Leveraging Multi-AI Agents for Cross-Domain Knowledge Discovery
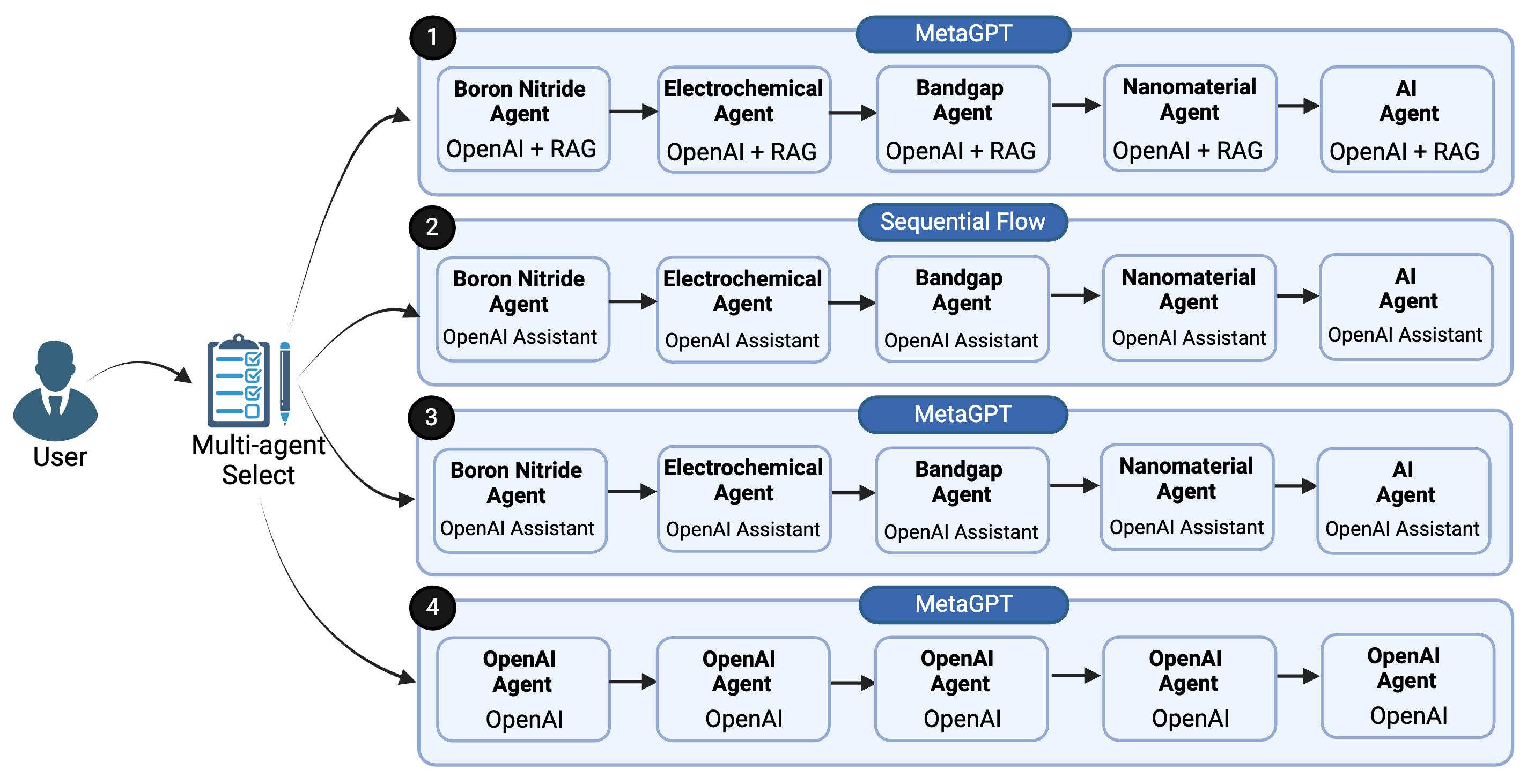
Abstract: In the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence, the ability to harness and integrate knowledge across various domains stands as a paramount challenge and opportunity. This study introduces a novel approach to cross-domain knowledge discovery through the deployment of multi-AI agents, each specialized in distinct knowledge domains. These AI agents, designed to function as domain-specific experts, collaborate in a unified framework to synthesize and provide comprehensive insights that transcend the limitations of single-domain expertise. By facilitating seamless interaction among these agents, our platform aims to leverage the unique strengths and perspectives of each, thereby enhancing the process of knowledge discovery and decision-making. We present a comparative analysis of the different multi-agent workflow scenarios evaluating their performance in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and the breadth of knowledge integration. Through a series of experiments involving complex, interdisciplinary queries, our findings demonstrate the superior capability of domain specific multi-AI agent system in identifying and bridging knowledge gaps. This research not only underscores the significance of collaborative AI in driving innovation but also sets the stage for future advancements in AI-driven, cross-disciplinary research and application. Our methods were evaluated on a small pilot data and it showed a trend we expected, if we increase the amount of data we custom train the agents, the trend is expected to be more smooth.
- Utilizing XGBoost for the Prediction of Material Corrosion Rates from Embedded Tabular Data using Large Language Model. In 2023 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), December 2023. DOI: 10.1109/BIBM58861.2023.10385544.
- NLPADADE: Leveraging Natural Language Processing for Automated Detection of Adverse Drug Effects. In 2023 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), December 2023. DOI: 10.1109/BIBM58861.2023.10385626.
- Comparative Study of Domain Driven Terms Extraction Using Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.02330, 2024. Archive Prefix: arXiv, Primary Class: cs.CL. Available at https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.02330.
- FAIR Enough: How Can We Develop and Assess a FAIR-Compliant Dataset for Large Language Models’ Training? arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.11033, January 2024. Available at http://arxiv.org/abs/2401.11033.
- Learning Transferable Time Series Classifier with Cross-Domain Pre-training from Language Model. Proceedings of ACM Conference (Conference’17), March 2024, Volume 1. Available at http://arxiv.org/abs/2403.12372.
- Mohammed Rizvi. Exploring the landscape of artificial intelligence in education: Challenges and opportunities. In HORA 2023 - 2023 5th International Congress on Human-Computer Interaction, Optimization and Robotic Applications, Proceedings. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2023. DOI: 10.1109/HORA58378.2023.10156773.
- MetaGPT: Meta Programming for A Multi-Agent Collaborative Framework. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.00352v5, August 2023. Available at https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.00352v5.
- ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.03629v3, October 2022. Available at https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.03629v3.
- Cross-Domain Recommendation with Cross-Graph Knowledge Transfer Network. In IEEE International Conference on Communications, June 2021. DOI: 10.1109/ICC42927.2021.9500882.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.