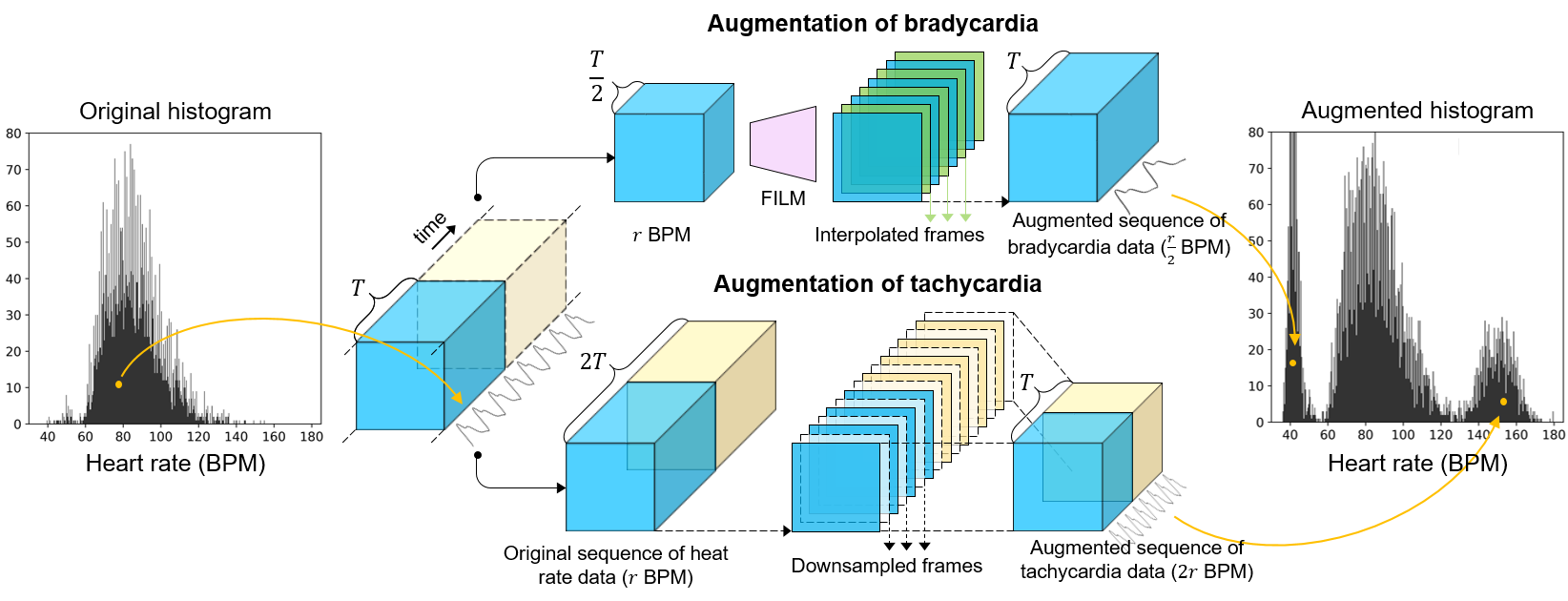
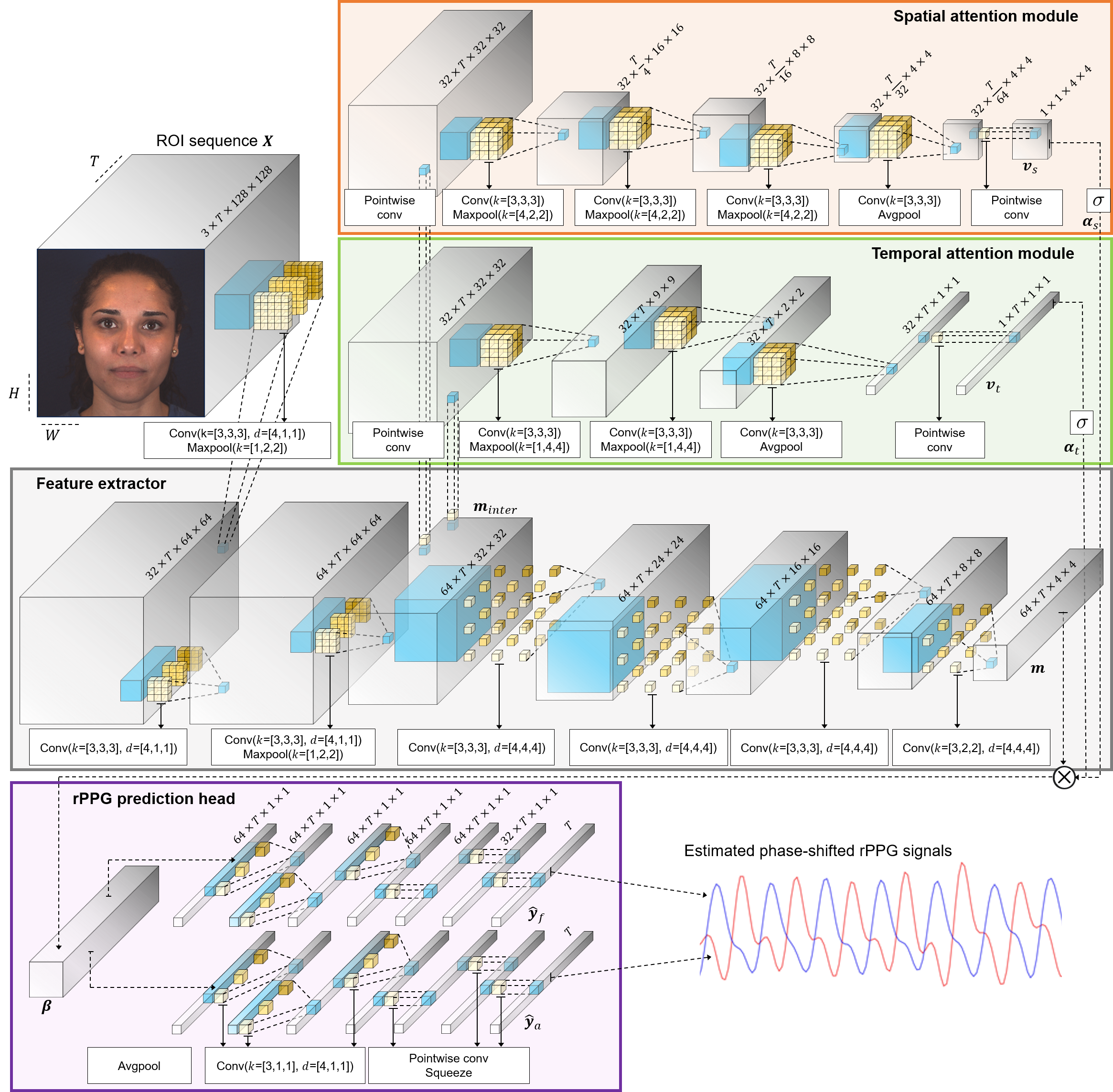
Phase-shifted remote photoplethysmography for estimating heart rate and blood pressure from facial video
Abstract: Human health can be critically affected by cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, arrhythmias, and stroke. Heart rate and blood pressure are important biometric information for the monitoring of cardiovascular system and early diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. Existing methods for estimating the heart rate are based on electrocardiography and photoplethyomography, which require contacting the sensor to the skin surface. Moreover, catheter and cuff-based methods for measuring blood pressure cause inconvenience and have limited applicability. Therefore, in this thesis, we propose a vision-based method for estimating the heart rate and blood pressure. This thesis proposes a 2-stage deep learning framework consisting of a dual remote photoplethysmography network (DRP-Net) and bounded blood pressure network (BBP-Net). In the first stage, DRP-Net infers remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) signals for the acral and facial regions, and these phase-shifted rPPG signals are utilized to estimate the heart rate. In the second stage, BBP-Net integrates temporal features and analyzes phase discrepancy between the acral and facial rPPG signals to estimate SBP and DBP values. To improve the accuracy of estimating the heart rate, we employed a data augmentation method based on a frame interpolation model. Moreover, we designed BBP-Net to infer blood pressure within a predefined range by incorporating a scaled sigmoid