- The paper presents a comprehensive systematic literature review that identifies 13 core DEAI building blocks and evaluates associated ethical and technical challenges.
- It details decentralized mechanisms such as blockchain integration, smart contracts, and secure model governance to enhance privacy and eliminate single points of failure.
- It provides actionable future research directions to standardize evaluation methods and advance real-world deployment of decentralized AI solutions.
A Review on Building Blocks of Decentralized Artificial Intelligence
This systematic literature review (SLR) investigates the nascent field of Decentralized Artificial Intelligence (DEAI) by identifying its fundamental building blocks. The central theme revolves around addressing ethical concerns in AI, including digital privacy, ownership, and control, which are inadequately addressed by Centralized AI (CEAI). The review analyzes 71 studies to provide a bottom-up perspective on the constituent components of DEAI solutions and networks, culminating in proposed future research directions and open problems.
Motivation and Contributions
Current research reviews predominantly focus on high-level advantages and disadvantages of DEAI or apply decentralization to specific domains, lacking a comprehensive view of the core components common across different solutions. This paper addresses this gap by performing an SLR to identify building blocks from a ground-up perspective.
The primary contributions include:
- A systematic literature review and analysis of the DEAI field.
- Identification of core DEAI building blocks as guidelines for designing new solutions.
- Identification of metrics for evaluating DEAI systems.
- Identification of significant DEAI issues and challenges.
Overview of Decentralized Artificial Intelligence
DEAI intersects AI and decentralized systems, often leveraging Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs) and blockchain. While sharing technical concepts with Distributed AI (DAI) and Edge AI, DEAI uniquely prioritizes:
- Eliminating single points of failure.
- Decentralized control.
- Open-source technologies.
- Self-sovereignty.
- Enhanced privacy.
- Resource sharing.
For instance, federated learning, typically centralized, can be decentralized using smart contracts to coordinate training, embodying the DEAI ethos.
Research Methodology Details
The SLR followed established guidelines and addressed key questions regarding the definition, architectural designs, advantages, and common building blocks of DEAI networks. The literature search encompassed seven sources, including scientific databases and gray literature, employing targeted keywords and search strings. The screening process involved two iterations, filtering articles based on predefined selection and exclusion criteria (Figure 1).
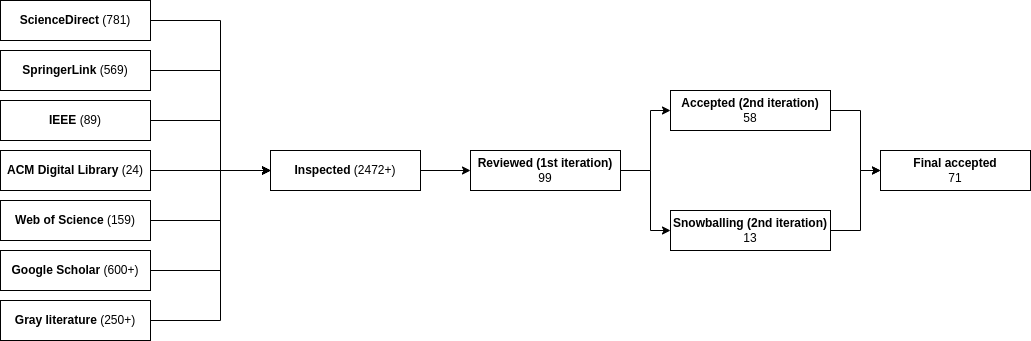
Figure 1: A depiction of the reduction of papers through the systematic screening process, highlighting the stringent selection criteria applied at each stage.
Data extraction focused on metadata and critical attributes such as building blocks, features, challenges, evaluation metrics, contribution type, AI model support, and network type. This rigorous approach ensured a comprehensive and systematic analysis of the DEAI landscape.
Building Blocks of DEAI Networks
The analysis identified 13 core building blocks crucial for DEAI networks, providing a foundation for future research and implementation (Table 1). These building blocks are interconnected, forming a cohesive framework for decentralized AI solutions (Figure 2).
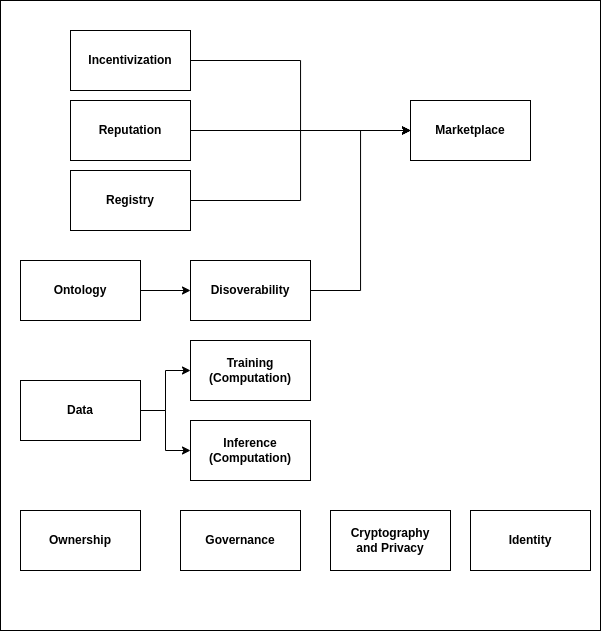
Figure 2: A graphical representation showcasing the connections between various building blocks, emphasizing their interdependencies and relationships within DEAI systems.
