- The paper converts Bitcoin’s raw binary data into a high fidelity graph model using Neo4j, enabling comprehensive analysis of transaction flows and network interactions.
- It introduces innovative visualization methods, such as heat-map adjacency matrices, to reveal circulation trends and potential mining identity leakage through extranonce patterns.
- The study applies monetary theory to Bitcoin’s fixed supply, assessing deflationary impacts and detecting network vulnerabilities like DoS attacks through algorithmic spam identification.
Toward Open Data Blockchain Analytics: A Bitcoin Perspective
Introduction
The paper "Toward Open Data Blockchain Analytics: A Bitcoin Perspective" (1802.07523) explores the implications and potential of open data blockchain analytics by focusing on Bitcoin as a case study. The authors leverage the inherently transparent and granular data provided by Bitcoin's public blockchain to perform a comprehensive analysis across several dimensions, including transaction behavior patterns, wealth accumulation, economic dynamics, and network security.
High Fidelity Graph Model
At the core of this research is the transformation of Bitcoin's cumbersome raw binary data into a high fidelity graph model. The authors utilize Neo4j, a graph database, to represent the intricate relationships between blocks, transactions, inputs, and outputs, thereby facilitating efficient traversal and complex query execution. This graph-based approach retains the full depth of Bitcoin's data, enabling comprehensive analysis and pattern recognition.
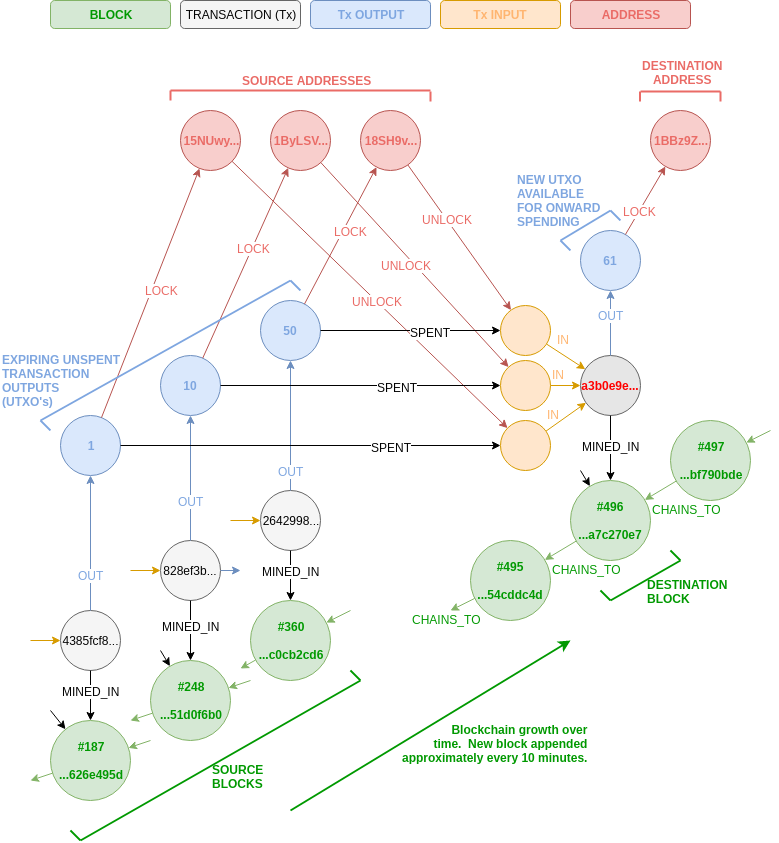
Figure 1: Example portion of the graph model of the Bitcoin blockchain showing the relationships between blocks, transactions, their inputs, outputs and associated addresses.
Visualization and Pattern Detection
The paper provides innovative visualization techniques to uncover patterns within the Bitcoin blockchain. By constructing a heat-map visualization of block transactions as an adjacency matrix, the authors identify significant circulation trends and transactional behaviors. This visualization highlights how most value transfers occur between recent blocks, indicative of high velocity in Bitcoin transactions.

Figure 2: Full Bitcoin blockchain visualization as an adjacency matrix representation, showing the flow of bitcoin amounts between blocks.
The analysis extends to mining-related data privacy concerns, specifically addressing the 'extranonce' used in mining operations. The paper examines how this incremental extranonce can inadvertently reveal continuous mining operations, potentially associating mined bitcoins with specific entities. Such insights are crucial for understanding wealth distribution and accumulation among early adopters and prominent miners.

Figure 3: Plots illustrating the use and implications of the extranonce values, indicative of discrete mining operations.
Economic Implications: Disinflation and Velocity of Circulation
The authors apply monetary theory to the Bitcoin blockchain, analyzing the disinflationary nature of Bitcoin's fixed supply mechanism. By calculating the velocity of circulation through a novel 'bitcoin dwell time' metric, the study confirms that there is no significant change in circulation behavior over time, despite the occurrence of supply-halving events. This constancy contributes to Bitcoin's deflationary characteristics, potentially influencing its purchasing power dynamics.

Figure 4: Bitcoin dwell time by block, showing no accelerating or decelerating trends over time.
Network Security and Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
The paper also explores the security vulnerabilities within the Bitcoin network, particularly Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. Using their graph model, the authors identify and analyze algorithmically generated spam transactions designed to flood the network with small-value transactions, thereby exploiting the Bitcoin block size limitations. This analysis informs strategies for mitigating such attacks and improving overall network resilience.

Figure 5: Algorithmically associated spam transactions forming visually anomalous structures during a DoS attack.
Conclusion
The study highlights the potential of open data blockchain analytics to drive insights into economic behaviors, privacy issues, and network security within the Bitcoin ecosystem. By effectively leveraging graph databases and novel metrics, the research demonstrates valuable methods for exploring blockchain data. These findings encourage further exploration across alternate blockchain systems and address both theoretical and practical implications in fields such as fraud detection, econometrics, and blockchain technology enhancements. The paper serves as a foundational blueprint for understanding the unique advantages and challenges of public permissionless blockchain architectures.