function. Our method resulted in estimating the heart rate with the mean absolute error (MAE) of 1.78 BPM, reducing the MAE by 34.31 % compared to the recent method, on the MMSE-HR dataset. The MAE for estimating the systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were 10.19 mmHg and 7.09 mmHg. On the V4V dataset, the MAE for the heart rate, SBP, and DBP were 3.83 BPM, 13.64 mmHg, and 9.4 mmHg, respectively.
- Early identification of pcos with commonly known diseases: obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure and heart disease using machine learning techniques. Expert Systems with Applications, 217, 119532.
- Video-based real-time monitoring for heart rate and respiration rate. Expert Systems with Applications, 225, 120135.
- Noninvasive continuous blood pressure estimation from pulse transit time: A review of the calibration models. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering, 15, 138–151.
- Unsupervised skin tissue segmentation for remote photoplethysmography. Pattern Recognition Letters, 124, 82–90.
- Estimation of blood pressure waveform from facial video using a deep u-shaped network and the wavelet representation of imaging photoplethysmographic signals. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 78, 103895.
- Deepphys: Video-based physiological measurement using convolutional attention networks. In Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 349–365).
- Remote blood pressure estimation via the spatiotemporal mapping of facial videos. Sensors, 23, 2963.
- Collins, J. R. (1976). Robust estimation of a location parameter in the presence of asymmetry. The Annals of Statistics, (pp. 68–85).