These building blocks include:
- Registry: A trusted repository of available AI models.
- Incentivization: Mechanisms rewarding AI model usage and development.
- Marketplace: An open platform for trading AI models.
- Reputation: Systems for ranking AI models and identifying reliable actors.
- Ontology: Standardized descriptions of AI models for interoperability.
- Discoverability: Efficiently locating needed AI models.
- Training (Computation): Support for AI model training.
- Inference (Computation): Support for AI model inference.
- Ownership: Transparent provenance and control of AI models.
- Data: Mechanisms for handling data and uploading it to AI models.
- Governance: Rules defining decision-making in the decentralized system.
- Cryptography and Privacy: Enabling verifiability, privacy, and secure identity.
- Identity: Unique identifiers for AI models and agents.
In addition to these building blocks, the review also identified features such as standards and specifications, security considerations, and the importance of transparency. Challenges, such as updating global models, were also noted.
DEAI Features and Evaluation Methods
Standards and Specifications
Interoperability is enhanced by adherence to standards and guidelines, similar to the role of Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) in the Web3 ecosystem. Strict standards for datasets and AI agents improve their composability.
Security
DEAI systems must address security concerns like malicious nodes and DDoS attacks through mechanisms like token staking and trusted execution environments (TEEs).
Transparency
Transparency is inherent in decentralized networks, enhancing data trustworthiness. Publicly available and cryptographically verifiable information improves end-user trust and regulatory compliance.
Evaluation Methods
Evaluation methods encompass blockchain-specific metrics (block times, throughput, gas usage), scalability metrics (model capacity, modality support), and AI model performance (training/inference time). Comparative analyses between centralized and decentralized solutions and security assessments are critical for demonstrating DEAI's advantages.
Discussion and Future Directions
The review culminates in a definition of a DEAI network as a decentralized system that enables AI agents to operate, communicate, and offer callable endpoints. While no analyzed architecture fully encompasses all building blocks and has been fully validated in production, some works approximate this ideal. DEAI offers advantages like censorship resistance and enhanced democratization but faces challenges in development time, scalability, and maturity compared to CEAI. Figure 3 visualizes the distribution of papers across the identified building blocks.
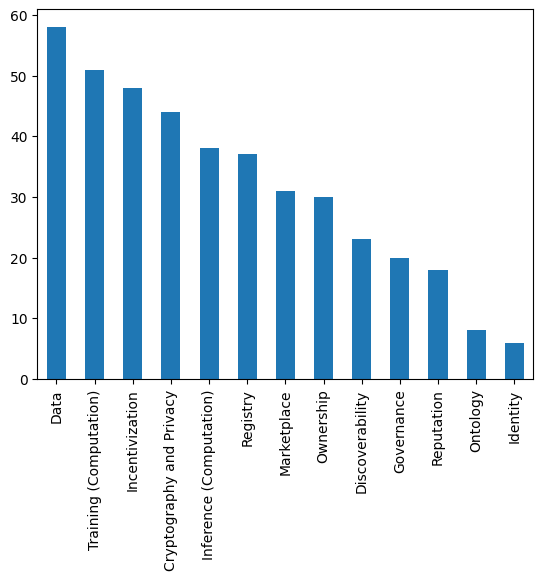
Figure 3: A bar chart illustrating the number of research papers associated with each specific building block of Decentralized Artificial Intelligence (DEAI).
Future research should focus on underexplored building blocks like identity, ontology, and reputation, as well as standardized evaluation methods. Collaboration between academia and industry is crucial for bridging the gap between theoretical solutions and real-world deployments. The screened attributes including publication place, contribution, database, year, supported AI models, and system/network type are visualized in (Figure 4), (Figure 5), (Figure 6), and (Figure 7) respectively.
