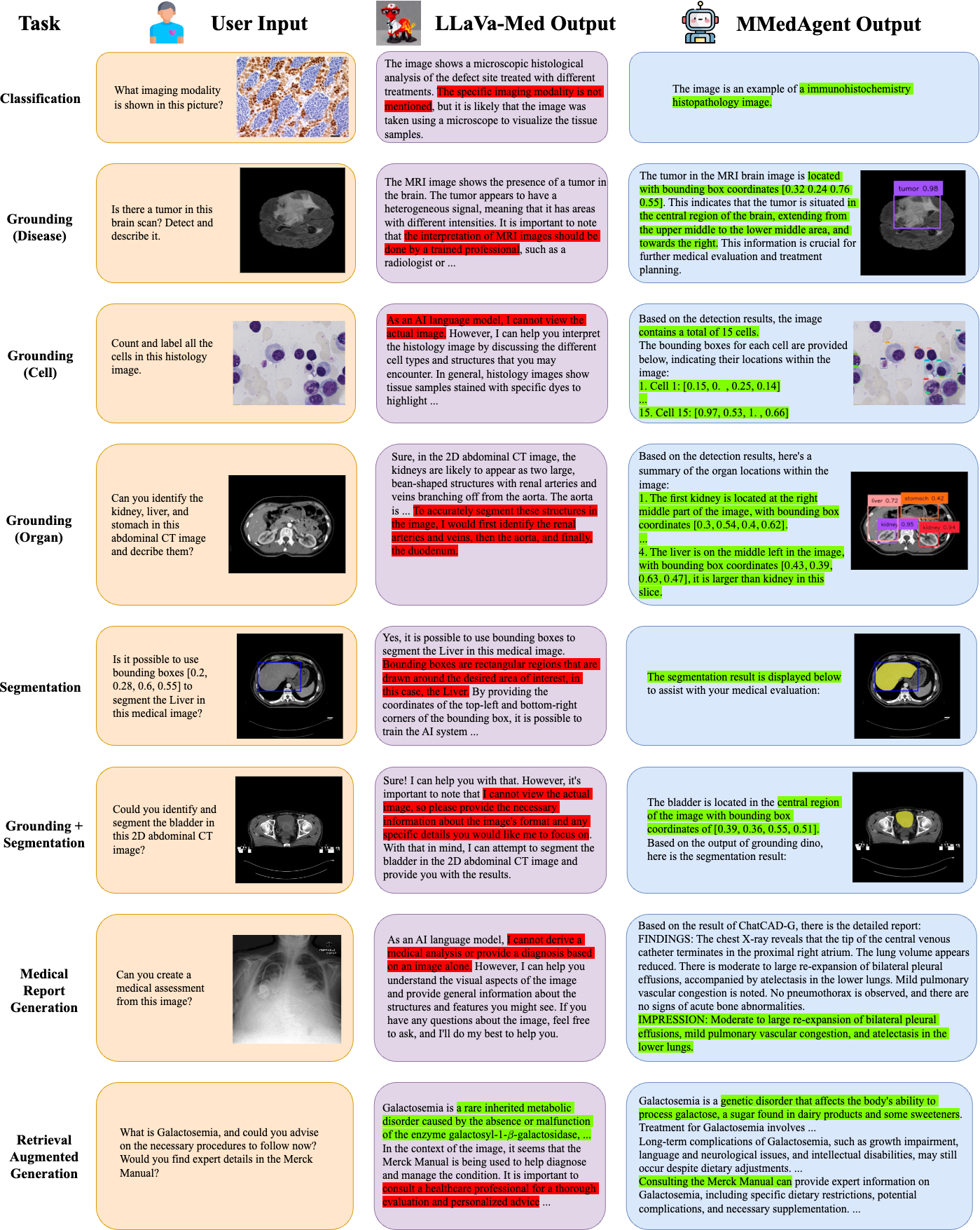
MMedAgent: Learning to Use Medical Tools with Multi-modal Agent
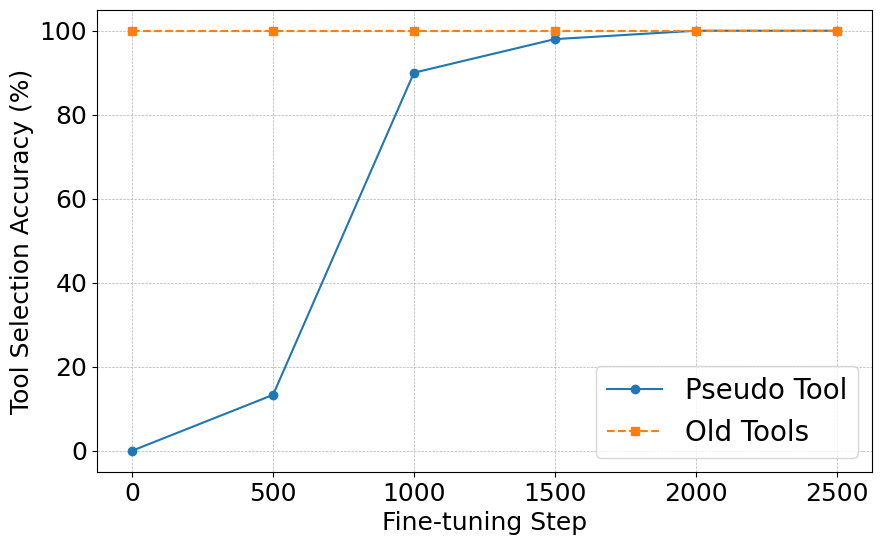
Abstract: Multi-Modal LLMs (MLLMs), despite being successful, exhibit limited generality and often fall short when compared to specialized models. Recently, LLM-based agents have been developed to address these challenges by selecting appropriate specialized models as tools based on user inputs. However, such advancements have not been extensively explored within the medical domain. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces the first agent explicitly designed for the medical field, named \textbf{M}ulti-modal \textbf{Med}ical \textbf{Agent} (MMedAgent). We curate an instruction-tuning dataset comprising six medical tools solving seven tasks across five modalities, enabling the agent to choose the most suitable tools for a given task. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that MMedAgent achieves superior performance across a variety of medical tasks compared to state-of-the-art open-source methods and even the closed-source model, GPT-4o. Furthermore, MMedAgent exhibits efficiency in updating and integrating new medical tools. Codes and models are all available.