- Robust pulse rate from chrominance-based rppg. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 60, 2878–2886.
- A systematic review of healthcare recommender systems: Open issues, challenges, and techniques. Expert Systems with Applications, 213, 118823.
- High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension, 75, 285–292.
- Global cardiovascular diseases death rate prediction. Current Problems in Cardiology, (p. 101622).
- Wearable cuff-less blood pressure estimation at home via pulse transit time. IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics, 25, 1926–1937.
- Pulse transit time as an indicator of arterial blood pressure. psychophysiology, 18, 71–74.
- A support system for automatic classification of hypertension using bcg signals. Expert Systems with Applications, 214, 119058.
- Neural network model combination for video-based blood pressure estimation: New approach and evaluation. Sensors, 23, 1753.
- Ppg-based blood pressure estimation can benefit from scalable multi-scale fusion neural networks and multi-task learning. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 78, 103891.
- Mlp-bp: A novel framework for cuffless blood pressure measurement with ppg and ecg signals based on mlp-mixer neural networks. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 73, 103404.
- Heart rate estimation network from facial videos using spatiotemporal feature image. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 151, 106307.
- Cebpm: A cloud-edge collaborative noncontact blood pressure estimation model. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 71, 1–12.
- A study of projection-based attentive spatial–temporal map for remote photoplethysmography measurement. Bioengineering, 9, 638.
- Measuring pulse rate with a webcam—a non-contact method for evaluating cardiac activity. In 2011 federated conference on computer science and information systems (FedCSIS) (pp. 405–410). IEEE.
- The obf database: A large face video database for remote physiological signal measurement and atrial fibrillation detection. In 2018 13th IEEE international conference on automatic face & gesture recognition (FG 2018) (pp. 242–249). IEEE.
- Efficientphys: Enabling simple, fast and accurate camera-based vitals measurement. arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.04447, .
- Dual-gan: Joint bvp and noise modeling for remote physiological measurement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 12404–12413).
- Using high-fidelity avatars to advance camera-based cardiac pulse measurement. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 69, 2646–2656.
- Continuous blood pressure measurement from one-channel electrocardiogram signal using deep-learning techniques. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 108, 101919.
- Vipl-hr: A multi-modal database for pulse estimation from less-constrained face video. In Computer Vision–ACCV 2018: 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, December 2–6, 2018, Revised Selected Papers, Part V 14 (pp. 562–576). Springer.
- The benefit of distraction: Denoising camera-based physiological measurements using inverse attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (pp. 4955–4964).
- The british hypertension society protocol for the evaluation of automated and semi-automated blood pressure measuring devices with special reference to ambulatory systems. Journal of hypertension, 8, 607–619.
- X-ippgnet: A novel one stage deep learning architecture based on depthwise separable convolutions for video-based pulse rate estimation. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 154, 106592.
- Pp-net: A deep learning framework for ppg-based blood pressure and heart rate estimation. IEEE Sensors Journal, 20, 10000–10011.
- Bam: Bottleneck attention module. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.06514, .
- Heart rate as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Progress in cardiovascular diseases, 52, 6–10.
- Advancements in noncontact, multiparameter physiological measurements using a webcam. IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering, 58, 7–11.
- Film: Frame interpolation for large motion. In European Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 250–266). Springer.
- The first vision for vitals (v4v) challenge for non-contact video-based physiological estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 2760–2767).
- A blood pressure prediction method based on imaging photoplethysmography in combination with machine learning. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 64, 102328.
- Assessment of non-invasive blood pressure prediction from ppg and rppg signals using deep learning. Sensors, 21, 6022.
- A multimodal database for affect recognition and implicit tagging. IEEE transactions on affective computing, 3, 42–55.
- A universal standard for the validation of blood pressure measuring devices: Association for the advancement of medical instrumentation/european society of hypertension/international organization for standardization (aami/esh/iso) collaboration statement. Hypertension, 71, 368–374.
- Non-contact video-based pulse rate measurement on a mobile service robot. In The 23rd IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (pp. 1056–1062). IEEE.
- Algorithmic principles of remote ppg. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 64, 1479–1491.
- A facial-image-based blood pressure measurement system without calibration. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 71, 1–13.
- Autohr: A strong end-to-end baseline for remote heart rate measurement with neural searching. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 27, 1245–1249.
- Remote photoplethysmograph signal measurement from facial videos using spatio-temporal networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.02419, .
- Physformer++: Facial video-based physiological measurement with slowfast temporal difference transformer. International Journal of Computer Vision, 131, 1307–1330.
- Physformer: Facial video-based physiological measurement with temporal difference transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 4186–4196).
- Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE signal processing letters, 23, 1499–1503.
- Multimodal spontaneous emotion corpus for human behavior analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 3438–3446).
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.