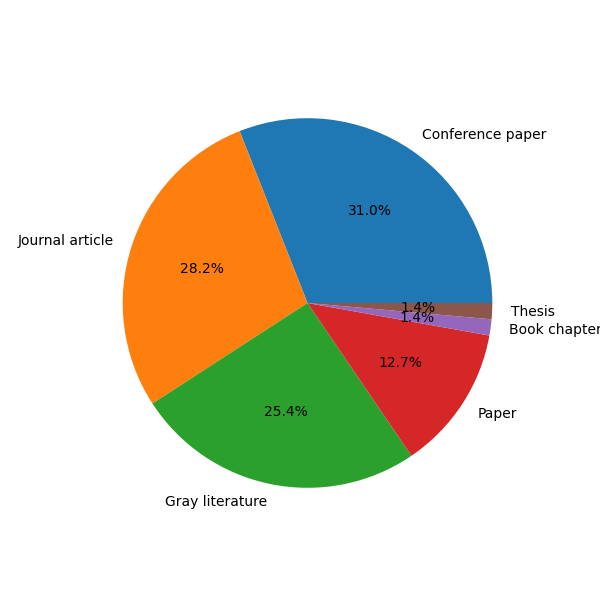
Figure 4: A pie chart detailing the percentages of papers based on their place of publication, categorized into journals, gray literature, conferences, and other sources.
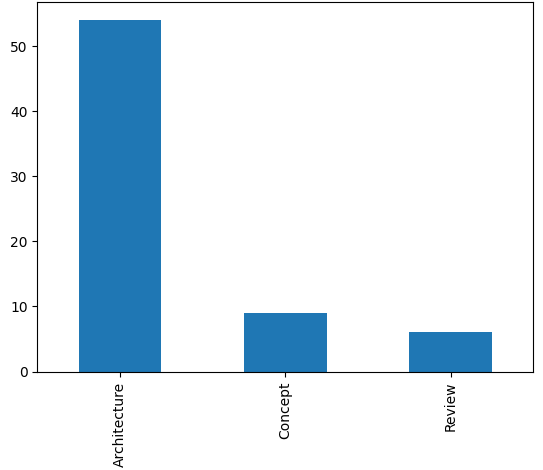
Figure 5: A bar graph indicating the number of papers categorized by their primary contribution, such as architecture proposals, conceptual frameworks, and review articles.
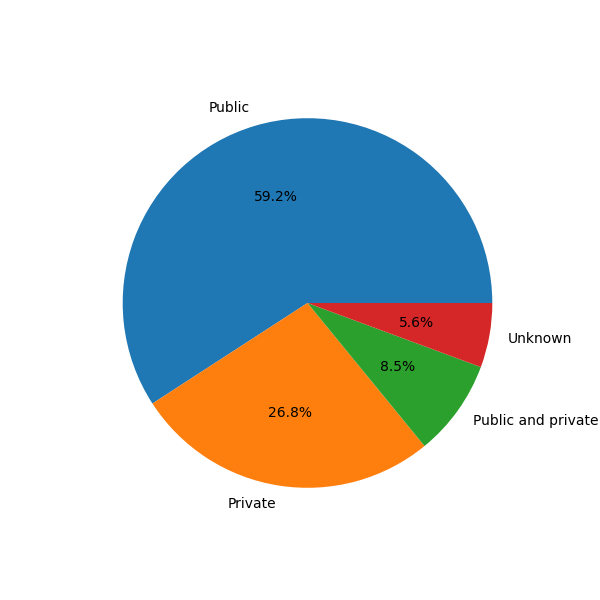
Figure 6: A pie chart showing the percentages of papers based on network type, distinguishing between private (permissioned) and public (permissionless) networks.
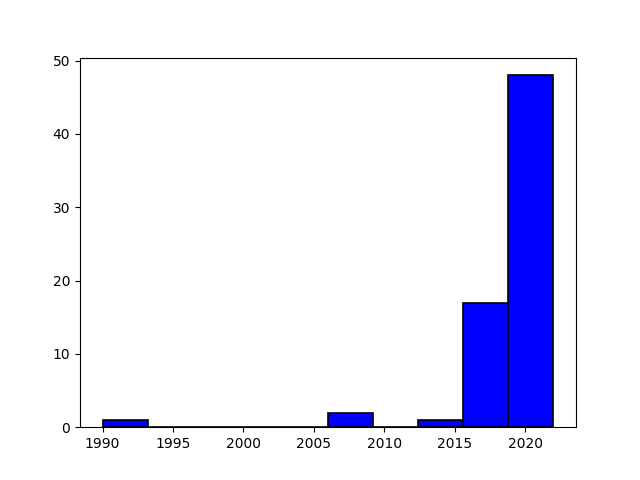
Figure 7: A line graph displaying the number of papers published per year, illustrating the trend and growth of research in Decentralized Artificial Intelligence (DEAI) over time.
The bottom-up approach, focusing on individual building blocks and their integration, should guide future DEAI research.
Conclusion
This systematic review highlights the advances in DEAI, identifying 71 relevant articles and projects. The analysis reveals 13 core building blocks, features, challenges, and evaluation methods crucial for DEAI solutions. While literature on DEAI is comprehensive, further real-world validation is needed. Future efforts should focus on bottom-up development, enhancing cooperation, and improving interoperability between DEAI systems.