- Lung segmentation in chest radiographs using anatomical atlases with nonrigid registration. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 33(2):577–590.
- Llava-interactive: An all-in-one demo for image chat, segmentation, generation and editing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.00571.
- Palm: Scaling language modeling with pathways. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 24(240):1–113.
- Ai hospital: Interactive evaluation and collaboration of llms as intern doctors for clinical diagnosis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.09742.
- A real-world webagent with planning, long context understanding, and program synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.12856.
- Ct2rep: Automated radiology report generation for 3d medical imaging. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.06801.
- Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.09685.
- Automatic tuberculosis screening using chest radiographs. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 33(2):233–245.
- Mimic-cxr-jpg, a large publicly available database of labeled chest radiographs. Preprint, arXiv:1901.07042.
- Segment anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pages 4015–4026.
- Medlsam: Localize and segment anything model for 3d ct images. Preprint, arXiv:2306.14752.
- Llava-med: Training a large language-and-vision assistant for biomedicine in one day. Preprint, arXiv:2306.00890.
- Agent hospital: A simulacrum of hospital with evolvable medical agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.02957.
- Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. 13.
- Llava-plus: Learning to use tools for creating multimodal agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.05437.
- Grounding dino: Marrying dino with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. Preprint, arXiv:2303.05499.
- Ilya Loshchilov and Frank Hutter. 2019. Decoupled weight decay regularization. Preprint, arXiv:1711.05101.
- Word: A large scale dataset, benchmark and clinical applicable study for abdominal organ segmentation from ct image. Medical Image Analysis, 82:102642.
- Segment anything in medical images. Nature Communications, 15(1).
- The multi-modality cell segmentation challenge: Towards universal solutions. Nature Methods.
- Fast and low-gpu-memory abdomen ct organ segmentation: The flare challenge. Medical Image Analysis, 82:102616.
- Segment anything model for medical image analysis: an experimental study. Medical Image Analysis, 89:102918.
- The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (brats). IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 34(10):1993–2024.
- Med-flamingo: a multimodal medical few-shot learner. In Machine Learning for Health (ML4H), pages 353–367. PMLR.
- Vindr-cxr: An open dataset of chest x-rays with radiologist’s annotations. Scientific Data, 9(1):429.
- OpenAI. 2024. Hello gpt-4o. https://openai.com/index/hello-gpt-4o/. Accessed: 2024-05-26.
- Flickr30k entities: Collecting region-to-phrase correspondences for richer image-to-sentence models. pages 2641–2649.
- Robert S. Porter and Justin L. Kaplan. 2011. The merck manual of diagnosis and therapy, 2011. Merck Research Laboratories.
- Mp5: A multi-modal open-ended embodied system in minecraft via active perception. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.07472.
- Agentclinic: a multimodal agent benchmark to evaluate ai in simulated clinical environments. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.07960.
- Large language models encode clinical knowledge. Nature, 620(7972):172–180.
- Pathasst: Redefining pathology through generative foundation ai assistant for pathology. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15072.
- Medagents: Large language models as collaborators for zero-shot medical reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.10537.
- Webwise: Web interface control and sequential exploration with large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.16042.
- Xraygpt: Chest radiographs summarization using medical vision-language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.07971.
- Towards generalist biomedical ai. NEJM AI, 1(3):AIoa2300138.
- Chatvideo: A tracklet-centric multimodal and versatile video understanding system. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.14407.
- Mobile-agent: Autonomous multi-modal mobile device agent with visual perception. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.16158.
- Chatcad: Interactive computer-aided diagnosis on medical image using large language models. Preprint, arXiv:2302.07257.
- Jarvis-1: Open-world multi-task agents with memory-augmented multimodal language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.05997.
- Michael Wooldridge and Nicholas R Jennings. 1995. Intelligent agents: Theory and practice. The knowledge engineering review, 10(2):115–152.
- Towards generalist foundation model for radiology by leveraging web-scale 2d&3d medical data. Preprint, arXiv:2308.02463.
- Large multimodal agents: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.15116.
- Advancing multimodal medical capabilities of gemini. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.03162.
- Zhuosheng Zhan and Aston Zhang. 2023. You only look at screens: Multimodal chain-of-action agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.11436.
- Biomedgpt: A unified and generalist biomedical generative pre-trained transformer for vision, language, and multimodal tasks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.17100.
- Biomedclip: a multimodal biomedical foundation model pretrained from fifteen million scientific image-text pairs. Preprint, arXiv:2303.00915.
- Biomedclip: a multimodal biomedical foundation model pretrained from fifteen million scientific image-text pairs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.00915.
- Pmc-vqa: Visual instruction tuning for medical visual question answering. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10415.
- Loop copilot: Conducting ai ensembles for music generation and iterative editing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.12404.
- Biomedparse: a biomedical foundation model for image parsing of everything everywhere all at once. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.12971.
- Chatcad+: Towards a universal and reliable interactive cad using llms. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, page 1–1.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.